常见问题
内存使用率高
客户端不规范使用没有关连接
如果 Client 侧发起大量连接而不关闭的话,极端情况下会有较大的资源浪费,随着时间的增长,可能会造成内存使用率高的问题。
解决办法
合理配置 idleTimeout,超时后 Hertz Server 会把连接关掉保证 Server 侧的稳定性。默认配置为3分钟。
超大请求/响应
- 如果请求和响应非常大,并且没有使用一些其他发送模式如 stream、chunk 时,数据会全部进入内存,给内存造成较大压力。
- netpoll 网络库下的流式为假流式。由于 netpoll 使用 LT 触发模式,当数据到达时,会触发 netpoll
读取数据;在接口设计上,也因此没有实现
Reader接口。为了实现流式的能力,Hertz 将 netpoll 封装为 Reader,但其本身数据仍然不可控的进入了内存,所以在超大流式请求的情况下,可能会造成内存压力。
解决办法
超大请求的场景下,使用流式 + go net 的组合。
常见错误码排查
如果框架报以下的错误码,可以按照可能原因进行排查。如果出现非以下错误码,则不是框架打出来的,需要由使用方定位一下是否自行设置或者由某些中间件设置了错误码。
404
- 访问到了错误的端口上了,常见访问到了 debug 端口
- 解决方案:区分框架服务的监听端口和 debug server 的监听端口,默认:8888
- 未匹配到路由
- 根据启动日志查看是否所有预期路由都正常注册
- 查看访问方法是否正确
417
server 在执行完自定义的 ContinueHandler 之后返回 false(server 主动拒绝掉 100 Continue 后续的 body)。
500
- 中间件或者
handlerFunc中抛 panic- 解决方案:panic 栈信息定位具体问题
- fs 场景 path 携带
/../,可能出现访问预期之外的文件,server 端 app log 中伴随错误日志:cannot serve path with '/../' at position %d due to security reasons: %q。- 解决方案:检查是否存在非法请求
上下文使用指南
说明
Hertz 在 HandlerFunc 设计上,同时提供了一个标准 context.Context 和一个请求上下文作为函数的入参。
handler/middleware 函数签名为:
type HandlerFunc func(c context.Context, ctx *RequestContext)
元数据存储方面
两个上下文都有储值能力,使用时具体选择哪一个的简单依据:所储存值的生命周期和所选择的上下文要匹配。
具体细节
ctx 主要用来存储请求级别的变量,请求结束就回收了,特点是查询效率高(底层是 map),协程不安全,且未实现 context.Context
接口。
c 作为上下文在中间件 /handler 之间传递。拥有 context.Context 的所有语义,协程安全。所有需要 context.Context
接口作为入参的地方,直接传递 c 即可。
除此之外,如果面对一定要异步传递 ctx 的场景,hertz 也提供了 ctx.Copy() 接口,方便业务能够获取到一个协程安全的副本。
精度丢失问题
说明
- JavaScript 的数字类型一旦数字超过限值时将会丢失精度,进而导致前后端的值出现不一致。
var s = '{"x":6855337641038665531}';
var obj = JSON.parse(s);
alert (obj.x);
// Output 6855337641038666000
- 在 JSON 的规范中,对于数字类型是不区分整形和浮点型的。 在使用
json.Unmarshal进行 JSON 的反序列化的时候,如果没有指定数据类型,使用interface{}作为接收变量,将默认采用float64作为其数字的接受类型,当数字的精度超过float能够表示的精度范围时就会造成精度丢失的问题。
解决办法
- 使用 json 标准包的
stringtag。
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
type User struct {
ID int `json:"id,string"`
}
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
var u User
u.ID = 6855337641038665531
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, u)
})
h.Spin()
}
- 使用
json.Number
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
type User struct {
ID json.Number `json:"id"`
}
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
var u User
err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(`{"id":6855337641038665531}`), &u)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, u)
})
h.Spin()
}
title: “快速开始” linkTitle: “快速开始” weight: 2 keywords: [“Hertz”, “开发环境”, “快速上手”, “代码生成工具”] description: “Hertz 开发环境准备、快速上手与代码生成工具 hz 基本使用。”
准备 Golang 开发环境
- 如果您之前未搭建 Golang 开发环境,可以参考 Golang 安装。
- 推荐使用最新版本的 Golang,或保证现有 Golang 版本 >= 1.15。小于 1.15 版本,可以自行尝试使用但不保障兼容性和稳定性。
- 确保打开 go mod 支持 (Golang >= 1.15 时,默认开启)。
目前,Hertz 支持 Linux、macOS、Windows 系统。
快速上手
在完成环境准备后,可以按照如下操作快速启动 Hertz Server:
-
在当前目录下创建 hertz_demo 文件夹,进入该目录中。
-
创建
main.go文件。 -
在
main.go文件中添加以下代码。package main import ( "context" "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app" "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server" "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils" "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts" ) func main() { h := server.Default() h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) { ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"message": "pong"}) }) h.Spin() } -
生成
go.mod文件。go mod init hertz_demo -
整理 & 拉取依赖。
go mod tidy -
运行示例代码。
go run hertz_demo如果成功启动,你将看到以下信息:
2022/05/17 21:47:09.626332 engine.go:567: [Debug] HERTZ: Method=GET absolutePath=/ping --> handlerName=main.main.func1 (num=2 handlers) 2022/05/17 21:47:09.629874 transport.go:84: [Info] HERTZ: HTTP server listening on address=[::]:8888接下来,我们可以对接口进行测试:
curl http://127.0.0.1:8888/ping如果不出意外,我们可以看到类似如下输出:
{"message":"pong"}
代码自动生成工具 hz
hz 是 Hertz 框架提供的一个用于生成代码的命令行工具,可以用于生成 Hertz 项目的脚手架。
安装命令行工具 hz
首先,我们需要安装使用本示例所需要的命令行工具 hz:
- 确保
GOPATH环境变量已经被正确地定义(例如export GOPATH=~/go)并且将$GOPATH/bin添加到PATH环境变量之中(例如export PATH=$GOPATH/bin:$PATH);请勿将GOPATH设置为当前用户没有读写权限的目录。 - 安装 hz:
go install github.com/cloudwego/hertz/cmd/hz@latest。
更多 hz 使用方法可参考: hz。
确定代码放置位置
-
若将代码放置于
$GOPATH/src下,需在$GOPATH/src下创建额外目录,进入该目录后再获取代码:mkdir -p $(go env GOPATH)/src/github.com/cloudwego cd $(go env GOPATH)/src/github.com/cloudwego -
若将代码放置于
GOPATH之外,可直接获取。
生成/编写示例代码
-
在当前目录下创建 hertz_demo 文件夹,进入该目录中。
-
生成代码
hz new,若当前不在GOPATH,需要添加-module或者-modflag 指定一个自定义的模块名称。详细参考这里。 -
整理 & 拉取依赖。
go mod init # 当前目录不在 GOPATH 下不需要 `go mod init` 这一步 go mod tidy
运行示例代码
完成以上操作后,我们可以直接编译并启动 Server。
go build -o hertz_demo && ./hertz_demo
如果成功启动,你将看到以下信息:
2022/05/17 21:47:09.626332 engine.go:567: [Debug] HERTZ: Method=GET absolutePath=/ping --> handlerName=main.main.func1 (num=2 handlers)
2022/05/17 21:47:09.629874 transport.go:84: [Info] HERTZ: HTTP server listening on address=[::]:8888
接下来,我们可以对接口进行测试:
curl http://127.0.0.1:8888/ping
如果不出意外,我们可以看到类似如下输出:
{"message":"pong"}
到现在,我们已经成功启动了 Hertz Server,并完成了一次调用。
更多示例
参考:代码示例
title: “开发指南” linkTitle: “开发指南” weight: 3 keywords: [“开发指南”, “代码示例”, “基本特性”, “可观测性”, “治理特性”, “框架拓展”, “hz 代码生成”, “迁移到 Hertz”] description: “Hertz 开发指南,包括代码示例、基本特性、可观测性、治理特性、框架拓展、hz 代码生成、迁移到 Hertz。”
title: “Sentinel” date: 2022-09-29 weight: 2 keywords: [“治理特性”, “Sentinel”] description: “Hertz 提供了 hertz-contrib/opensergo, 以方便用户集成 sentinel-golang。”
Hertz 提供了 hertz-contrib/opensergo, 以方便用户集成 sentinel-golang。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/opensergo
配置
前置介绍:
热点参数限流会统计传入参数中的热点参数,并根据配置的限流阈值与模式,对包含热点参数的资源调用进行限流。热点参数限流可以看做是一种特殊的流量控制,仅对包含热点参数的资源调用生效。
sentinel-golang
关于 sentinel-golang 的基本配置,详情参考 文档
服务端
SentinelServerMiddleware
SentinelServerMiddleware() 返回 app.HandlerFunc 类型,用于将 sentinel-golang 集成进入 hertz server
默认资源名称为 {method}:{path},如 “GET:/api/users/:id”, 默认 block 时返回 429 状态码
可以通过 WithServerXxx() 函数来进行自定义格式
示例代码:
package main
// ...
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8081"))
h.Use(adaptor.SentinelServerMiddleware())
// ...
}
WithServerResourceExtractor
WithResourceExtractor 为设置网络请求的自定义函数,通过自定义的资源名和 sentinel-golang 中的热点参数流控规则
的 Resource 相匹配以达到自定义规则的目的
示例代码:
package main
// ...
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8081"))
h.Use(adaptor.SentinelServerMiddleware(
// customize resource extractor if required
// method_path by default
adaptor.WithServerResourceExtractor(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) string {
return "server_test"
}),
))
// ...
}
WithServerBlockFallback
WithServerBlockFallback 为设置请求被阻断时的自定义回调函数,可以通过 context.Context 和 app.RequestContext
分别来进行错误日志打印和自定义回调处理
示例代码:
package main
// ...
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8081"))
h.Use(adaptor.SentinelServerMiddleware(
// customize block fallback if required
// abort with status 429 by default
adaptor.WithServerBlockFallback(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.AbortWithStatusJSON(400, utils.H{
"err": "too many request; the quota used up",
"code": 10222,
})
}),
))
// ...
}
客户端
SentinelClientMiddleware
SentinelClientMiddleware() 返回一个 client.Middleware 类型,用于将 sentinel-golang 集成进入 hertz client
默认的资源名格式为 {method}:{path}, 例如 “GET:/api/users”, 默认 block 时返回 blockError
可以通过 WithClientXxx() 函数来进行自定义格式
示例代码:
package main
// ...
func main() {
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unexpected error: %+v", err)
return
}
c.Use(adaptor.SentinelClientMiddleware())
}
WithClientResourceExtractor
WithClientResourceExtractor 为设置网络请求的自定义函数,通过自定义的资源名和 sentinel-golang 中的 热点参数 流控规则
的 Resource 相匹配以达到自定义规则的目的
示例代码:
package main
// ...
func main() {
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unexpected error: %+v", err)
return
}
c.Use(adaptor.SentinelClientMiddleware(
// customize resource extractor if required
// method_path by default
adaptor.WithClientResourceExtractor(func(ctx context.Context, request *protocol.Request, response *protocol.Response) string {
return "client_test"
}),
))
}
WithClientBlockFallback
WithClientBlockFallback 为设置请求被阻断时的自定义回调函数,可以通过 context.Context, protocol.Request
, protocol.Response 来进行错误日志打印等功能,也可以通过自定义回调处理 error 来进行自定义错误处理。
示例代码:
package main
// ...
func main() {
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Unexpected error: %+v", err)
return
}
c.Use(adaptor.SentinelClientMiddleware(
// customize resource extractor if required
// method_path by default
adaptor.WithClientBlockFallback(func(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, blockError error) error {
resp.SetStatusCode(http.StatusBadRequest)
resp.SetBody([]byte("request failed"))
return blockError
}),
))
}
完整示例代码
完整用法示例详见 example
title: “治理特性” linkTitle: “治理特性” weight: 4 keywords: [“治理特性”, “服务注册与发现”, “Sentinel”] description: “Hertz 提供的治理特性。”
title: “consul” date: 2023-04-22 weight: 3 keywords: [“服务注册与发现”, “consul”] description: “Hertz 提供的服务注册与发现 consul 拓展。”
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/consul
服务注册
Option
Consul 拓展在服务注册部分中提供了 option 配置。
WithCheck
Consul 扩展提供了 WithCheck 用于帮助用户配置 Consul 中的 AgentServiceCheck 选项。若不使用,则默认设置 check.Timeout
为 5 秒,check.Internal 为 5 秒,check.DeregisterCriticalServiceAfter 为 1 分钟。
函数签名:
func WithCheck(check *api.AgentServiceCheck) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
consulClient, err := consulapi.NewClient(config)
// ...
check := &consulapi.AgentServiceCheck{
// ...
}
r := consul.NewConsulRegister(consulClient, consul.WithCheck(check))
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
NewConsulRegister
NewConsulRegister 使用 consul 创建一个可配置客户端的服务注册中心,需要传入客户端,其中客户端使用 NewClient
创建。可自定义服务注册中心配置。
函数签名:
func NewConsulRegister(consulClient *api.Client, opts ...Option) registry.Registry
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
consulClient, err := consulapi.NewClient(config)
// ...
r := consul.NewConsulRegister(consulClient)
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
服务发现
NewConsulResolver
NewConsulResolver 使用 consul 创建一个新的服务发现中心,需要传入客户端,其中客户端使用 NewClient 创建。可自定义服务发现中心配置。
函数签名:
func NewConsulResolver(consulClient *api.Client) discovery.Resolver
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
consulClient, err := consulapi.NewClient(consulConfig)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
r := consul.NewConsulResolver(consulClient)
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
}
使用示例
服务端
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/registry"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
consulapi "github.com/hashicorp/consul/api"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/consul"
)
func main() {
// build a consul client
config := consulapi.DefaultConfig()
config.Address = "127.0.0.1:8500"
consulClient, err := consulapi.NewClient(config)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
// build a consul register with the consul client
r := consul.NewConsulRegister(consulClient)
// run Hertz with the consul register
addr := "127.0.0.1:8888"
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong1"})
})
h.Spin()
}
客户端
import (
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/client/sd"
consulapi "github.com/hashicorp/consul/api"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/consul"
)
func main() {
// build a consul client
consulConfig := consulapi.DefaultConfig()
consulConfig.Address = "127.0.0.1:8500"
consulClient, err := consulapi.NewClient(consulConfig)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
// build a consul resolver with the consul client
r := consul.NewConsulResolver(consulClient)
// build a hertz client with the consul resolver
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
}
配置
可自定义 Consul 客户端以及服务端的配置,参考 consul 配置。
完整实例
完整用法示例详见 example 。
title: “nacos” date: 2023-04-22 weight: 2 keywords: [“服务注册与发现”, “nacos”] description: “Hertz 提供的服务注册与发现 nacos 拓展。”
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/nacos
服务注册
Option
Nacos 拓展在服务注册部分中提供了 option 配置。
WithRegistryCluster
Nacos 扩展提供了 WithRegistryCluster 用于帮助用户配置自定义的集群。默认为“DEFAULT” 。
函数签名:
func WithRegistryCluster(cluster string) RegistryOption
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := nacos.NewDefaultNacosRegistry(
nacos.WithRegistryCluster("Cluster123"),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
WithRegistryGroup
Nacos 扩展提供了 WithRegistryGroup 用于帮助用户配置自定义的集群。默认为 “DEFAULT_GROUP” 。
函数签名:
func WithRegistryGroup(group string) RegistryOption
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := nacos.NewDefaultNacosRegistry(
nacos.WithRegistryGroup("Group1"),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
NewDefaultNacosRegistry
NewDefaultNacosRegistry 使用 nacos 创建一个默认的服务注册中心。会调用 NewDefaultNacosConfig 读取环境变量来创建一个默认的
nacos 客户端,并设置 RegionId 为 cn-hangzhou,且不会在启动时自动预加载服务实例信息到本地缓存。可自定义服务注册中心配置。
环境变量:
| 环境变量名 | 环境变量默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| serverAddr | 127.0.0.1 | nacos 服务器地址 |
| serverPort | 8848 | nacos 服务器端口 |
| namespace | nacos 中的 namespace Id |
函数签名:
func NewDefaultNacosRegistry(opts ...RegistryOption) (registry.Registry, error)
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := nacos.NewDefaultNacosRegistry()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
NewNacosRegistry
NewNacosRegistry使用 nacos 创建一个可配置客户端的服务注册中心,需要传入自行配置的客户端。可自定义服务注册中心配置。
函数签名:
func NewNacosRegistry(client naming_client.INamingClient, opts ...RegistryOption) registry.Registry
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
cli, err := clients.NewNamingClient(
vo.NacosClientParam{
ClientConfig: &cc,
ServerConfigs: sc,
},
)
// ...
r := nacos.NewNacosRegistry(cli)
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
// ...
}
服务发现
Option
Nacos 拓展在服务发现部分中提供了 option 配置。
WithResolverCluster
Nacos 扩展提供了 WithResolverCluster 用于帮助用户配置自定义的集群。默认为“DEFAULT” 。
函数签名:
func WithResolverCluster(cluster string) ResolverOption
示例代码:
func main() {
client, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r, err := nacos.NewDefaultNacosResolver(
nacos.WithResolverCluster("Cluster123"),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
client.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
WithResolverGroup
Nacos 扩展提供了 WithResolverGroup 用于帮助用户配置自定义的集群。默认为 “DEFAULT_GROUP” 。
函数签名:
func WithResolverGroup(group string) ResolverOption
示例代码:
func main() {
client, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r, err := nacos.NewDefaultNacosResolver(
nacos.WithResolverGroup("Group1"),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
client.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
NewDefaultNacosResolver
NewDefaultNacosResolver 使用 nacos 创建一个默认的服务发现中心。会调用 NewDefaultNacosConfig 读取环境变量来创建一个默认的
nacos 客户端,并设置 RegionId 为 cn-hangzhou,且不会在启动时自动预加载服务实例信息到本地缓存。可自定义服务注册中心配置。
环境变量:
| 环境变量名 | 环境变量默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| serverAddr | 127.0.0.1 | nacos 服务器地址 |
| serverPort | 8848 | nacos 服务器端口 |
| namespace | nacos 中的 namespace Id |
函数签名:
func NewDefaultNacosResolver(opts ...ResolverOption) (discovery.Resolver, error)
示例代码:
func main() {
client, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r, err := nacos.NewDefaultNacosResolver()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
client.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
NewNacosResolver
NewNacosResolver 使用 nacos 创建一个可配置客户端的服务发现中心,需要传入自行配置的客户端。可自定义服务发现中心配置。
函数签名:
func NewNacosResolver(cli naming_client.INamingClient, opts ...ResolverOption) discovery.Resolver
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// ...
nacosCli, err := clients.NewNamingClient(
vo.NacosClientParam{
ClientConfig: &cc,
ServerConfigs: sc,
})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r := nacos.NewNacosResolver(nacosCli)
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
使用示例
服务端
- 使用
server.WithRegistry设置注册扩展以及注册信息。
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/registry"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/nacos"
)
func main() {
addr := "127.0.0.1:8888"
r, err := nacos.NewDefaultNacosRegistry()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
客户端
- 使用内置的
sd.Discovery中间件,支持传入自定义的服务发现扩展以及负载均衡扩展。 - 使用服务发现时需要将 url 中的域名替换为服务名,并使用
config.WithSD确定本次请求使用服务注册。
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/client/sd"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/config"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/nacos"
)
func main() {
client, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r, err := nacos.NewDefaultNacosResolver()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
client.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
status, body, err := client.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://hertz.test.demo/ping", config.WithSD(true))
if err != nil {
hlog.Fatal(err)
}
hlog.Infof("code=%d,body=%s\n", status, string(body))
}
}
配置
可自定义 Nacos 客户端以及服务端的配置,参考 nacos-sdk-go 配置。
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example 。
title: “etcd” date: 2023-04-22 weight: 4 keywords: [“服务注册与发现”, “etcd”] description: “Hertz 提供的服务注册与发现 etcd 拓展。”
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/etcd
服务注册
Option
Etcd 拓展在服务注册部分中提供了 option 配置。
WithTLSOpt
Etcd 扩展提供了 WithTLSOpt 用于帮助用户配置 Etcd 中的TLS选项。
函数签名:
func WithTLSOpt(certFile, keyFile, caFile string) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
r, err := etcd.NewEtcdRegistry([]string{"127.0.0.1:2379"},
etcd.WithTLSOpt(certFile, keyFile, caFile),
)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// ...
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
// ...
}
WithAuthOpt
Etcd 扩展提供了WithAuthOpt用于帮助用户配置 Etcd 中的Username和Password选项。
函数签名:
func WithAuthOpt(username, password string) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
r, err := etcd.NewEtcdRegistry([]string{"127.0.0.1:2379"},
etcd.WithAuthOpt("root","123456"),
)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// ...
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
// ...
}
NewEtcdRegistry
NewEtcdRegistry 使用 etcd 创建一个新的服务注册中心,需要传入端点值。可自定义服务注册中心配置。
函数签名:
func NewEtcdRegistry(endpoints []string, opts ...Option) (registry.Registry, error)
示例代码:
func main() {
r, err := etcd.NewEtcdRegistry([]string{"127.0.0.1:2379"})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// ...
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
// ...
}
服务发现
Option
Etcd 拓展在服务发现部分中提供了 option 配置。
WithTLSOpt
Etcd 扩展提供了 WithTLSOpt 用于帮助用户配置 Etcd 中的TLS选项。
函数签名:
func WithTLSOpt(certFile, keyFile, caFile string) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r, err := etcd.NewEtcdResolver([]string{"127.0.0.1:2379"},
etcd.WithTLSOpt(certFile, keyFile, caFile),
)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
WithAuthOpt
Etcd 扩展提供了WithAuthOpt用于帮助用户配置 Etcd 中的Username和Password选项。
函数签名:
func WithAuthOpt(username, password string) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r, err := etcd.NewEtcdResolver([]string{"127.0.0.1:2379"},
etcd.WithAuthOpt("root","123456"),
)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
NewEtcdResolver
NewEtcdResolver 使用 etcd 创建一个新的服务发现中心,需要传入端点值。可自定义服务发现中心配置。
函数签名:
func NewEtcdResolver(endpoints []string, opts ...Option) (discovery.Resolver, error)
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r, err := etcd.NewEtcdResolver([]string{"127.0.0.1:2379"})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
使用示例
服务端
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/registry"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/etcd"
)
func main() {
r, err := etcd.NewEtcdRegistry([]string{"127.0.0.1:2379"})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
addr := "127.0.0.1:8888"
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
h.GET("/ping", func(_ context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong2"})
})
h.Spin()
}
客户端
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/client/sd"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/config"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/etcd"
)
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r, err := etcd.NewEtcdResolver([]string{"127.0.0.1:2379"})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
status, body, err := cli.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://hertz.test.demo/ping", config.WithSD(true))
if err != nil {
hlog.Fatal(err)
}
hlog.Infof("HERTZ: code=%d,body=%s", status, string(body))
}
}
配置
可自定义 Etcd 客户端以及服务端的配置,参考 etcd-client 配置。
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example 。
title: “redis” date: 2023-04-22 weight: 9 keywords: [“服务注册与发现”, “redis”] description: “Hertz 提供的服务注册与发现 redis 拓展。”
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/redis
服务注册
Option
Redis 拓展在服务注册部分中提供了 option 配置。
WithPassword
Redis 扩展提供了 WithPassword 配置 redis 的密码,此密码必须匹配服务器配置选项中指定的密码。默认为空。
函数签名:
func WithPassword(password string) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
r := redis.NewRedisRegistry("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithPassword("123456"))
// ...
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
WithDB
Redis 扩展提供了 WithDB 配置连接到服务器后要选择的数据库。默认为 0。
函数签名:
func WithDB(db int) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
r := redis.NewRedisRegistry("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithDB(1))
// ...
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
WithTLSConfig
Redis 扩展提供了 WithTLSConfig 配置 TLS 的配置项。
函数签名:
func WithTLSConfig(t *tls.Config) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
r := redis.NewRedisRegistry("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithTLSConfig(&tls.Config{
// ...
}))
// ...
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
WithDialer
Redis 扩展提供了 WithDialer 配置 Dialer,Dialer 将会创建新的网络连接并优先于 Network 和 Addr 选项。
函数签名:
func WithDialer(dialer func(ctx context.Context, network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
r := redis.NewRedisRegistry("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithDialer(
// ...
))
// ...
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
WithReadTimeout
Redis 扩展提供了 WithReadTimeout 配置读取 socket 超时的时间,默认为 3 秒。
函数签名:
func WithReadTimeout(t time.Duration) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
r := redis.NewRedisRegistry("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithReadTimeout(5*time.Second))
// ...
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
WithWriteTimeout
Redis 扩展提供了 WithWriteTimeout 配置写入 socket 超时的时间,默认等同于 ReadTimeout。
函数签名:
func WithWriteTimeout(t time.Duration) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
r := redis.NewRedisRegistry("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithWriteTimeout(5*time.Second))
// ...
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
NewRedisRegistry
NewRedisRegistry 使用 redis 创建一个新的服务注册中心,需要传入目标地址。可自定义客户端配置并传入 NewClient 创建一个新的客户端。
函数签名:
func NewRedisRegistry(addr string, opts ...Option) registry.Registry
示例代码:
func main() {
r := redis.NewRedisRegistry("127.0.0.1:6379")
// ...
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
服务发现
Option
Redis 拓展在服务发现部分中提供了 option 配置。
WithPassword
Redis 扩展提供了 WithPassword 配置 redis 的密码,此密码必须匹配服务器配置选项中指定的密码。默认为空。
函数签名:
func WithPassword(password string) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
// ...
r := redis.NewRedisResolver("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithPassword("123456"))
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
WithDB
Redis 扩展提供了 WithDB 配置连接到服务器后要选择的数据库。默认为 0。
函数签名:
func WithDB(db int) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
// ...
r := redis.NewRedisResolver("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithDB(1))
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
WithTLSConfig
Redis 扩展提供了 WithTLSConfig 配置 TLS 的配置项。
函数签名:
func WithTLSConfig(t *tls.Config) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
// ...
r := redis.NewRedisResolver("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithTLSConfig(&tls.Config{
// ...
}))
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
WithDialer
Redis 扩展提供了 WithDialer 配置 Dialer,Dialer 将会创建新的网络连接并优先于 Network 和 Addr 选项。
函数签名:
func WithDialer(dialer func(ctx context.Context, network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
// ...
r := redis.NewRedisRegistry("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithDialer(
// ...
))
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
WithReadTimeout
Redis 扩展提供了 WithReadTimeout 配置读取 socket 超时的时间,默认为 3 秒。
函数签名:
func WithReadTimeout(t time.Duration) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
// ...
r := redis.NewRedisRegistry("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithReadTimeout(5*time.Second))
// ...
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
WithWriteTimeout
Redis 扩展提供了 WithWriteTimeout 配置写入 socket 超时的时间,默认等同于 ReadTimeout。
函数签名:
func WithWriteTimeout(t time.Duration) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
// ...
r := redis.NewRedisRegistry("127.0.0.1:6379", redis.WithWriteTimeout(5*time.Second))
// ...
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
NewRedisResolver
NewRedisResolver 使用 redis 创建一个新的服务发现中心,需要传入目标地址。可自定义客户端配置并传入 NewClient 创建一个新的客户端。
函数签名:
func NewRedisResolver(addr string, opts ...Option) discovery.Resolver
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
// ...
r := redis.NewRedisResolver("127.0.0.1:6379")
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
使用示例
服务端
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/registry"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/redis"
)
func main() {
r := redis.NewRedisRegistry("127.0.0.1:6379")
addr := "127.0.0.1:8888"
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
h.GET("/ping", func(_ context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
客户端
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/client/sd"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/config"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/redis"
)
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r := redis.NewRedisResolver("127.0.0.1:6379")
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
status, body, err := cli.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://hertz.test.demo/ping", config.WithSD(true))
if err != nil {
hlog.Fatal(err)
}
hlog.Infof("HERTZ: code=%d,body=%s", status, string(body))
}
}
配置
可自定义 redis 客户端以及服务端的配置,参考 go-redis 配置。
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example 。
title: “eureka” date: 2023-04-22 weight: 5 keywords: [“服务注册与发现”, “eureka”] description: “Hertz 提供的服务注册与发现 eureka 拓展。”
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/eureka
服务注册
NewEurekaRegistry
NewEurekaRegistry 使用 eureka 创建一个新的服务注册中心,需要将服务 Url 通过一个字符串切片传入 NewConn,并同时传入心跳间隔时长。
函数签名:
func NewEurekaRegistry(servers []string, heatBeatInterval time.Duration) *eurekaRegistry
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r := eureka.NewEurekaRegistry([]string{"http://127.0.0.1:8761/eureka"}, 40*time.Second)
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.discovery.eureka",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
//...
}
NewEurekaRegistryFromConfig
NewEurekaRegistryFromConfig 使用 eureka 创建一个新的服务注册中心,需要传入配置并调用 NewConnFromConfig,也需要传入心跳间隔时长。
函数签名:
func NewEurekaRegistryFromConfig(config fargo.Config, heatBeatInterval time.Duration) *eurekaRegistry
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
config := fargo.Config{
// ...
}
r := eureka.NewEurekaRegistryFromConfig(config, 40*time.Second)
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.discovery.eureka",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
//...
}
NewEurekaRegistryFromConn
NewEurekaRegistryFromConn 使用 eureka 创建一个新的服务注册中心,需要直接传入 conn,也需要传入心跳间隔时长。
函数签名:
func NewEurekaRegistryFromConn(conn fargo.EurekaConnection, heatBeatInterval time.Duration) *eurekaRegistry
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
conn := fargo.EurekaConnection{
// ...
}
r := eureka.NewEurekaRegistryFromConn(conn, 40*time.Second)
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.discovery.eureka",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
//...
}
服务发现
NewEurekaResolver
NewEurekaResolver 使用 eureka 创建一个新的服务发现中心,需要将服务 Url 通过一个字符串切片传入 NewConn。
函数签名:
func NewEurekaResolver(servers []string) *eurekaResolver
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
hlog.Fatal(err)
return
}
r := eureka.NewEurekaResolver([]string{"http://127.0.0.1:8761/eureka"})
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
NewEurekaResolverFromConfig
NewEurekaResolverFromConfig 使用 eureka 创建一个新的服务发现中心,需要传入配置并调用 NewConnFromConfig。
函数签名:
func NewEurekaResolverFromConfig(config fargo.Config) *eurekaResolver
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
config := fargo.Config{
// ...
}
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
hlog.Fatal(err)
return
}
r := eureka.NewEurekaResolverFromConfig(config)
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
NewEurekaResolverFromConn
NewEurekaResolverFromConn 使用 eureka 创建一个新的服务发现中心,需要直接传入 conn。
函数签名:
func NewEurekaResolverFromConn(conn fargo.EurekaConnection) *eurekaResolver
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
conn := fargo.EurekaConnection{
// ...
}
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
hlog.Fatal(err)
return
}
r := eureka.NewEurekaResolverFromConn(conn)
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
使用示例
服务端
import (
"context"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/registry"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/eureka"
)
func main() {
addr := "127.0.0.1:8888"
r := eureka.NewEurekaRegistry([]string{"http://127.0.0.1:8761/eureka"}, 40*time.Second)
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.discovery.eureka",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong2"})
})
h.Spin()
}
客户端
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/client/sd"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/config"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/eureka"
)
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
hlog.Fatal(err)
return
}
r := eureka.NewEurekaResolver([]string{"http://127.0.0.1:8761/eureka"})
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
status, body, err := cli.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://hertz.discovery.eureka/ping", config.WithSD(true))
if err != nil {
hlog.Fatal(err)
}
hlog.Infof("code=%d,body=%s", status, string(body))
}
}
配置
本项目使用 fargo 作为 eureka 客户端。您应该参考 fargo 文档以了解高级配置。
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example 。
title: “servicecomb” date: 2023-04-22 weight: 7 keywords: [“服务注册与发现”, “servicecomb”] description: “Hertz 提供的服务注册与发现 servicecomb 拓展。”
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/servicecomb
服务注册
Option
Servicecomb 拓展在服务注册部分中提供了 option 配置。
WithAppId
Servicecomb 扩展提供了 WithAppId 用于帮助用户配置 Servicecomb 的 AppId。默认为“DEFAULT" 。
函数签名:
func WithAppId(appId string) RegistryOption
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := servicecomb.NewDefaultSCRegistry([]string{scAddr},
servicecomb.WithAppId("appID"),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.servicecomb.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
WithRegistryVersionRule
Servicecomb 扩展提供了 WithRegistryVersionRule 用于帮助用户配置 Servicecomb 的版本要求。默认为 1.0.0。
函数签名:
func WithRegistryVersionRule(versionRule string) RegistryOption
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := servicecomb.NewDefaultSCRegistry([]string{scAddr},
servicecomb.WithRegistryVersionRule("1.1.0"),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.servicecomb.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
WithRegistryHostName
Servicecomb 扩展提供了 WithRegistryHostName 用于帮助用户配置 Servicecomb 的主机名。默认为”DEFAULT" 。
函数签名:
func WithRegistryHostName(hostName string) RegistryOption
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := servicecomb.NewDefaultSCRegistry([]string{scAddr},
servicecomb.WithRegistryHostName("hostName"),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.servicecomb.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
WithRegistryHeartbeatInterval
Servicecomb 扩展提供了 WithRegistryHeartbeatInterval 用于帮助用户配置发送心跳包的间隔时长。默认为 5。
函数签名:
func WithRegistryHeartbeatInterval(second int32) RegistryOption
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := servicecomb.NewDefaultSCRegistry([]string{scAddr},
servicecomb.WithRegistryHeartbeatInterval(10),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.servicecomb.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
NewDefaultSCRegistry
NewDefaultSCRegistry 使用 service-comb 创建一个默认服务注册中心,需要传入端点值。可自定义服务注册中心配置。
函数签名:
func NewDefaultSCRegistry(endPoints []string, opts ...RegistryOption) (registry.Registry, error)
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := servicecomb.NewDefaultSCRegistry([]string{scAddr})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.servicecomb.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
NewSCRegistry
NewSCRegistry 使用 service-comb 创建一个新的服务注册中心。需要传入自定义客户端。可自定义服务注册中心配置。
函数签名:
func NewSCRegistry(client *sc.Client, opts ...RegistryOption) registry.Registry
示例代码:
func main() {
client := &sc.Client{
// ...
}
// ...
r, err := servicecomb.NewSCRegistry(client)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.servicecomb.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
// ...
}
服务发现
Option
Servicecomb 拓展在服务发现部分中提供了 option 配置。
WithAppId
Servicecomb 扩展提供了 WithAppId 用于帮助用户配置 Servicecomb 的 AppId。默认为“DEFAULT" 。
函数签名:
func WithResolverAppId(appId string) ResolverOption
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := servicecomb.NewDefaultSCRegistry([]string{scAddr},
servicecomb.WithAppId("appID"),
)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
WithResolverVersionRule
Servicecomb 扩展提供了 WithResolverVersionRule 用于帮助用户配置 Servicecomb 的版本要求。默认为 latest。
函数签名:
func WithResolverVersionRule(versionRule string) ResolverOption
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := servicecomb.NewDefaultSCRegistry([]string{scAddr},
servicecomb.WithResolverVersionRule("1.0.0"),
)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
WithResolverConsumerId
Servicecomb 扩展提供了 WithResolverConsumerId 用于帮助用户配置 Servicecomb 的 ConsumerId。默认为空。
函数签名:
func WithResolverConsumerId(consumerId string) ResolverOption
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := servicecomb.NewDefaultSCRegistry([]string{scAddr},
servicecomb.WithResolverConsumerId("1"),
)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
NewDefaultSCResolver
NewDefaultSCResolver 使用 service-comb 创建一个默认服务发现中心,需要传入端点值。可自定义服务发现中心配置。
函数签名:
func NewDefaultSCResolver(endPoints []string, opts ...ResolverOption) (discovery.Resolver, error)
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := servicecomb.NewDefaultSCResolver([]string{scAddr})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
NewSCResolver
NewSCReslover 使用 service-comb 创建一个新的服务发现中心。需要传入自定义客户端。可自定义服务发现中心配置。
函数签名:
func NewSCResolver(cli *sc.Client, opts ...ResolverOption) discovery.Resolver
示例代码:
func main() {
client := &sc.Client{
// ...
}
// ...
r, err := servicecomb.NewSCResolver(client)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
使用示例
服务端
import (
"context"
"log"
"sync"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/registry"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/servicecomb"
)
func main() {
const scAddr = "127.0.0.1:30100"
const addr = "127.0.0.1:8701"
r, err := servicecomb.NewDefaultSCRegistry([]string{scAddr})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.servicecomb.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}),
)
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong1"})
})
h.Spin()
}
客户端
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/client/sd"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/config"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/servicecomb"
)
func main() {
const scAddr = "127.0.0.1:30100"
// build a servicecomb resolver
r, err := servicecomb.NewDefaultSCResolver([]string{scAddr})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// build a hertz client with the servicecomb resolver
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
status, body, err := cli.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://hertz.servicecomb.demo/ping", config.WithSD(true))
if err != nil {
hlog.Fatal(err)
}
hlog.Infof("code=%d,body=%s", status, string(body))
}
}
配置
可自定义 Servicecomb 客户端以及服务端的配置,参考 go-chassis/sc-client 配置
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example 。
title: “polaris” date: 2023-04-22 weight: 6 keywords: [“服务注册与发现”, “polaris”] description: “Hertz 提供的服务注册与发现 polaris 拓展。”
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/polaris
服务注册
NewPolarisRegistry
NewPolarisRegistry 使用 polaris 创建一个新的服务注册中心,可传入配置文件并调用 GetPolarisConfig,若不传入则使用默认配置。
函数签名:
func NewPolarisRegistry(configFile ...string) (Registry, error)
示例代码:
func main() {
r, err := polaris.NewPolarisRegistry(confPath)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
Info := ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", "127.0.0.1:8888"),
Tags: map[string]string{
"namespace": Namespace,
},
}
h := server.Default(server.WithRegistry(r, Info), server.WithExitWaitTime(10*time.Second))
// ...
}
服务发现
NewPolarisResolver
NewPolarisResolver 使用 polaris 创建一个新的服务发现中心,可传入配置文件并调用 GetPolarisConfig,若不传入则使用默认配置。
函数签名:
func NewPolarisResolver(configFile ...string) (Resolver, error)
示例代码:
func main() {
r, err := polaris.NewPolarisResolver(confPath)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
client, err := hclient.NewClient()
client.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
//...
}
使用示例
服务端
import (
"context"
"log"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/registry"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/polaris"
)
const (
confPath = "polaris.yaml"
Namespace = "Polaris"
// At present,polaris server tag is v1.4.0,can't support auto create namespace,
// If you want to use a namespace other than default,Polaris ,before you register an instance,
// you should create the namespace at polaris console first.
)
func main() {
r, err := polaris.NewPolarisRegistry(confPath)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
Info := ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", "127.0.0.1:8888"),
Tags: map[string]string{
"namespace": Namespace,
},
}
h := server.Default(server.WithRegistry(r, Info), server.WithExitWaitTime(10*time.Second))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "Hello,Hertz!")
})
h.Spin()
}
客户端
import (
"context"
"log"
hclient "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/client/sd"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/config"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/polaris"
)
const (
confPath = "polaris.yaml"
Namespace = "Polaris"
// At present,polaris server tag is v1.4.0,can't support auto create namespace,
// if you want to use a namespace other than default,Polaris ,before you register an instance,
// you should create the namespace at polaris console first.
)
func main() {
r, err := polaris.NewPolarisResolver(confPath)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
client, err := hclient.NewClient()
client.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
// config.WithTag sets the namespace tag for service discovery
status, body, err := client.Get(context.TODO(), nil, "http://hertz.test.demo/hello", config.WithSD(true), config.WithTag("namespace", Namespace))
if err != nil {
hlog.Fatal(err)
}
hlog.Infof("code=%d,body=%s\n", status, body)
}
}
配置
可自定义 polaris 客户端以及服务端的配置,参考 polaris-go 配置。
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example 。
title: “服务注册与发现” date: 2023-04-22 weight: 1 keywords: [“服务注册与发现”, “nacos”, “consul”, “etcd”, “eureka”, “polaris”, “servicecomb”, “zookeeper”, “redis”] description: “Hertz 提供的服务注册与发现拓展。”
目前在 Hertz 的开源版本支持的服务发现拓展都存放在 registry 中,欢迎大家参与项目贡献与维护。
到现在为止,支持的服务发现拓展有
配置
使用服务发现时会提供一些可选配置给用户。
| 配置 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| WithSD | 配合服务发现使用,传递 true 时,本次请求使用服务发现。 |
| WithTag | 配合服务发现使用,设置 Tag 信息。 |
| WithCustomizedAddrs | 自定义目标实例地址。 |
| WithLoadBalanceOptions | 配置负载均衡选项。 |
WithSD
提供 WithSD 配置项,传入参数为 true 时,本次请求使用服务发现。使用服务发现请求时必须使用 WithSD 配置项。
函数签名:
func WithSD(b bool) RequestOption
示例代码:
status, body, err := cli.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://hertz.test.demo/ping", config.WithSD(true))
WithTag
提供 WithTag 配置项,使用此配置用于设置 Tag 信息。
函数签名:
func WithTag(k, v string) RequestOption
示例代码:
status, body, err := cli.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://hertz.test.demo/ping", config.WithTag("foo", "var"))
WithCustomizedAddrs
WithCustomizedAddrs配置项指定服务发现时的目标实例地址。它将会覆盖来自 Resolver 的结果。Resolver 是服务发现中心,用于服务发现。
函数签名:
func WithCustomizedAddrs(addrs ...string) ServiceDiscoveryOption
示例代码:
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r, sd.WithCustomizedAddrs("127.0.0.1:8088")))
WithLoadBalanceOptions
WithLoadBalanceOptions为客户端配置负载均衡实现和负载均衡参数。可以通过传递loadbalance.Options
配置负载均衡参数,或者通过传递loadbalance.DefaultOpts使用默认负载均衡参数。若不使用此配置项,则客户端默认使用
WeightedRandom 负载均衡实现并且使用默认负载均衡参数。
可以设置的负载均衡参数:
| 负载均衡参数名 | 负载均衡参数默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| RefreshInterval | 5秒 | 刷新服务端信息间隔 |
| ExpireInterval | 15秒 | 服务端信息过期间隔 |
函数签名:
func WithLoadBalanceOptions(lb loadbalance.Loadbalancer, options loadbalance.Options) ServiceDiscoveryOption
示例代码:
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r, sd.WithLoadBalanceOptions(loadbalance.NewWeightedBalancer(), loadbalance.Options{
RefreshInterval: 5 * time.Second,
ExpireInterval: 15 * time.Second,
})))
自定义负载均衡扩展详见负载均衡扩展。
title: “zookeeper” date: 2023-04-22 weight: 8 keywords: [“服务注册与发现”, “zookeeper”] description: “Hertz 提供的服务注册与发现 zookeeper 拓展。”
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/zookeeper
服务注册
NewZookeeperRegistry
NewZookeeperRegistry 使用 zookeeper 创建一个服务注册中心,需要将服务通过一个字符串切片与会话超时时间共同传入 Connect。
函数签名:
func NewZookeeperRegistry(servers []string, sessionTimeout time.Duration) (registry.Registry, error)
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := zookeeper.NewZookeeperRegistry([]string{"127.0.0.1:2181"}, 40*time.Second)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
// ...
}
NewZookeeperRegistryWithAuth
NewZookeeperRegistryWithAuth 使用 zookeeper
创建一个服务注册中心,需要将服务通过一个字符串切片与会话超时时间共同传入 Connect
。除此之外还需要传入用户与密码来调用 AddAuth,用户与密码不能为空。
函数签名:
func NewZookeeperRegistryWithAuth(servers []string, sessionTimeout time.Duration, user, password string)
示例代码:
func main() {
// ...
r, err := zookeeper.NewZookeeperRegistryWithAuth([]string{"127.0.0.1:2181"}, 20*time.Second, "hertzuser", "hertzpass")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
// ...
}
服务发现
NewZookeeperResolver
NewZookeeperResolver 使用 zookeeper 创建一个服务发现中心,需要将服务通过一个字符串切片与会话超时时间共同传入 Connect。
函数签名:
func NewZookeeperResolver(servers []string, sessionTimeout time.Duration) (discovery.Resolver, error)
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r, err := zookeeper.NewZookeeperResolver([]string{"127.0.0.1:2181"}, 40*time.Second)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
NewZookeeperResolverWithAuth
NewZookeeperResolverWithAuth 使用 zookeeper
创建一个服务发现中心,需要将服务通过一个字符串切片与会话超时时间共同传入 Connect
。除此之外还需要传入用户与密码来调用 AddAuth,用户与密码不能为空。
函数签名:
func NewZookeeperResolverWithAuth(servers []string, sessionTimeout time.Duration, user, password string)
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r, err := zookeeper.NewZookeeperResolverWithAuth([]string{"127.0.0.1:2181"}, 40*time.Second, "hertzuser", "hertzpass")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
// ...
}
使用示例
服务端
import (
"context"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/registry"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/zookeeper"
)
func main() {
addr := "127.0.0.1:8888"
r, err := zookeeper.NewZookeeperRegistry([]string{"127.0.0.1:2181"}, 40*time.Second)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong2"})
})
h.Spin()
}
客户端
import (
"context"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/client/sd"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/config"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/registry/zookeeper"
)
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r, err := zookeeper.NewZookeeperResolver([]string{"127.0.0.1:2181"}, 40*time.Second)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
status, body, err := cli.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://hertz.test.demo/ping", config.WithSD(true))
if err != nil {
hlog.Fatal(err)
}
hlog.Infof("code=%d,body=%s", status, string(body))
}
}
配置
可自定义 zookeeper 客户端以及服务端的配置,参考 go-zookeeper/zk 配置。
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example 。
title: “绑定与校验” date: 2022-05-23 weight: 8 keywords: [“绑定与校验”, “go-tagexpr”, “tag”, “参数绑定优先级”] description: “Hertz 支持的参数绑定与校验相关功能及用法。”
hertz 使用开源库 go-tagexpr 进行参数的绑定及验证,下面分别介绍参数绑定和参数验证的用法。
使用方法
func main() {
r := server.New()
r.GET("/hello", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// 参数绑定需要配合特定的 go tag 使用
type Test struct {
A string `query:"a" vd:"$!='Hertz'"`
}
// BindAndValidate
var req Test
err := ctx.BindAndValidate(&req)
...
// Bind
req = Test{}
err = ctx.Bind(&req)
...
// Validate,需要使用 "vd" tag
err = ctx.Validate(&req)
...
})
...
}
支持的 tag 及参数绑定优先级
支持的 tag
不通过 IDL 生成代码时若字段不添加任何 tag 则会遍历所有 tag 并按照优先级绑定参数,添加 tag 则会根据对应的 tag 按照优先级去绑定参数。
通过 IDL 生成代码时若不添加 api注解
则字段默认添加 form、json、query tag,添加 api注解
会为字段添加相应需求的 tag。
| go tag | 说明 |
|---|---|
| path | 绑定 url 上的路径参数,相当于 hertz 路由{:param}或{*param}中拿到的参数。例如:如果定义的路由为:/v:version/example,可以把 path 的参数指定为路由参数:path:"version",此时,url: http://127.0.0.1:8888/v1/example,可以绑定path参数"1" |
| form | 绑定请求的 body 内容。content-type -> multipart/form-data 或 application/x-www-form-urlencoded,绑定 form 的 key-value |
| query | 绑定请求的 query 参数 |
| cookie | 绑定请求的 cookie 参数 |
| header | 绑定请求的 header 参数 |
| json | 绑定请求的 body 内容 content-type -> application/json,绑定 json 参数 |
| raw_body | 绑定请求的原始 body(bytes),绑定的字段名不指定,也能绑定参数。(注:raw_body 绑定优先级最低,当指定多个 tag 时,一旦其他 tag 成功绑定参数,则不会绑定 body 内容。) |
| vd | 参数校验,校验语法 |
| default | 设置默认值 |
参数绑定优先级
path > form > query > cookie > header > json > raw_body
注:如果请求的 content-type 为
application/json,那么会在参数绑定前做一次 json unmarshal 处理作为兜底。
必传参数
通过在 tag 中添加 required,可以将参数标记为必传。当绑定失败时 Bind 和 BindAndValidate 将会返回错误。当多个 tag
包含 required 时,将会按照优先级绑定。如果所有 tag 都没有绑定上,则会返回错误。
type TagRequiredReq struct {
// 当 JSON 中没有 hertz 字段时,会返回 required 错误:binding: expr_path=hertz, cause=missing required parameter
Hertz string `json:"hertz,required"`
// 当 query 和 JSON 中同时没有 kitex 字段时,会返回 required 错误:binding: expr_path=hertz, cause=missing required parameter"
Kitex string `query:"kitex,required" json:"kitex,required" `
}
常见用法
自定义 bind 和 validate 的 Error
绑定参数发生错误和参数校验失败的时候,用户可以自定义的 Error(demo ),使用方法如下:
import "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/binding"
type BindError struct {
ErrType, FailField, Msg string
}
// Error implements error interface.
func (e *BindError) Error() string {
if e.Msg != "" {
return e.ErrType + ": expr_path=" + e.FailField + ", cause=" + e.Msg
}
return e.ErrType + ": expr_path=" + e.FailField + ", cause=invalid"
}
type ValidateError struct {
ErrType, FailField, Msg string
}
// Error implements error interface.
func (e *ValidateError) Error() string {
if e.Msg != "" {
return e.ErrType + ": expr_path=" + e.FailField + ", cause=" + e.Msg
}
return e.ErrType + ": expr_path=" + e.FailField + ", cause=invalid"
}
func init() {
CustomBindErrFunc := func(failField, msg string) error {
err := BindError{
ErrType: "bindErr",
FailField: "[bindFailField]: " + failField,
Msg: "[bindErrMsg]: " + msg,
}
return &err
}
CustomValidateErrFunc := func(failField, msg string) error {
err := ValidateError{
ErrType: "validateErr",
FailField: "[validateFailField]: " + failField,
Msg: "[validateErrMsg]: " + msg,
}
return &err
}
binding.SetErrorFactory(CustomBindErrFunc, CustomValidateErrFunc)
}
自定义类型解析
在参数绑定的时候,所有的 request 参数都是 string 或者 []string;当有一些 field
的类型为非基础类型或者无法直接通过 string
转换,则可以自定义类型解析(demo
)。使用方法如下:
import "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/binding"
type Nested struct {
B string
C string
}
type TestBind struct {
A Nested `query:"a,required"`
}
func init() {
binding.MustRegTypeUnmarshal(reflect.TypeOf(Nested{}), func(v string, emptyAsZero bool) (reflect.Value, error) {
if v == "" && emptyAsZero {
return reflect.ValueOf(Nested{}), nil
}
val := Nested{
B: v[:5],
C: v[5:],
}
return reflect.ValueOf(val), nil
})
}
自定义验证函数
可以通过注册自定义验证函数,在’vd' 注解中实现复杂的验证逻辑(demo ),使用方法如下:
import "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/binding"
func init() {
binding.MustRegValidateFunc("test", func(args ...interface{}) error {
if len(args) != 1 {
return fmt.Errorf("the args must be one")
}
s, _ := args[0].(string)
if s == "123" {
return fmt.Errorf("the args can not be 123")
}
return nil
})
}
配置 looseZero
在一些场景下,前端有时候传来的信息只有 key 没有
value,这会导致绑定数值类型的时候,会报错 cause=parameter type does not match binding data。
这时需要配置 looseZero 模式(demo ),使用方法如下:
import "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/binding"
func init() {
// 默认 false,全局生效
binding.SetLooseZeroMode(true)
}
配置其他 json unmarshal 库
在绑定参数的时候,如果请求体为 json,会进行一次 json 的 unmarshal,如果用户需要使用特定的 json 库可以自己配置(hertz 默认使用开源 json 库 sonic )。使用方法如下:
import "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/binding"
func init() {
// 使用标准库
binding.UseStdJSONUnmarshaler()
// 使用 gjson
binding.UseGJSONUnmarshaler()
// 使用第三方 json unmarshal 方法
binding.UseThirdPartyJSONUnmarshaler()
}
设置默认值
参数支持 “default” tag 进行默认值的配置,使用方法如下:
// 生成的代码
type UserInfoResponse struct {
NickName string `default:"Hertz" json:"NickName" query:"nickname"`
}
绑定文件
参数绑定支持绑定文件,使用方法如下:
// 需要请求的 content-type 为:multipart/form-data
type FileParas struct {
F *multipart.FileHeader `form:"F1"`
}
h.POST("/upload", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
var req FileParas
err := binding.BindAndValidate(c, &req)
})
常见问题分析
1. string 转 int 报错:json: cannot unmarshal string into Go struct field xxx of type intxx
原因:默认不支持 string 和 int 互转
解决方法:
-
建议使用标准包 json 的
stringtag, 例如:A int `json:"A, string"` -
配置其他支持这种行为的 json 库
title: “重试” date: 2022-10-01 weight: 13 keywords: [“重试”, “Client”] description: “Hertz 为用户提供的自定义重试逻辑。”
Hertz 为用户提供了自定义的重试逻辑,下面来看一下 Client 的 Retry 使用方法。注意:Hertz 版本 >= v0.4.0
Retry 次数及延迟策略配置
首先创建 Client,使用配置项 WithRetryConfig() 来配置 Retry 相关逻辑(这一部分主要配置 Retry 的次数和延时部分)
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client/retry"
)
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient(
client.WithRetryConfig(
retry.WithXxx(), // 设置 Retry 配置的方式
),
)
}
| 配置名称 | 类型 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| WithMaxAttemptTimes | uint | 用于设置最大尝试次数,默认 1 次(即只请求 1 次不重试) |
| WithInitDelay | time.Duration | 用于设置初始延迟时间,默认 1ms |
| WithMaxDelay | time.Duration | 用于设置最大延迟时间,默认 100ms |
| WithMaxJitter | time.Duration | 用于设置最大扰动时间,需要配合 RandomDelayPolicy 使用,会生成不超过最大扰动时间的随机时间,默认 20ms |
| WithDelayPolicy | type DelayPolicyFunc func(attempts uint, err error, retryConfig *Config) time.Duration | 用于设置延迟策略,可以使用以下四种的任意结合,FixedDelayPolicy, BackOffDelayPolicy, RandomDelayPolicy, DefaultDelayPolicy(详情见下一小节:延迟策略)默认使用 DefaultDelayPolicy(即重试延迟为 0) |
延迟策略
retry.WithDelayPolicy() 使用方法
cli, err := client.NewClient(
client.WithRetryConfig(
...
retry.WithDelayPolicy(retry.CombineDelay(retry.FixedDelayPolicy, retry.BackOffDelayPolicy, retry.RandomDelayPolicy)),
...
),
)
| 函数名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| CombineDelay | 用于将下面四种策略进行任意组合,将所选策略计算出的值进行加和。当你只需要下面四种策略中的一种时,你可以选择使用 CombineDelay 或选择直接将任意一种策略传入 WithDelayPolicy 作为参数 |
| FixedDelayPolicy | 用于设置固定延迟时间,使用 WithInitDelay 设置的值,来生成等值的延迟时间 |
| BackOffDelayPolicy | 用于设置指数级延迟时间,使用 WithInitDelay 设置的值,根据当前是第几次重试,指数级生成延迟时间 |
| RandomDelayPolicy | 用于设置随机延迟时间,使用 WithMaxJitter 设置的值,生成不超过该值的随机延迟时间 |
| DefaultDelayPolicy | 用于设置默认延迟时间,返回 0,一般单独使用,和其他策略结合没有效果 |
完整示例
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client/retry"
)
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient(
client.WithRetryConfig(
retry.WithMaxAttemptTimes(3), // 最大的尝试次数,包括初始调用
retry.WithInitDelay(1*time.Millisecond), // 初始延迟
retry.WithMaxDelay(6*time.Millisecond), // 最大延迟,不管重试多少次,策略如何,都不会超过这个延迟
retry.WithMaxJitter(2*time.Millisecond), // 延时的最大扰动,结合 RandomDelayPolicy 才会有效果
/*
配置延迟策略,你可以选择下面四种中的任意组合,最后的结果为每种延迟策略的加和
FixedDelayPolicy 使用 retry.WithInitDelay 所设置的值,
BackOffDelayPolicy 在 retry.WithInitDelay 所设置的值的基础上随着重试次数的增加,指数倍数增长,
RandomDelayPolicy 生成 [0,2*time.Millisecond)的随机数值,2*time.Millisecond 为 retry.WithMaxJitter 所设置的值,
DefaultDelayPolicy 生成 0 值,如果单独使用则立刻重试,
retry.CombineDelay() 将所设置的延迟策略所生成的值加和,最后结果即为当前次重试的延迟时间,
第一次调用失败 -> 重试延迟:1 + 1<<1 + rand[0,2)ms -> 第二次调用失败 -> 重试延迟:min(1 + 1<<2 + rand[0,2) , 6)ms -> 第三次调用成功/失败
*/
retry.WithDelayPolicy(retry.CombineDelay(retry.FixedDelayPolicy, retry.BackOffDelayPolicy, retry.RandomDelayPolicy)),
),
)
}
Retry 条件配置
如果你想要自定义配置重试发生的条件,你可以使用 client.SetRetryIfFunc() 配置,该函数的参数是一个函数,签名为:
func(req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, err error) bool
相关参数包括 Hertz 请求中的 req、resp 和 err 字段,你可以通过这些参数,判断这个请求该不该重试。在如下例子中,当请求返回的状态码不是
200 或者调用过程中 err != nil 时我们返回 true,即进行重试。
cli.SetRetryIfFunc(func(req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, err error) bool {
return resp.StatusCode() != 200 || err != nil
})
需要注意的是,如果你没有设置 client.SetRetryIfFunc()。我们将会按照 Hertz
默认的重试发生条件进行判断,即判断请求是否满足下面的 DefaultRetryIf()
函数并且判断该调用是否是幂等调用(幂等调用:即 pkg/protocol/http1/client.go::Do()
和 pkg/protocol/http1/client.go::doNonNilReqResp()
中 canIdempotentRetry 为 true 的 情况)
// DefaultRetryIf Default retry condition, mainly used for idempotent requests.
// If this cannot be satisfied, you can implement your own retry condition.
func DefaultRetryIf(req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, err error) bool {
// cannot retry if the request body is not rewindable
if req.IsBodyStream() {
return false
}
if isIdempotent(req, resp, err) {
return true
}
// Retry non-idempotent requests if the server closes
// the connection before sending the response.
//
// This case is possible if the server closes the idle
// keep-alive connection on timeout.
//
// Apache and nginx usually do this.
if err == io.EOF {
return true
}
return false
}
func isIdempotent(req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, err error) bool {
return req.Header.IsGet() ||
req.Header.IsHead() ||
req.Header.IsPut() ||
req.Header.IsDelete() ||
req.Header.IsOptions() ||
req.Header.IsTrace()
}
Table - 1 Hertz
源码 doNonNilReqResp()
中 canIdempotentRetry 为 true 的情况
| doNonNilReqResp() 返回 true 的情况 |
|---|
| err = conn.SetWriteDeadline(currentTime.Add(c.WriteTimeout)) |
| err = reqI.Write(req, zw) |
| err = reqI.ProxyWrite(req, zw) |
| err = zw.Flush() |
| err = conn.SetReadTimeout(c.ReadTimeout) |
| ( err = respI.ReadHeaderAndLimitBody() || err = respI.ReadBodyStream() ) && (err != errs.ErrBodyTooLarge) |
title: “适配器”
date: 2023-01-11
weight: 16
keywords: [“适配器”, “http.Request”, “http.ResponseWriter”, “net/http”]
description: “Hertz 提供获取 Go 标准库的 http.Request 和 http.ResponseWriter 的方式及其相关方法。”
Hertz 提供了获取 Go 标准库的 http.Request 和 http.ResponseWriter 的方式及其相关方法,以便于用户集成 net/http 进行开发。
注意:这种适配性是以性能损耗为代价的。
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/adaptor"
)
func handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.WriteHeader(200)
_, err := w.Write([]byte("Hello World"))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
}
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
req, err := adaptor.GetCompatRequest(&c.Request)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// You may build more logic on req
fmt.Println(req.URL.String())
// caution: don't pass in c.GetResponse() as it return a copy of response
rw := adaptor.GetCompatResponseWriter(&c.Response)
handler(rw, req)
})
h.Spin()
}
http.Request
| 函数 | 函数签名 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| GetCompatRequest | func GetCompatRequest(req *protocol.Request) (*http.Request, error) |
通过 Hertz protocol.Request 构建并获取 Go 标准库 http.Request |
| CopyToHertzRequest | func CopyToHertzRequest(req *http.Request, hreq *protocol.Request) |
拷贝 Go 标准库 http.Request 的 URI,Host,Method,Protocol,Header 到 Hertz protocol.Request,对于 Body 属性会以共享 Reader 的方式进行适配 |
http.ResponseWriter
| 函数 / 结构体 | 函数签名 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| GetCompatResponseWriter | func GetCompatResponseWriter(resp *protocol.Response) http.ResponseWriter |
通过 Hertz protocol.Response 构建并获取 Go 标准库 http.ResponseWriter |
| compatResponse | / | compatResponse 结构体实现了 http.ResponseWriter 接口并对 Header,Write,WriteHeader 函数进行了适配 |
Handler
Hertz 的 pprof 中间件提供了 Go 标准库 http.Handler 和 http.HandlerFunc 的适配方法,以便用户适配为
Hertz app.HandlerFunc 进行开发。
| 函数 | 函数签名 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| NewHertzHTTPHandlerFunc | func NewHertzHTTPHandlerFunc(h http.HandlerFunc) app.HandlerFunc |
用于将 Go 标准库 http.HandlerFunc 转换为 Hertz app.HandlerFunc |
| NewHertzHTTPHandler | func NewHertzHTTPHandler(h http.Handler) app.HandlerFunc |
用于将 Go 标准库 http.Handler 转换为 Hertz app.HandlerFunc |
参考 hertz-example 和 pprof 以获取更多示例
title: “Engine” date: 2023-08-18 weight: 1 description: >
server.Hertz 是 Hertz 的核心类型,它由 route.Engine 以及 signalWaiter 组成,Hertz
服务器的启动、路由注册、中间件注册以及退出等重要方法均包含在 server.Hertz 中。以下是 server.Hertz 的定义:
type Hertz struct {
*route.Engine
// 用于接收信号以实现优雅退出
signalWaiter func (err chan error) error
}
route.Engine 为 server.Hertz 的重要组成部分,Engine
的定义位于 Engine。
配置
| 配置项 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| WithTransport | network.NewTransporter | 更换底层 transport |
| WithHostPorts | :8888 |
指定监听的地址和端口 |
| WithKeepAliveTimeout | 1min | tcp 长连接保活时间,一般情况下不用修改,更应该关注 idleTimeout |
| WithReadTimeout | 3min | 底层读取数据超时时间 |
| WithIdleTimeout | 3min | 长连接请求链接空闲超时时间 |
| WithMaxRequestBodySize | 4 * 1024 * 1024 | 配置最大的请求体大小 |
| WithRedirectTrailingSlash | true | 自动根据末尾的 / 转发,例如:如果 router 只有 /foo/,那么 /foo 会重定向到 /foo/ ;如果只有 /foo,那么 /foo/ 会重定向到 /foo |
| WithRemoveExtraSlash | false | RemoveExtraSlash 当有额外的 / 时也可以当作参数。如:user/:name,如果开启该选项 user//xiaoming 也可匹配上参数 |
| WithUnescapePathValues | true | 如果开启,请求路径会被自动转义(eg. ‘%2F’ -> ‘/')。如果 UseRawPath 为 false(默认情况),则 UnescapePathValues 实际上为 true,因为 .URI().Path() 将被使用,它已经是转义后的。设置该参数为 false,需要配合 WithUseRawPath(true) |
| WithUseRawPath | false | 如果开启,会使用原始 path 进行路由匹配 |
| WithHandleMethodNotAllowed | false | 如果开启,当当前路径不能被匹配上时,server 会去检查其他方法是否注册了当前路径的路由,如果存在则会响应"Method Not Allowed",并返回状态码 405; 如果没有,则会用 NotFound 的 handler 进行处理 |
| WithDisablePreParseMultipartForm | false | 如果开启,则不会预处理 multipart form。可以通过 ctx.Request.Body() 获取到 body 后由用户处理 |
| WithStreamBody | false | 如果开启,则会使用流式处理 body |
| WithNetwork | “tcp” | 设置网络协议,可选:tcp,udp,unix(unix domain socket),默认为 tcp |
| WithExitWaitTime | 5s | 设置优雅退出时间。Server 会停止建立新的连接,并对关闭后的每一个请求设置 Connection: Close 的 header,当到达设定的时间关闭 Server。当所有连接已经关闭时,Server 可以提前关闭 |
| WithTLS | nil | 配置 server tls 能力,详情可见 TLS |
| WithListenConfig | nil | 设置监听器配置,可用于设置是否允许 reuse port 等 |
| WithALPN | false | 是否开启 ALPN |
| WithTracer | []interface{}{} | 注入 tracer 实现,如不注入 Tracer 实现,默认关闭 |
| WithTraceLevel | LevelDetailed | 设置 trace level |
| WithWriteTimeout | 无限长 | 写入数据超时时间 |
| WithRedirectFixedPath | false | 如果开启,当当前请求路径不能匹配上时,server 会尝试修复请求路径并重新进行匹配,如果成功匹配并且为 GET 请求则会返回状态码 301 进行重定向,其他请求方式返回 308 进行重定向 |
| WithBasePath | / |
设置基本路径,前缀和后缀必须为 / |
| WithMaxKeepBodySize | 4 * 1024 * 1024 | 设置回收时保留的请求体和响应体的最大大小。单位:字节 |
| WithGetOnly | false | 如果开启则只接受 GET 请求 |
| WithKeepAlive | true | 如果开启则使用 HTTP 长连接 |
| WithAltTransport | network.NewTransporter | 设置备用 transport |
| WithH2C | false | 设置是否开启 H2C |
| WithReadBufferSize | 4 * 1024 | 设置读缓冲区大小,同时限制 HTTP header 大小 |
| WithRegistry | registry.NoopRegistry, nil | 设置注册中心配置,服务注册信息 |
| WithAutoReloadRender | false, 0 | 设置自动重载渲染配置 |
| WithDisablePrintRoute | false | 设置是否禁用 debugPrintRoute |
| WithOnAccept | nil | 设置在 netpoll 中当一个连接被接受但不能接收数据时的回调函数,在 go net 中在转换 TLS 连接之前被调用 |
| WithOnConnect | nil | 设置 onConnect 函数。它可以接收来自 netpoll 连接的数据。在 go net 中,它将在转换 TLS 连接后被调用 |
Server Connection 数量限制:
- 如果是使用标准网络库,无此限制
- 如果是使用 netpoll,最大连接数为 10000
(这个是 netpoll
底层使用的 gopool
)控制的,修改方式也很简单,调用 gopool 提供的函数即可:
gopool.SetCap(xxx)(main.go 中调用一次即可)。
Server 侧的配置项均在初始化 Server 时采用 server.WithXXX 的方式,如:
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithXXXX())
...
}
初始化服务
func Default(opts ...config.Option) *Hertz
func New(opts ...config.Option) *Hertz
Default
Default 用于初始化服务,默认使用了 Recovery 中间件以保证服务在运行时不会因为 panic 导致服务崩溃。
函数签名:
func Default(opts ...config.Option) *Hertz
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Spin()
}
New
New 用于初始化服务,没有使用默认的 Recovery 中间件。
函数签名:
func New(opts ...config.Option) *Hertz
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
h.Spin()
}
服务运行与退出
func (h *Hertz) Spin()
func (engine *Engine) Run() (err error)
func (h *Hertz) SetCustomSignalWaiter(f func(err chan error) error)
Spin
Spin 函数用于运行 Hertz 服务器,接收到退出信号后可退出服务。
该函数支持服务的优雅退出,优雅退出的详细内容请看 优雅退出。
在使用 服务注册发现
的功能时,Spin 会在服务启动时将服务注册进入注册中心,并使用 signalWaiter 监测服务异常。
函数签名:
func (h *Hertz) Spin()
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Spin()
}
Run
Run 函数用于运行 Hertz 服务器,接收到退出信号后可退出服务。
该函数不支持服务的优雅退出,除非有特殊需求,不然一般使用 Spin 函数用于运行服务。
函数签名:
func (engine *Engine) Run() (err error)
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.Default()
if err := h.Run(); err != nil {
// ...
panic(err)
}
}
SetCustomSignalWaiter
SetCustomSignalWaiter 函数用于自定义服务器接收信号后的处理函数,若没有设置自定义函数,Hertz 使用 waitSignal
函数作为信号处理的默认实现方式,详细内容请看优雅退出。
函数签名:
func (h *Hertz) SetCustomSignalWaiter(f func(err chan error) error)
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
h.SetCustomSignalWaiter(func(err chan error) error {
return nil
})
h.Spin()
}
中间件
func (engine *Engine) Use(middleware ...app.HandlerFunc) IRoutes
Use
Use 函数用于将中间件注册进入路由。
Hertz 支持用户自定义中间件,Hertz 已经实现了一些常用的中间件,详情见 hertz-contrib。
Hertz 支持的中间件的使用方法包括全局注册、路由组级别和单一路由 级别的注册,详情见 服务端中间件。
Use 函数中 middleware 的形参必须为 app.HandlerFunc 的 http 处理函数:
type HandlerFunc func (ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext)
函数签名:
func (engine *Engine) Use(middleware ...app.HandlerFunc) IRoutes
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
// 将内置的 Recovery 中间件注册进入路由
h.Use(recovery.Recovery())
// 使用自定义的中间件
h.Use(exampleMiddleware())
}
func exampleMiddleware() app.handlerFunc {
return func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
// 在 Next 中的函数执行之前打印日志
hlog.Info("print before...")
// 使用 Next 使得路由匹配的函数执行
c.Next(ctx)
// 在 Next 中的函数执行之后打印日志
hlog.Ingo("print after...")
}
}
流式处理
Hertz 支持 Server 的流式处理,包括流式读和流式写。
注意:由于 netpoll 和 go net 触发模式不同,netpoll 流式为 “伪” 流式(由于 LT 触发,会由网络库将数据读取到网络库的 buffer 中),在大包的场景下(如:上传文件等)可能会有内存问题,推荐使用 go net。
流式读
Hertz Server 支持流式读取请求内容。
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"), server.WithStreamBody(true), server.WithTransport(standard.NewTransporter))
h.POST("/bodyStream", handler)
h.Spin()
}
func handler(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
// Acquire body streaming
bodyStream := c.RequestBodyStream()
// Read half of body bytes
p := make([]byte, c.Request.Header.ContentLength()/2)
r, err := bodyStream.Read(p)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
left, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(bodyStream)
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "bytes streaming_read: %d\nbytes left: %d\n", r, len(left))
}
流式写
Hertz Server 支持流式写入响应。
提供了两种方式:
-
用户在 handler 中通过
ctx.SetBodyStream函数传入一个io.Reader,然后按与示例代码(利用 channel 控制数据分块及读写顺序)类似的方式分块读写数据。注意,数据需异步写入。若用户事先知道传输数据的总长度,可以在
ctx.SetBodyStream函数中传入该长度进行流式写,示例代码如/streamWrite1。若用户事先不知道传输数据的总长度,可以在
ctx.SetBodyStream函数中传入 -1 以Transfer-Encoding: chunked的方式进行流式写,示例代码如/streamWrite2。示例代码:
func main() { h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"), server.WithStreamBody(true), server.WithTransport(standard.NewTransporter)) h.GET("/streamWrite1", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) { rw := newChunkReader() line := []byte("line\r\n") ctx.SetBodyStream(rw, 500*len(line)) go func() { for i := 1; i <= 500; i++ { // For each streaming_write, the upload_file prints rw.Write(line) fmt.Println(i) time.Sleep(10 * time.Millisecond) } rw.Close() }() go func() { <-ctx.Finished() fmt.Println("request process end") }() }) h.GET("/streamWrite2", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) { rw := newChunkReader() // Content-Length may be negative: // -1 means Transfer-Encoding: chunked. ctx.SetBodyStream(rw, -1) go func() { for i := 1; i < 1000; i++ { // For each streaming_write, the upload_file prints rw.Write([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("===%d===\n", i))) fmt.Println(i) time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond) } rw.Close() }() go func() { <-ctx.Finished() fmt.Println("request process end") }() }) h.Spin() } type ChunkReader struct { rw bytes.Buffer w2r chan struct{} r2w chan struct{} } func newChunkReader() *ChunkReader { var rw bytes.Buffer w2r := make(chan struct{}) r2w := make(chan struct{}) cr := &ChunkReader{rw, w2r, r2w} return cr } var closeOnce = new(sync.Once) func (cr *ChunkReader) Read(p []byte) (n int, err error) { for { _, ok := <-cr.w2r if !ok { closeOnce.Do(func() { close(cr.r2w) }) n, err = cr.rw.Read(p) return } n, err = cr.rw.Read(p) cr.r2w <- struct{}{} if n == 0 { continue } return } } func (cr *ChunkReader) Write(p []byte) (n int, err error) { n, err = cr.rw.Write(p) cr.w2r <- struct{}{} <-cr.r2w return } func (cr *ChunkReader) Close() { close(cr.w2r) } -
用户可以在 handler 中使用
pkg/protocol/http1/resp/writer下提供的NewChunkedBodyWriter方法劫持 response 的 writer,然后使用ctx.Write函数将分块数据写入 Body 并将分块数据使用ctx.Flush函数立即发送给客户端。示例代码:
h.GET("/flush/chunk", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) { // Hijack the writer of response ctx.Response.HijackWriter(resp.NewChunkedBodyWriter(&ctx.Response, ctx.GetWriter())) for i := 0; i < 10; i++ { ctx.Write([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("chunk %d: %s", i, strings.Repeat("hi~", i)))) // nolint: errcheck ctx.Flush() // nolint: errcheck time.Sleep(200 * time.Millisecond) } })
**这两种方式的区别:第一种在执行完 handler 逻辑后再将数据按分块发送给客户端,第二种在 handler 逻辑中就可以将分块数据发送出去。 **
更多示例代码可参考 example。
注册自定义协议
func (engine *Engine) AddProtocol(protocol string, factory interface{})
详细信息可见 注册自定义协议。
SetClientIPFunc
该函数的参数 f 会被传递到 RequestContext.SetClientIPFunc
函数中,作用及示例代码见 SetClientIPFunc。
函数签名:
func (engine *Engine) SetClientIPFunc(f app.ClientIP)
SetFormValueFunc
该函数的参数 f 会被传递到 RequestContext.SetFormValueFunc
函数中,作用及示例代码见 SetFormValueFunc。
函数签名:
func (engine *Engine) SetFormValueFunc(f app.FormValueFunc)
钩子函数
钩子函数(Hooks)是一个通用的概念,表示某事件触发时所伴随的操作。
Hertz 提供了全局的 Hook 注入能力,用于在服务触发启动后和退出前注入自己的处理逻辑,详细信息可见 Hooks。
Panic 处理函数
用于设置当程序发生 panic 时的处理函数,默认为 nil。
注意: 如果同时设置了
PanicHandler和Recovery中间件,则Recovery中间件会覆盖PanicHandler的处理逻辑。
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
// 在 panic 时,会触发 PanicHandler 中的函数,返回 500 状态码并携带错误信息
h.PanicHandler = func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(500, utils.H{
"message": "panic",
})
}
h.GET("/hello", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
panic("panic")
})
h.Spin()
}
ContinueHandler
在接收到客户端发来的 Expect 100 Continue 头之后调用 ContinueHandler。使用 ContinueHandler,服务器可以决定是否读取可能很大的请求正文,默认情况下会读取。
示例代码:
h := server.Default()
h.ContinueHandler = func(header *protocol.RequestHeader) bool {
return false
}
渲染 template
Hertz 提供了 Delims, SetFuncMap, LoadHTMLGlob, LoadHTMLFiles 等方法用于渲染 HTML
或模板文件,详细内容可参考 HTML。
NoRoute 与 NoMethod 使用
Hertz 提供了 NoRoute 与 NoMethod 方法用于全局处理 HTTP 404 与 405
请求,详细内容可参考 NoRoute 与 NoMethod 使用。
获取路由信息
func (engine *Engine) Routes() (routes RoutesInfo)
Routes
Routes 函数返回一个按 HTTP 方法划分的包含路由信息(HTTP 方法名,路由路径,请求处理函数名)的切片。
函数签名:
func (engine *Engine) Routes() (routes RoutesInfo)
示例代码:
func getHandler() app.HandlerFunc {
return func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "get handler")
}
}
func postHandler() app.HandlerFunc {
return func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "post handler")
}
}
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.GET("/get", getHandler())
h.POST("/post", postHandler())
routesInfo := h.Routes()
fmt.Printf("%v\n", routesInfo)
// [{GET /get main.getHandler.func1 0xb2afa0} {POST /post main.postHandler.func1 0xb2b060}]
}
底层网络库
func (engine *Engine) GetTransporterName() (tName string)
func SetTransporter(transporter func (options *config.Options) network.Transporter)
GetTransporterName
获取当前使用的网络库名称,现在有原生的 go net 和 netpoll 两种。
linux 默认使用 netpoll, windows 只能使用 go net。
如果对如何使用对应的网络库有疑惑,请查看 此处。
函数签名:
func (engine *Engine) GetTransporterName() (tName string)
示例代码:
h := server.New()
tName := h.GetTransporterName()
SetTransporter
SetTransporter 用于设置网络库。
注意:
SetTransporter只设置 Engine 的全局默认值,所以在初始化 Engine 时使用WithTransporter来设置网络库会覆盖掉SetTransporter的设置。
函数签名:
func SetTransporter(transporter func (options *config.Options) network.Transporter)
示例代码:
route.SetTransporter(standard.NewTransporter)
链路追踪
Hertz 提供了链路追踪的能力,也支持用户自定义链路跟踪,详情可参考 链路追踪。
Hijack
NoHijackConnPool
Hertz 连接劫持时所使用的 hijack conn 是池化管理的,因此被劫持的连接在 websocket 中使用的时候,不支持异步操作。
劫持的连接仅能被关闭一次,第二次关闭会导致空指针异常。
NoHijackConnPool 将控制是否使用缓存池来获取/释放劫持连接。如果使用池,将提升内存资源分配的性能,但无法避免二次关闭连接导致的异常。
如果很难保证 hijackConn 不会被反复关闭,可以将其设置为 true。
示例代码:
package main
func main() {
// https://github.com/cloudwego/hertz/issues/121
h.NoHijackConnPool = true
}
HijackConnHandle
设置 Hijack 连接处理函数。
函数签名:
func (engine *Engine) HijackConnHandle(c network.Conn, h app.HijackHandler)
title: “网络库” date: 2022-05-20 weight: 4 keywords: [“netpoll”, “go net”] description: “Hertz 默认集成了 Netpoll 和 Golang 原生网络库两个网络库,用户可以根据自己的场景选择合适的网络库以达到最佳性能。”
使用方式
对于 Server 来说,默认使用 netpoll,可以通过配置项进行更改:
注意:netpoll 目前不支持 Windows,Windows 会通过条件编译将网络库自动切换为 go net。
server.New(server.WithTransport(standard.NewTransporter))
server.New(server.WithTransport(netpoll.NewTransporter))
对于 Client 来说,可以通过配置项进行更改:
client.NewClient(client.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()))
client.NewClient(client.WithDialer(netpoll.NewDialer()))
网络库选择
- 如果有启动 TLS Server 的需求,请使用
go net网络库。netpoll正在实现对 TLS 的支持。 - 由于网络库触发模式的不同:
go net为 ET 模型,netpoll为 LT 模型,使得两个网络库的适用场景有一些不同。 在 ET 模型下,由框架处理 Read / Write 事件;在 LT 模型下,由网络库处理 Read / Write 事件。 使得在小包场景下,由于更优的调度策略使得 LT 性能更好;在大包场景下,由于读 / 写不受框架层控制,使得大量数据被读入内存而不能及时处理,可能会造成内存压力。
- 在较大 request size 下(request size > 1M),推荐使用 go net 网络库加流式。
- 在其他场景下,推荐使用 netpoll 网络库,会获得极致的性能。
title: “JSON Marshal 库” linkTitle: “JSON Marshal 库” date: 2023-08-03 weight: 19 keywords: [“JSON Marshal”, “Sonic”, “条件编译”, “自定义 JSON Marshall 库”] description: “Hertz 使用的 JSON Marshal 库及自定义能力。”
Hertz 默认集成并使用 Sonic 用于序列化 ctx.JSON 接口,以及反序列化 binding
包中的请求。Sonic 是一款超高性能 golang json 库,详情参考 Sonic README 。
开启 Sonic 需要满足以下条件:
- Go 1.16 以上
- Linux / darwin OS / Windows
- Amd64 CPU with AVX instruction set
当上述条件不能满足时,Sonic 会自动 fallback 到 golang 的 encoding/json 库。
自定义 JSON Marshall 库
如果 Sonic 不能够满足您的需求,你可以使用以下方式自定义 json marshal 库的实现:
import (
"encoding/json"
"github.com/bytedance/go-tagexpr/v2/binding"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server/render"
)
func main() {
// Render
render.ResetJSONMarshal(json.Marshal)
// Binding
binding.ResetJSONUnmarshaler(json.Unmarshal)
}
条件编译
Hertz 支持条件编译来控制实际使用的 json 库,你可以通过 -tags stdjson 来选择使用标准库。
go build -tags stdjson
Sonic 相关问题
若出现与 Sonic 相关的问题,可参考 Sonic README 或提 issue 解决。
title: “优雅退出” date: 2022-05-23 weight: 11 keywords: [“优雅退出”] description: “Hertz 停止服务时提供的优雅退出功能。”
Hertz 支持优雅退出,优雅退出过程如下:
- 设置
engine状态为closed - 顺序非阻塞触发回调函数
[]OnShutDown(与标准包 net/http 一致),Select等待回调函数执行完成或者超时返回 Select等待业务协程退出:- 对于 netpoll 网络库,开启默认 1s(netpoll 中设置,暂时不可更改)的
ticker,定时查看active conn(业务 handle 退出且连接不处于阻塞读状态)是否为 0;对于 go net 网络库,则关闭监听,不对连接做处理。 - 等待超时时间为
ExitWaitTime的 context 触发,默认 5s
- 对于 netpoll 网络库,开启默认 1s(netpoll 中设置,暂时不可更改)的
- 注册中心注销对应服务
- 关闭网络库的信号监听
- 对处于关闭过程中的请求回包统一带上
Connection:Close header
如需修改等待超时时间,可通过 server.WithExitWaitTime() 进行配置。
如需注册退出 hook 函数,可通过获取到 Engine 后进行注册:
h.Engine.OnShutdown = append(h.Engine.OnShutdown, shutDownFunc)
Hertz 使用 waitSignal 函数作为信号处理的默认实现方式,处理如下:
- 当接收到
SIGTERM系统信号时触发立即退出。 - 当接收到
SIGHUP|SIGINT系统信号时触发优雅退出。
当信号处理的默认实现方式无法满足需求时,可通过 SetCustomSignalWaiter 来自定义信号处理方式。
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
func main() {
h := server.New()
h.SetCustomSignalWaiter(func(err chan error) error {
return nil
})
...
}
当自定义信号处理函数返回 error 时 Hertz 会立即退出,其他情况下则会优雅退出。
title: ‘渲染’ date: 2023-06-01 weight: 18 keywords: [“渲染”, “JSON”, “Data”, “HTML”, “Protobuf”, “Text”, “XML”, “自定义渲染”] description: “Hertz 提供的渲染能力。”
Hertz 支持对 JSON,HTML,Protobuf 等的渲染。
JSON
JSON
Hertz 支持渲染 JSON。
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
// utils.H is a shortcut for map[string]interface{}
h.GET("/someJSON", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"message": "hey", "status": consts.StatusOK})
})
h.Spin()
}
你也可以使用一个结构体。
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.GET("/moreJSON", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
var msg struct {
Company string `json:"company"`
Location string
Number int
}
msg.Company = "company"
msg.Location = "location"
msg.Number = 123
// Note that msg.Company becomes "company" in the JSON
// Will output : {"company": "company", "Location": "location", "Number": 123}
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, msg)
})
h.Spin()
}
PureJSON
JSON 使用 Unicode 替换特殊的 HTML 字符,如果你想要按照字面意义编码这些字符,你可以使用 PureJSON。
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.GET("/pureJson", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.PureJSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{
"html": "<p> Hello World </p>",
})
h.Spin()
}
IndentedJSON
IndentedJSON 将给定的结构序列化为优雅的 JSON (通过缩进 + 换行)。
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.GET("/indentedJSON", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
var msg struct {
Company string
Location string
Number int
}
msg.Company = "company"
msg.Location = "location"
msg.Number = 123
c.IndentedJSON(consts.StatusOK, msg)
/*
will output : {
"Company": "company",
"Location": "location",
"Number": 123
}
*/
h.Spin()
}
Data
Data 需要你自行设置 Content-Type,而且 Data 只接收 []byte。
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.GET("/someData", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.Data(consts.StatusOK, "text/plain; charset=utf-8", []byte("hello"))
})
h.Spin()
}
HTML
加载模板文件
Hertz 提供 LoadHTMLGlob 和 LoadHTMLFiles 来加载模板文件。
示例代码:
func main(){
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.LoadHTMLGlob("render/html/*")
//h.LoadHTMLFiles("render/html/index.tmpl")
h.GET("/index", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.tmpl", utils.H{
"title": "Main website",
})
})
}
自定义分隔符
Hertz 支持自定义分隔符。
示例代码:
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.Delims("{[{", "}]}")
//Left delimiter, defaults to {{.
//Right delimiter, defaults to }}.
自定义模板功能
Hertz 支持自定义模板功能,示例代码如下。
main.go:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"html/template"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
func formatAsDate(t time.Time) string {
year, month, day := t.Date()
return fmt.Sprintf("%d/%02d/%02d", year, month, day)
}
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.Delims("{[{", "}]}")
h.SetFuncMap(template.FuncMap{
"formatAsDate": formatAsDate,
})
h.LoadHTMLGlob("render/html/*")
h.GET("/raw", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.HTML(http.StatusOK, "template1.html", map[string]interface{}{
"now": time.Date(2017, 0o7, 0o1, 0, 0, 0, 0, time.UTC),
})
})
h.Spin()
}
template1.html:
<h1>Date: {[{.now | formatAsDate}]}</h1>
查看详细 [示例代码](hertz-examples/render/html at main · cloudwego/hertz-examples · GitHub)。
Protobuf
Hertz 支持渲染 Protobuf。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz-examples/render/protobuf/body"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.GET("/somePb", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
//The specific definition of protobuf is written in the "protobuf/body" file.
body := body.BodyStruct{
Body: []byte("Hello World"),
}
c.ProtoBuf(200, &body)
})
h.Spin()
}
示例代码中的 body.bodyStruct 具体定义如下。
type BodyStruct struct {
state protoimpl.MessageState
sizeCache protoimpl.SizeCache
unknownFields protoimpl.UnknownFields
Body []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=body" json:"body,omitempty"`
}
Text
Hertz 支持渲染 string,它需要你自行设置 format。
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.GET("someText", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "message", "hello,world")
})
h.Spin()
}
XML
Hertz 支持渲染 XML。
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.GET("/someXML", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.XML(consts.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
自定义渲染
Hertz 在 app 包内提供了 Render 方法。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Render(code int, r render.Render)
如果你想要进行自定义渲染,首先要自行实现 render 包内的 Render 接口。
type Render interface {
// Render writes data with custom ContentType.
// Do not panic inside, RequestContext will handle it.
Render(resp *protocol.Response) error
// WriteContentType writes custom ContentType.
WriteContentType(resp *protocol.Response)
}
以实现 YAML 渲染为例。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"gopkg.in/yaml.v3"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.GET("/someXML", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.Render(consts.StatusOK, YAML{Data: "hello,world"})
})
h.Spin()
}
type YAML struct {
Data interface{}
}
var yamlContentType = "application/yaml; charset=utf-8"
func (r YAML) Render(resp *protocol.Response) error {
writeContentType(resp, yamlContentType)
yamlBytes, err := yaml.Marshal(r.Data)
if err != nil {
return err
}
resp.AppendBody(yamlBytes)
return nil
}
func (r YAML) WriteContentType(w *protocol.Response) {
writeContentType(w, yamlContentType)
}
func writeContentType(resp *protocol.Response, value string) {
resp.Header.SetContentType(value)
}
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example。
title: “Hooks” date: 2022-10-16 weight: 14 keywords: [“Hooks”, “StartHook”, “ShutdownHook”, “OnAccept”, “OnConnect”] description: “Hertz 提供的钩子函数功能。”
钩子函数(Hooks)是一个通用的概念,表示某事件触发时所伴随的操作。
Hertz 提供了全局的 Hook 注入能力,用于在服务触发启动后和退出前注入自己的处理逻辑。
StartHook
StartHook 在 Hertz 当中表示服务触发启动后需调用的函数,使用 CtxErrCallback 类型表示。Hertz 使用 OnRun
属性存储 StartHook 列表。
// CtxErrCallback 参见下方其函数签名
OnRun []CtxErrCallback
触发 Server 启动后,框架会按函数声明顺序依次调用所有的 StartHook 函数,完成调用之后,才会正式开始端口监听,如果发生错误,则立刻终止服务。
函数签名:
type CtxErrCallback func(ctx context.Context) error
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.OnRun = append(h.OnRun, func(ctx context.Context) error {
hlog.Info("run the first start hook")
return nil
})
h.OnRun = append(h.OnRun, func(ctx context.Context) error {
hlog.Info("run the second start hook")
return nil
})
h.OnRun = append(h.OnRun, func(ctx context.Context) error {
hlog.Info("run the third start hook")
return nil
})
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
提示:启动服务,将在控制台顺序打印三个 StartHook 函数的日志。
main.go:17: [Info] run the first start hook
main.go:21: [Info] run the second start hook
main.go:25: [Info] run the third start hook
ShutdownHook
ShutdownHook 在 Hertz 当中表示服务退出前需调用的函数,使用 CtxCallback 类型表示。Hertz 使用 OnShutdown
属性存储 ShutdownHook 列表。
Server 退出前,框架会并发地调用所有声明的 ShutdownHook 函数,并且可以通过 server.WithExitWaitTime配置最大等待时长,默认为
5 秒,如果超时,则立刻终止服务。
ShutdownHook 的调用本质上是
Hertz 优雅退出 的一环。
函数签名:
type CtxCallback func(ctx context.Context)
示例代码 1:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.OnShutdown = append(h.OnShutdown, func(ctx context.Context) {
hlog.Info("run the first shutdown hook")
})
h.OnShutdown = append(h.OnShutdown, func(ctx context.Context) {
hlog.Info("run the second shutdown hook")
})
h.OnShutdown = append(h.OnShutdown, func(ctx context.Context) {
hlog.Info("run the third shutdown hook")
})
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
提示:终止服务,将在控制台乱序打印三个 ShutdownHook 函数的日志。
hertz.go:77: [Info] HERTZ: Begin graceful shutdown, wait at most num=5 seconds...
main.go:22: [Info] run the third shutdown hook
main.go:16: [Info] run the first shutdown hook
main.go:19: [Info] run the second shutdown hook
engine.go:279: [Info] HERTZ: Execute OnShutdownHooks finish
示例代码 2:
package main
import (
"context"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithExitWaitTime(time.Second * 2))
h.OnShutdown = append(h.OnShutdown, func(ctx context.Context) {
hlog.Info("run shutdown hook")
time.Sleep(time.Second * 5)
})
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
提示:终止服务时,因为钩子函数执行时间超过 2 秒,打印超时日志。
hertz.go:77: [Info] HERTZ: Begin graceful shutdown, wait at most num=2 seconds...
main.go:17: [Info] run shutdown hook
engine.go:276: [Info] HERTZ: Execute OnShutdownHooks timeout: error=context deadline exceeded
OnAccept
OnAccept 是一个在连接建立后且被添加到 epoll 前调用的函数。
OnAccept func(conn net.Conn) context.Context
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"net"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(
server.WithOnAccept(func(conn net.Conn) context.Context {
hlog.Info("run the onAccept")
return context.Background()
}),
server.WithHostPorts("localhost:9230"))
h.GET("", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
hlog.Info("pong")
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
提示:在发出请求后,将在控制台打印 OnAccept 函数的日志。
main.go:32: [Info] run the onAccept
main.go:38: [Info] pong
OnConnect
OnConnect 是一个在其被添加到 epoll 后调用的函数。它和 OnAccept 的不同之处在于它可以获取数据但是 OnAccept 不可以。
OnConnect func(ctx context.Context, conn network.Conn) context.Context
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/network"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(
server.WithHostPorts("localhost:9229"),
server.WithOnConnect(func(ctx context.Context, conn network.Conn) context.Context {
b, _ := conn.Peek(3)
hlog.Info("onconnect")
hlog.Info(b)
return ctx
}))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
提示:在发出请求后,将在控制台打印 OnConnect 函数的日志。
main.go:19: [Info] onconnect
main.go:20: [Info] [71 69 84]
title: “错误处理”
date: 2022-05-23 weight: 10 keywords: [“错误处理”, “自定义错误”] description: “Hertz 提供的错误处理功能。”
错误
在 Hertz 中,定义了如下的错误结构体:
type Error struct {
Err error
Type ErrorType
Meta interface{}
}
其中 Err 为标准错误,Type 为自定义错误类型,Meta 为错误元数据。
错误类型
为了更高效的处理错误,Hertz 针对错误类型做了如下预定义:
// binding 过程的错误
ErrorTypeBind ErrorType = 1 << iota
// rendering 过程的错误
ErrorTypeRender
// Hertz 内部错误,业务无需感知
ErrorTypePrivate
// 相对于 Private 来说,需要外部感知的错误
ErrorTypePublic
// 其他错误
ErrorTypeAny
建议按照错误类别定义相应的错误。
自定义错误
使用如下接口自定义错误:
// shortcut for creating a public *Error from string
func NewPublic(err string) *Error {
return New(errors.New(err), ErrorTypePublic, nil)
}
// shortcut for creating a private *Error from string
func NewPrivate(err string) *Error {
return New(errors.New(err), ErrorTypePrivate, nil)
}
func New(err error, t ErrorType, meta interface{}) *Error {
return &Error{
Err: err,
Type: t,
Meta: meta,
}
}
func Newf(t ErrorType, meta interface{}, format string, v ...interface{}) *Error {
return New(fmt.Errorf(format, v...), t, meta)
}
func NewPublicf(format string, v ...interface{}) *Error {
return New(fmt.Errorf(format, v...), ErrorTypePublic, nil)
}
func NewPrivatef(format string, v ...interface{}) *Error {
return New(fmt.Errorf(format, v...), ErrorTypePrivate, nil)
}
相关方法
| 函数签名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| SetType(flags ErrorType) *Error | 将 Error 的 ErrorType 设置为给定的 flags |
| Error() string | 实现标准 error 接口 |
| Unwrap() error | 抛出错误 |
| SetMeta(data interface{}) *Error | 设置元数据 |
| IsType(flags ErrorType) bool | 判断 Error 的 ErrorType 是否为给定的 flags |
| JSON() interface{} | 将错误转换为 json 对象 |
ErrorChain
除了针对错误定义的约定以外,框架同时提供 ErrorChain(错误链)能力。顾名思义,能够方便业务将一次请求处理上所遇到的所有错误绑定到错误链上,可以方便后续(一般是在中间件中)对所有错误进行统一处理。
相关方法
| 函数签名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| String() string | 返回一个可读性强的文本用于展示所有错误 |
| Errors() []string | 将错误链转换为标准错误数组 |
| ByType(typ ErrorType) ErrorChain | 按给定的错误类型返回对应的子错误链 |
| Last() *Error | 返回最后(最新)的一个错误 |
| JSON() interface{} | 将所有错误转换为 json 对象 |
如何使用
对应的 API 为:RequestContext.Error(err),调用该 API 会将 err 绑到对应的请求上下文上之上。
获取请求上下文已绑定的所有错误的方式:RequestContext.Errors。
// 运行此代码并打开游览器访问 localhost:8080/error
package main
import (
"context"
"errors"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.GET("/error", handle1, handle2, handle3)
h.Spin()
}
func handle1(_ context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
_ = c.Error(errors.New("first err"))
}
func handle2(_ context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
_ = c.Error(errors.New("second err"))
}
func handle3(_ context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, c.Errors.Errors())
}
title: “正向代理和反向代理” date: 2022-09-08 weight: 12 keywords: [“正向代理”, “反向代理”] description: “Hertz 提供的正向代理和反向代理能力。”
正向代理
正向代理是一种特殊的网络服务,允许一个网络终端(一般为客户端)通过这个服务与另一个网络终端(一般为服务器)进行非直接的连接。一些网关、路由器等网络设备具备网络代理功能。一般认为代理服务有利于保障网络终端的隐私或安全,防止攻击。
一个完整的代理请求过程为:客户端(Client)首先与代理服务器创建连接,接着根据代理服务器所使用的代理协议,请求对目标服务器创建连接、或者获得目标服务器的指定资源。
安装
hertz 内置了访问正向代理的功能
定义
// Proxy 结构体,根据 request 来选定访问的代理 uri
type Proxy func(*protocol.Request) (*protocol.URI, error)
// ProxyURI 用来生成只会返回固定代理 uri 的 Proxy
func ProxyURI(fixedURI *protocol.URI) Proxy
// SetProxy 用来设置 client 的 proxy,设置后 client 会与 proxy 建连发请求
func (c *Client) SetProxy(p protocol.Proxy)
示例
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
)
func main() {
proxyURL := "http://<__user_name__>:<__password__>@<__proxy_addr__>:<__proxy_port__>"
// 将代理的 uri 转成 *protocol.URI 的形式
parsedProxyURL := protocol.ParseURI(proxyURL)
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
// 设置代理
c.SetProxy(protocol.ProxyURI(parsedProxyURL))
upstreamURL := "http://google.com"
_, body, _ := c.Get(context.Background(), nil, upstreamURL)
}
客户端默认不支持 TLS,如果要访问 https 地址,应该使用标准库
c, err := client.NewClient(client.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()))
如果报证书错误还需要跳过证书验证
clientCfg := &tls.Config{
InsecureSkipVerify: true,
}
c, err := client.NewClient(client.WithTLSConfig(clientCfg), client.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()))
反向代理
反向代理在计算机网络中是代理服务器的一种。
服务器根据客户端的请求,从其关系的一组或多组后端服务器(如 Web 服务器)上获取资源,然后再将这些资源返回给客户端,客户端只会得知反向代理的 IP 地址,而不知道在代理服务器后面的服务器集群的存在。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/reverseproxy
具体实现
type ReverseProxy struct {
// 用于转发的客户端,可以通过 SetClient 方法对其进行配置
client *client.Client
// 设置反向代理的目标地址
target string
// 用于转换 request,可以通过 SetDirector 方法来自定义
// director 必须是将一个请求转换为一个新的请求的函数。
// 响应直接未经修改重定向返回给原始客户端
// 请求返回后 direcotr 不得访问
director func (*protocol.Request)
// modifyResponse 这是一个可选的函数,用于修改来自后端的响应
// 可以通过 SetModifyResponse 方法进行修改
// 如果后端返回任意响应,不管状态码是什么,这个方法将会被调用。
// 如果后端不可访问,errorHandler 方法会使用错误信息做入参被调用。
// 如果 modifyResponse 方法返回一个错误,errorHandler 方法将会使用错误做入参被调用。
// 如果 errorHandler 未设置,将使用默认实现。
modifyResponse func(*protocol.Response) error
// errorHandler 是一个可选的函数,用于处理到达后台的错误或来自 modifyResponse 的错误。
// 如果未进行设置,默认返回 StatusBadGateway (502)
errorHandler func(*app.RequestContext, error)
}
// NewSingleHostReverseProxy 返回一个新的反向代理来路由请求到指定后端。如果后端路径是”/base“请求路径是”/dir” ,目标路径将会是“/base/dir” 。
// NewSingleHostReverseProxy 不会重写 Host 请求头。
// 要想覆盖 Host 请求头,可以选择自定义 director
func NewSingleHostReverseProxy(target string, opts ...config.Option) (*reverseProxy, error)
NewSingleHostReverseProxy方法如果没有设置config.ClientOption将会使用默认的全局client.Client实例, 如果设置了config.ClientOption将会初始化一个client.Client实例。 如果你需要共享一个client.Client实例,可以使用ReverseProxy.SetClient来设置。- 反向代理会重置响应头,如果在请求之前修改了响应头将不会生效。
我们提供了 SetXxx() 函数用于设置私有属性
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
SetDirector |
用于指定 protocol.Request |
SetClient |
用于指定转发的客户端 |
SetModifyResponse |
用于指定响应修改方法 |
SetErrorHandler |
用于指定处理到达后台的错误或来自 modifyResponse 的错误 |
示例
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/reverseproxy"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8000"))
// 设置目标地址
proxy, err := reverseproxy.NewSingleHostReverseProxy("http://127.0.0.1:8000/proxy")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
h.GET("/proxy/backend", func(cc context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(200, utils.H{
"msg": "proxy success!!",
})
})
// 设置代理
h.GET("/backend", proxy.ServeHTTP)
h.Spin()
}
FAQ
如何代理 HTTPS
Netpoll 不支持 TLS,Client 需要使用标准网络库.
代理 HTTPS 需要在额外做一些配置.
NewSingleHostReverseProxy方法中使用WithDialer传递standard.NewDialer()指定标准网络库。- 使用
SetClient设置一个使用标准网络库的 Hertz Client。
如何配合中间件使用
可以在 hertz handler 中也使用 ReverseProxy.ServeHTTP 来实现复杂的需求而不是直接将 ReverseProxy.ServeHTTP 注册到路由。
示例代码
package main
import (
//...
)
func main() {
//...
r.Use(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
if ctx.Query("country") == "cn" {
proxy.ServeHTTP(c, ctx)
ctx.Response.Header.Set("key", "value")
ctx.Abort()
} else {
ctx.Next(c)
}
})
//...
}
更多示例
| 用途 | 示例代码 |
|---|---|
| 代理 tls | code |
| 使用服务发现 | code |
| 配合中间件使用 | code |
更多使用方法可参考如下 examples。
title: “常量” date: 2023-05-24 weight: 17 keywords: [“常量”, “HTTP 请求方法”, “HTTP 常用 MIME 类型”, “HTTP 状态码”, “HTTP 头信息”, “HTTP 协议版本”] description: “Hertz 中定义的供用户使用的常量。”
在 Hertz 中定义了一系列的常量以供用户使用,它们都位于 github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts 。
HTTP 请求方法
// HTTP methods were copied from net/http.
const (
MethodGet = "GET" // RFC 7231, 4.3.1
MethodHead = "HEAD" // RFC 7231, 4.3.2
MethodPost = "POST" // RFC 7231, 4.3.3
MethodPut = "PUT" // RFC 7231, 4.3.4
MethodPatch = "PATCH" // RFC 5789
MethodDelete = "DELETE" // RFC 7231, 4.3.5
MethodConnect = "CONNECT" // RFC 7231, 4.3.6
MethodOptions = "OPTIONS" // RFC 7231, 4.3.7
MethodTrace = "TRACE" // RFC 7231, 4.3.8
)
HTTP 常用 MIME 类型
const (
// MIME text
MIMETextPlain = "text/plain"
MIMETextPlainUTF8 = "text/plain; charset=utf-8"
MIMETextPlainISO88591 = "text/plain; charset=iso-8859-1"
MIMETextPlainFormatFlowed = "text/plain; format=flowed"
MIMETextPlainDelSpaceYes = "text/plain; delsp=yes"
MiMETextPlainDelSpaceNo = "text/plain; delsp=no"
MIMETextHtml = "text/html"
MIMETextCss = "text/css"
MIMETextJavascript = "text/javascript"
// MIME application
MIMEApplicationOctetStream = "application/octet-stream"
MIMEApplicationFlash = "application/x-shockwave-flash"
MIMEApplicationHTMLForm = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
MIMEApplicationHTMLFormUTF8 = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8"
MIMEApplicationTar = "application/x-tar"
MIMEApplicationGZip = "application/gzip"
MIMEApplicationXGZip = "application/x-gzip"
MIMEApplicationBZip2 = "application/bzip2"
MIMEApplicationXBZip2 = "application/x-bzip2"
MIMEApplicationShell = "application/x-sh"
MIMEApplicationDownload = "application/x-msdownload"
MIMEApplicationJSON = "application/json"
MIMEApplicationJSONUTF8 = "application/json; charset=utf-8"
MIMEApplicationXML = "application/xml"
MIMEApplicationXMLUTF8 = "application/xml; charset=utf-8"
MIMEApplicationZip = "application/zip"
MIMEApplicationPdf = "application/pdf"
MIMEApplicationWord = "application/msword"
MIMEApplicationExcel = "application/vnd.ms-excel"
MIMEApplicationPPT = "application/vnd.ms-powerpoint"
MIMEApplicationOpenXMLWord = "application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document"
MIMEApplicationOpenXMLExcel = "application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet"
MIMEApplicationOpenXMLPPT = "application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation"
// MIME image
MIMEImageJPEG = "image/jpeg"
MIMEImagePNG = "image/png"
MIMEImageGIF = "image/gif"
MIMEImageBitmap = "image/bmp"
MIMEImageWebP = "image/webp"
MIMEImageIco = "image/x-icon"
MIMEImageMicrosoftICO = "image/vnd.microsoft.icon"
MIMEImageTIFF = "image/tiff"
MIMEImageSVG = "image/svg+xml"
MIMEImagePhotoshop = "image/vnd.adobe.photoshop"
// MIME audio
MIMEAudioBasic = "audio/basic"
MIMEAudioL24 = "audio/L24"
MIMEAudioMP3 = "audio/mp3"
MIMEAudioMP4 = "audio/mp4"
MIMEAudioMPEG = "audio/mpeg"
MIMEAudioOggVorbis = "audio/ogg"
MIMEAudioWAVE = "audio/vnd.wave"
MIMEAudioWebM = "audio/webm"
MIMEAudioAAC = "audio/x-aac"
MIMEAudioAIFF = "audio/x-aiff"
MIMEAudioMIDI = "audio/x-midi"
MIMEAudioM3U = "audio/x-mpegurl"
MIMEAudioRealAudio = "audio/x-pn-realaudio"
// MIME video
MIMEVideoMPEG = "video/mpeg"
MIMEVideoOgg = "video/ogg"
MIMEVideoMP4 = "video/mp4"
MIMEVideoQuickTime = "video/quicktime"
MIMEVideoWinMediaVideo = "video/x-ms-wmv"
MIMEVideWebM = "video/webm"
MIMEVideoFlashVideo = "video/x-flv"
MIMEVideo3GPP = "video/3gpp"
MIMEVideoAVI = "video/x-msvideo"
MIMEVideoMatroska = "video/x-matroska"
)
HTTP 状态码
// HTTP status codes were stolen from net/http.
const (
StatusContinue = 100 // RFC 7231, 6.2.1
StatusSwitchingProtocols = 101 // RFC 7231, 6.2.2
StatusProcessing = 102 // RFC 2518, 10.1
StatusOK = 200 // RFC 7231, 6.3.1
StatusCreated = 201 // RFC 7231, 6.3.2
StatusAccepted = 202 // RFC 7231, 6.3.3
StatusNonAuthoritativeInfo = 203 // RFC 7231, 6.3.4
StatusNoContent = 204 // RFC 7231, 6.3.5
StatusResetContent = 205 // RFC 7231, 6.3.6
StatusPartialContent = 206 // RFC 7233, 4.1
StatusMultiStatus = 207 // RFC 4918, 11.1
StatusAlreadyReported = 208 // RFC 5842, 7.1
StatusIMUsed = 226 // RFC 3229, 10.4.1
StatusMultipleChoices = 300 // RFC 7231, 6.4.1
StatusMovedPermanently = 301 // RFC 7231, 6.4.2
StatusFound = 302 // RFC 7231, 6.4.3
StatusSeeOther = 303 // RFC 7231, 6.4.4
StatusNotModified = 304 // RFC 7232, 4.1
StatusUseProxy = 305 // RFC 7231, 6.4.5
_ = 306 // RFC 7231, 6.4.6 (Unused)
StatusTemporaryRedirect = 307 // RFC 7231, 6.4.7
StatusPermanentRedirect = 308 // RFC 7538, 3
StatusBadRequest = 400 // RFC 7231, 6.5.1
StatusUnauthorized = 401 // RFC 7235, 3.1
StatusPaymentRequired = 402 // RFC 7231, 6.5.2
StatusForbidden = 403 // RFC 7231, 6.5.3
StatusNotFound = 404 // RFC 7231, 6.5.4
StatusMethodNotAllowed = 405 // RFC 7231, 6.5.5
StatusNotAcceptable = 406 // RFC 7231, 6.5.6
StatusProxyAuthRequired = 407 // RFC 7235, 3.2
StatusRequestTimeout = 408 // RFC 7231, 6.5.7
StatusConflict = 409 // RFC 7231, 6.5.8
StatusGone = 410 // RFC 7231, 6.5.9
StatusLengthRequired = 411 // RFC 7231, 6.5.10
StatusPreconditionFailed = 412 // RFC 7232, 4.2
StatusRequestEntityTooLarge = 413 // RFC 7231, 6.5.11
StatusRequestURITooLong = 414 // RFC 7231, 6.5.12
StatusUnsupportedMediaType = 415 // RFC 7231, 6.5.13
StatusRequestedRangeNotSatisfiable = 416 // RFC 7233, 4.4
StatusExpectationFailed = 417 // RFC 7231, 6.5.14
StatusTeapot = 418 // RFC 7168, 2.3.3
StatusUnprocessableEntity = 422 // RFC 4918, 11.2
StatusLocked = 423 // RFC 4918, 11.3
StatusFailedDependency = 424 // RFC 4918, 11.4
StatusUpgradeRequired = 426 // RFC 7231, 6.5.15
StatusPreconditionRequired = 428 // RFC 6585, 3
StatusTooManyRequests = 429 // RFC 6585, 4
StatusRequestHeaderFieldsTooLarge = 431 // RFC 6585, 5
StatusUnavailableForLegalReasons = 451 // RFC 7725, 3
StatusInternalServerError = 500 // RFC 7231, 6.6.1
StatusNotImplemented = 501 // RFC 7231, 6.6.2
StatusBadGateway = 502 // RFC 7231, 6.6.3
StatusServiceUnavailable = 503 // RFC 7231, 6.6.4
StatusGatewayTimeout = 504 // RFC 7231, 6.6.5
StatusHTTPVersionNotSupported = 505 // RFC 7231, 6.6.6
StatusVariantAlsoNegotiates = 506 // RFC 2295, 8.1
StatusInsufficientStorage = 507 // RFC 4918, 11.5
StatusLoopDetected = 508 // RFC 5842, 7.2
StatusNotExtended = 510 // RFC 2774, 7
StatusNetworkAuthenticationRequired = 511 // RFC 6585, 6
)
HTTP 头信息
const (
HeaderDate = "Date"
HeaderIfModifiedSince = "If-Modified-Since"
HeaderLastModified = "Last-Modified"
// Redirects
HeaderLocation = "Location"
// Transfer coding
HeaderTE = "TE"
HeaderTrailer = "Trailer"
HeaderTrailerLower = "trailer"
HeaderTransferEncoding = "Transfer-Encoding"
// Controls
HeaderCookie = "Cookie"
HeaderExpect = "Expect"
HeaderMaxForwards = "Max-Forwards"
HeaderSetCookie = "Set-Cookie"
HeaderSetCookieLower = "set-cookie"
// Connection management
HeaderConnection = "Connection"
HeaderKeepAlive = "Keep-Alive"
HeaderProxyConnection = "Proxy-Connection"
// Authentication
HeaderAuthorization = "Authorization"
HeaderProxyAuthenticate = "Proxy-Authenticate"
HeaderProxyAuthorization = "Proxy-Authorization"
HeaderWWWAuthenticate = "WWW-Authenticate"
// Range requests
HeaderAcceptRanges = "Accept-Ranges"
HeaderContentRange = "Content-Range"
HeaderIfRange = "If-Range"
HeaderRange = "Range"
// Response context
HeaderAllow = "Allow"
HeaderServer = "Server"
HeaderServerLower = "server"
// Request context
HeaderFrom = "From"
HeaderHost = "Host"
HeaderReferer = "Referer"
HeaderReferrerPolicy = "Referrer-Policy"
HeaderUserAgent = "User-Agent"
// Message body information
HeaderContentEncoding = "Content-Encoding"
HeaderContentLanguage = "Content-Language"
HeaderContentLength = "Content-Length"
HeaderContentLocation = "Content-Location"
HeaderContentType = "Content-Type"
// Content negotiation
HeaderAccept = "Accept"
HeaderAcceptCharset = "Accept-Charset"
HeaderAcceptEncoding = "Accept-Encoding"
HeaderAcceptLanguage = "Accept-Language"
HeaderAltSvc = "Alt-Svc"
)
HTTP 协议版本
const(
// Protocol
HTTP11 = "HTTP/1.1"
HTTP10 = "HTTP/1.0"
HTTP20 = "HTTP/2.0"
)
title: “基本特性” linkTitle: “基本特性” weight: 2 keywords: [“Engine”, “路由”, “客户端”, “网络库”, “请求上下文”, “中间件”, “协议”, “绑定与校验”, “流式处理”, “错误处理”, “优雅退出”, “正向代理和反向代理”, “重试”, “Hooks”, “单测”, “适配器”, “常量”, “渲染”, “JSON Marshal 库”] description: “Hertz 基本特性。”
title: “路由” date: 2022-09-06 weight: 2 keywords: [“路由”, “路由组”, “静态路由”, “参数路由”, “路由优先级”, “NoRoute”, “NoMethod”] description: “Hertz 提供的路由功能。”
路由注册
Hertz 提供了 GET、POST、PUT、DELETE、ANY 等方法用于注册路由。
| 方法 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
Hertz.GET |
用于注册 HTTP Method 为 GET 的方法 |
Hertz.POST |
用于注册 HTTP Method 为 POST 的方法 |
Hertz.DELETE |
用于注册 HTTP Method 为 DELETE 的方法 |
Hertz.PUT |
用于注册 HTTP Method 为 PUT 的方法 |
Hertz.PATCH |
用于注册 HTTP Method 为 PATCH 的方法 |
Hertz.HEAD |
用于注册 HTTP Method 为 HEAD 的方法 |
Hertz.OPTIONS |
用于注册 HTTP Method 为 OPTIONS 的方法 |
Hertz.Handle |
这个方法支持用户手动传入 HTTP Method 用来注册方法,当用于注册普通的 HTTP Method 方法时和上述的方法作用是一致的,并且这个方法同时也支持用于注册自定义 HTTP Method 方法 |
Hertz.Any |
用于注册所有 HTTP Method 方法 |
Hertz.StaticFile/Static/StaticFS |
用于注册静态文件 |
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main(){
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.StaticFS("/", &app.FS{Root: "./", GenerateIndexPages: true})
h.GET("/get", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "get")
})
h.POST("/post", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "post")
})
h.PUT("/put", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "put")
})
h.DELETE("/delete", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "delete")
})
h.PATCH("/patch", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "patch")
})
h.HEAD("/head", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "head")
})
h.OPTIONS("/options", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "options")
})
h.Any("/ping_any", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "any")
})
h.Handle("LOAD","/load", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "load")
})
h.Spin()
}
路由组
Hertz 提供了路由组 ( Group ) 的能力,用于支持路由分组的功能,同时中间件也可以注册到路由组上。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main(){
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
v1 := h.Group("/v1")
v1.GET("/get", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "get")
})
v1.POST("/post", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "post")
})
v2 := h.Group("/v2")
v2.PUT("/put", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "put")
})
v2.DELETE("/delete", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "delete")
})
h.Spin()
}
在路由组中使用中间件
如下示例在路由组中使用 BasicAuth 中间件。
示例代码 1:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/server/basic_auth"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
// use middleware
v1 := h.Group("/v1", basic_auth.BasicAuth(map[string]string{"test": "test"}))
v1.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK,"ping")
})
h.Spin()
}
示例代码 2:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/server/basic_auth"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
v1 := h.Group("/v1")
// use `Use` method
v1.Use(basic_auth.BasicAuth(map[string]string{"test": "test"}))
v1.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK,"ping")
})
h.Spin()
}
路由类型
Hertz 支持丰富的路由类型用于实现复杂的功能,包括静态路由、参数路由 (命名参数、通配参数)。
路由的优先级:静态路由 > 命名参数路由 > 通配参数路由
静态路由
具体示例可参见上文
命名参数路由
Hertz 支持使用 :name 这样的命名参数设置路由,并且命名参数只匹配单个路径段。
如果我们设置/user/:name路由,匹配情况如下
| 路径 | 是否匹配 |
|---|---|
| /user/gordon | 匹配 |
| /user/you | 匹配 |
| /user/gordon/profile | 不匹配 |
| /user/ | 不匹配 |
通过使用 RequestContext.Param 方法,我们可以获取路由中携带的参数。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main(){
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
// This handler will match: "/hertz/version", but will not match : "/hertz/" or "/hertz"
h.GET("/hertz/:version", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
version := c.Param("version")
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "Hello %s", version)
})
h.Spin()
}
通配参数路由
Hertz 支持使用 *path 这样的通配参数设置路由,并且通配参数会匹配所有内容。
如果我们设置/src/*path路由,匹配情况如下
| 路径 | 是否匹配 |
|---|---|
| /src/ | 匹配 |
| /src/somefile.go | 匹配 |
| /src/subdir/somefile.go | 匹配 |
通过使用 RequestContext.Param 方法,我们可以获取路由中携带的参数。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main(){
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
// However, this one will match "/hertz/v1/" and "/hertz/v2/send"
h.GET("/hertz/:version/*action", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
version := c.Param("version")
action := c.Param("action")
message := version + " is " + action
c.String(consts.StatusOK, message)
})
h.Spin()
}
完整用法示例详见 example
注意
使用匿名函数与装饰器注册路由
在使用匿名函数或装饰器注册路由时,如果我们使用 RequestContext.HandlerName() 获取 handler 名称则会获取到错误的名称。
这里需要使用 Hertz 提供的 GETEX、POSTEX、PUTEX、DELETEEX、HEADEX、AnyEX、HandleEX 方法并手动传入 handler
名称注册路由,使用 app.GetHandlerName 获取 handler 名称。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.AnyEX("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, app.GetHandlerName(ctx.Handler()))
}, "ping_handler")
h.Spin()
}
获取路由注册信息
Hertz 提供了 Routes 获取注册的路由信息供用户使用。
路由信息结构:
// RouteInfo represents a request route's specification which contains method and path and its handler.
type RouteInfo struct {
Method string // http method
Path string // url path
Handler string // handler name
HandlerFunc app.HandlerFunc
}
// RoutesInfo defines a RouteInfo array.
type RoutesInfo []RouteInfo
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
routeInfo := h.Routes()
hlog.Info(routeInfo)
h.Spin()
}
NoRoute 与 NoMethod 使用
Hertz 提供了 NoRoute 与 NoMethod 方法用于全局处理 HTTP 404 与 405 请求。
当使用 NoMethod 时需要与 WithHandleMethodNotAllowed 配合使用。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHandleMethodNotAllowed(true))
h.POST("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
// set NoRoute handler
h.NoRoute(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "no route")
})
// set NoMethod handler
h.NoMethod(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "no method")
})
h.Spin()
}
重定向尾斜杠
Hertz 在默认情况下会根据请求 path 末尾的 / 自动进行转发。如果 router 中只有 /foo/,那么请求 /foo 会被自动重定向到
/foo/;如果 router 中只有 /foo,那么 /foo/ 会被重定向到 /foo。
这样的请求除 GET 以外的请求方法都会触发 307 Temporary Redirect 状态码,而 GET 请求会触发 301 Moved Permanently
状态码。
可以在配置中取消,如下:
package main
import "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithRedirectTrailingSlash(false))
...
}
获取更多配置相关信息:https://www.cloudwego.io/zh/docs/hertz/reference/config/
title: “单测” date: 2022-05-23 weight: 15 keywords: [“单测”] description: “Hertz 为用户提供的单元测试能力。”
一个好的项目的构建离不开单元测试。为了帮助使用者构建出好的项目,hertz 当然也提供了单元测试的工具。
原理和 golang httptest 类似,都是不经过网络只执行 ServeHTTP 返回执行后的 response。
创建请求上下文
func CreateUtRequestContext(method, url string, body *Body, headers ...Header) *app.RequestContext
CreateUtRequestContext
返回一个 app.RequestContext 对象,用于单元测试。
函数签名:
func CreateUtRequestContext(method, url string, body *Body, headers ...Header) *app.RequestContext
示例代码:
import (
"bytes"
"testing"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/test/assert"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/ut"
)
func TestCreateUtRequestContext(t *testing.T) {
body := "1"
method := "PUT"
path := "/hey/dy"
headerKey := "Connection"
headerValue := "close"
ctx := ut.CreateUtRequestContext(method, path, &ut.Body{Body: bytes.NewBufferString(body), Len: len(body)},
ut.Header{Key: headerKey, Value: headerValue})
assert.DeepEqual(t, method, string(ctx.Method()))
assert.DeepEqual(t, path, string(ctx.Path()))
body1, err := ctx.Body()
assert.DeepEqual(t, nil, err)
assert.DeepEqual(t, body, string(body1))
assert.DeepEqual(t, headerValue, string(ctx.GetHeader(headerKey)))
}
发送请求
func PerformRequest(engine *route.Engine, method, url string, body *Body, headers ...Header) *ResponseRecorder
PerformRequest
PerformRequest 函数在没有网络传输的情况下向指定 engine 发送构造好的请求。
url 可以是标准的相对路径也可以是绝对路径。
如果想设置流式的请求体,可以通过 server.WithStreamBody(true) 将 engine.streamRequestBody 设置为 true 或者将 body 的 len
设置为 -1。
该函数返回 ResponseRecorder 对象。
函数签名:
func PerformRequest(engine *route.Engine, method, url string, body *Body, headers ...Header) *ResponseRecorder
示例代码:
import (
"bytes"
"context"
"testing"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/config"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/test/assert"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/ut"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/route"
)
func TestPerformRequest(t *testing.T) {
router := route.NewEngine(config.NewOptions([]config.Option{}))
router.GET("/hey/:user", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
user := c.Param("user")
assert.DeepEqual(t, "close", c.Request.Header.Get("Connection"))
c.Response.SetConnectionClose()
c.JSON(201, map[string]string{"hi": user})
})
w := ut.PerformRequest(router, "GET", "/hey/hertz", &ut.Body{bytes.NewBufferString("1"), 1},
ut.Header{"Connection", "close"})
resp := w.Result()
assert.DeepEqual(t, 201, resp.StatusCode())
assert.DeepEqual(t, "{\"hi\":\"hertz\"}", string(resp.Body()))
}
接收响应
在执行 PerformRequest 函数时,内部已经调用了 NewRecorder, Header, Write, WriteHeader, Flush
等函数,用户只需调用 Result 函数拿到返回的 protocol.Response 对象进行单测即可。
ResponseRecorder 对象
用于记录 handler 的响应信息,内容如下:
type ResponseRecorder struct {
// Code is the HTTP response code set by WriteHeader.
//
// Note that if a Handler never calls WriteHeader or Write,
// this might end up being 0, rather than the implicit
// http.StatusOK. To get the implicit value, use the Result
// method.
Code int
// header contains the headers explicitly set by the Handler.
// It is an internal detail.
header *protocol.ResponseHeader
// Body is the buffer to which the Handler's Write calls are sent.
// If nil, the Writes are silently discarded.
Body *bytes.Buffer
// Flushed is whether the Handler called Flush.
Flushed bool
result *protocol.Response // cache of Result's return value
wroteHeader bool
}
该对象提供的方法如下:
| 函数签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
func NewRecorder() *ResponseRecorder |
返回初始化后的 ResponseRecorder 对象 |
func (rw *ResponseRecorder) Header() *protocol.ResponseHeader |
返回 ResponseRecorder.header |
func (rw *ResponseRecorder) Write(buf []byte) (int, error) |
将 []byte 类型的数据写入 ResponseRecorder.Body |
func (rw *ResponseRecorder) WriteString(str string) (int, error) |
将 string 类型的数据写入 ResponseRecorder.Body |
func (rw *ResponseRecorder) WriteHeader(code int) |
设置 ResponseRecorder.Code 以及 ResponseRecorder.header.SetStatusCode(code) |
func (rw *ResponseRecorder) Flush() |
实现了 http.Flusher,将 ResponseRecorder.Flushed 设置为 true |
func (rw *ResponseRecorder) Result() *protocol.Response |
返回 handler 生成的响应信息,至少包含 StatusCode, Header, Body 以及可选的 Trailer,未来将支持返回更多的响应信息 |
与业务 handler 配合使用
假如已经创建了 handler 以及一个函数 Ping():
package handler
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
)
// Ping .
func Ping(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(200, utils.H{
"message": "pong",
})
}
可以在单元测试中直接对 Ping() 函数进行测试:
package handler
import (
"bytes"
"testing"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/test/assert"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/ut"
)
func TestPerformRequest(t *testing.T) {
h := server.Default()
h.GET("/ping", Ping)
w := ut.PerformRequest(h.Engine, "GET", "/ping", &ut.Body{bytes.NewBufferString("1"), 1},
ut.Header{"Connection", "close"})
resp := w.Result()
assert.DeepEqual(t, 201, resp.StatusCode())
assert.DeepEqual(t, "{\"message\":\"pong\"}", string(resp.Body()))
}
之后对 Ping() 函数进行修改,单元测试文件不需要复制相同的业务逻辑。
更多 examples 参考 pkg/common/ut 中的单测文件。
title: “客户端” date: 2023-07-25 weight: 3 keywords: [“Client 配置”, “发送请求”, “请求超时”, “流式处理”, “中间件”, “服务发现”] description: “Hertz 客户端相关功能。”
快速开始
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func performRequest() {
c, _ := client.NewClient()
req, resp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetRequestURI("http://localhost:8080/hello")
req.SetMethod("GET")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("get response: %s\n", resp.Body()) // status == 200 resp.Body() == []byte("hello hertz")
}
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.GET("/hello", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, "hello hertz")
})
go performRequest()
h.Spin()
}
Client 配置
| 配置项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| WithDialTimeout | 1s | 拨号超时时间 |
| WithMaxConnsPerHost | 512 | 每个主机可能建立的最大连接数 |
| WithMaxIdleConnDuration | 10s | 最大的空闲连接持续时间,空闲的连接在此持续时间后被关闭 |
| WithMaxConnDuration | 0s | 最大的连接持续时间,keep-alive 连接在此持续时间后被关闭 |
| WithMaxConnWaitTimeout | 0s | 等待空闲连接的最大时间 |
| WithKeepAlive | true | 是否使用 keep-alive 连接,默认使用 |
| WithClientReadTimeout | 0s | 完整读取响应(包括 body)的最大持续时间 |
| WithTLSConfig | nil | 设置用于创建 tls 连接的 tlsConfig,具体配置信息请看 tls |
| WithDialer | network.Dialer | 设置指定的拨号器 |
| WithResponseBodyStream | false | 是否在流中读取 body,默认不在流中读取 |
| WithDisableHeaderNamesNormalizing | false | 是否禁用头名称规范化,默认不禁用,如 cONTENT-lenGTH -> Content-Length |
| WithName | "" | 用户代理头中使用的客户端名称 |
| WithNoDefaultUserAgentHeader | false | 是否没有默认的 User-Agent 头,默认有 User-Agent 头 |
| WithDisablePathNormalizing | false | 是否禁用路径规范化,默认规范路径,如 http://localhost:8080/hello/../ hello -> http://localhost:8080/hello |
| WithRetryConfig | nil | HTTP 客户端的重试配置,重试配置详细说明请看 重试 |
| WithWriteTimeout | 0s | HTTP 客户端的写入超时时间 |
| WithConnStateObserve | nil, 5s | 设置观察和记录 HTTP 客户端的连接状态的函数以及观察执行间隔 |
| WithDialFunc | network.Dialer | 设置 HTTP 客户端拨号器函数,会覆盖自定义拨号器 |
示例代码:
func main() {
observeInterval := 10 * time.Second
stateFunc := func(state config.HostClientState) {
fmt.Printf("state=%v\n", state.ConnPoolState().Addr)
}
var customDialFunc network.DialFunc = func(addr string) (network.Conn, error) {
return nil, nil
}
c, err := client.NewClient(
client.WithDialTimeout(1*time.Second),
client.WithMaxConnsPerHost(1024),
client.WithMaxIdleConnDuration(10*time.Second),
client.WithMaxConnDuration(10*time.Second),
client.WithMaxConnWaitTimeout(10*time.Second),
client.WithKeepAlive(true),
client.WithClientReadTimeout(10*time.Second),
client.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()),
client.WithResponseBodyStream(true),
client.WithDisableHeaderNamesNormalizing(true),
client.WithName("my-client"),
client.WithNoDefaultUserAgentHeader(true),
client.WithDisablePathNormalizing(true),
client.WithRetryConfig(
retry.WithMaxAttemptTimes(3),
retry.WithInitDelay(1000),
retry.WithMaxDelay(10000),
retry.WithDelayPolicy(retry.DefaultDelayPolicy),
retry.WithMaxJitter(1000),
),
client.WithWriteTimeout(10*time.Second),
client.WithConnStateObserve(stateFunc, observeInterval),
client.WithDialFunc(customDialFunc, netpoll.NewDialer()),
)
if err != nil {
return
}
status, body, _ := c.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://www.example.com")
fmt.Printf("status=%v body=%v\n", status, string(body))
}
Client Request 配置
| 配置项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| WithDialTimeout | 0s | 拨号超时时间,该配置项的优先级高于 Client 配置,即会覆盖相应的 Client 配置项 |
| WithReadTimeout | 0s | 完整读取响应(包括 body)的最大持续时间,该配置项的优先级高于 Client 配置,即会覆盖相应的 Client 配置项 |
| WithWriteTimeout | 0s | HTTP 客户端的写入超时时间,该配置项的优先级高于 Client 配置,即会覆盖相应的 Client 配置项 |
| WithRequestTimeout | 0s | 完整的 HTTP 请求的超时时间 |
| WithTag | make(map[string]string) | 以 key-value 形式设置 tags 字段,配合服务发现使用,详情见 WithTag |
| WithSD | false | 配合服务发现使用,传递 true 时,本次请求使用服务发现,详情见 WithSD |
示例代码:
func main() {
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
req, res := &protocol.Request{}, &protocol.Response{}
req.SetOptions(config.WithDialTimeout(1*time.Second),
config.WithReadTimeout(3*time.Second),
config.WithWriteTimeout(3*time.Second),
config.WithReadTimeout(5*time.Second),
config.WithSD(true),
config.WithTag("tag", "tag"))
req.SetMethod(consts.MethodGet)
req.SetRequestURI("http://www.example.com")
err = cli.Do(context.Background(), req, res)
fmt.Printf("resp = %v,err = %+v", string(res.Body()), err)
}
发送请求
func (c *Client) Do(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response) error
func (c *Client) DoRedirects(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, maxRedirectsCount int) error
func (c *Client) Get(ctx context.Context, dst []byte, url string, requestOptions ...config.RequestOption) (statusCode int, body []byte, err error)
func (c *Client) Post(ctx context.Context, dst []byte, url string, postArgs *protocol.Args, requestOptions ...config.RequestOption) (statusCode int, body []byte, err error)
Do
Do 函数执行给定的 http 请求并填充给定的 http 响应。请求必须包含至少一个非零的 RequestURI,其中包含完整的 URL 或非零的 Host header + RequestURI。
该函数不会跟随重定向,请使用 Get 函数或 DoRedirects 函数或 Post 函数来跟随重定向。
如果 resp 为 nil,则会忽略响应。如果所有针对请求主机的 DefaultMaxConnsPerHost 连接都已忙,则会返回 ErrNoFreeConns
错误。在性能关键的代码中,建议通过 AcquireRequest 和 AcquireResponse 获取 req 和 resp。
函数签名:
func (c *Client) Do(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response) error
示例代码:
func main() {
// hertz server:http://localhost:8080/ping ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "pong")
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
req, res := &protocol.Request{}, &protocol.Response{}
req.SetMethod(consts.MethodGet)
req.SetRequestURI("http://localhost:8080/ping")
err = c.Do(context.Background(), req, res)
fmt.Printf("resp = %v,err = %+v", string(res.Body()), err)
// resp.Body() == []byte("pong") err == <nil>
}
DoRedirects
DoRedirects 函数执行给定的 http 请求并填充给定的 http 响应,遵循最多 maxRedirectsCount 次重定向。当重定向次数超过
maxRedirectsCount 时,将返回 ErrTooManyRedirects 错误。
函数签名:
func (c *Client) DoRedirects(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, maxRedirectsCount int) error
示例代码:
func main() {
// hertz server
// http://localhost:8080/redirect ctx.Redirect(consts.StatusMovedPermanently, []byte("/redirect2"))
// http://localhost:8080/redirect2 ctx.Redirect(consts.StatusMovedPermanently, []byte("/redirect3"))
// http://localhost:8080/redirect3 ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "pong")
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
req, res := &protocol.Request{}, &protocol.Response{}
req.SetMethod(consts.MethodGet)
req.SetRequestURI("http://localhost:8080/redirect")
err = c.DoRedirects(context.Background(), req, res, 1)
fmt.Printf("resp = %v,err = %+v\n", string(res.Body()), err)
// res.Body() == []byte("") err.Error() == "too many redirects detected when doing the request"
err = c.DoRedirects(context.Background(), req, res, 2)
fmt.Printf("resp = %v,err = %+v\n", string(res.Body()), err)
// res.Body() == []byte("pong") err == <nil>
}
Get
Get 函数返回 URL 的状态码和响应体。如果 dst 太小,则将被响应体替换并返回,否则将分配一个新的切片。
该函数会自动跟随重定向。
函数签名:
func (c *Client) Get(ctx context.Context, dst []byte, url string, requestOptions ...config.RequestOption) (statusCode int, body []byte, err error)
示例代码:
func main() {
// hertz server:http://localhost:8080/ping ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "pong")
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
status, body, err := c.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://localhost:8080/ping")
fmt.Printf("status=%v body=%v err=%v\n", status, string(body), err)
// status == 200 res.Body() == []byte("pong") err == <nil>
}
Post
Post 函数使用给定的 POST 参数向指定的 URL 发送 POST 请求。如果 dst 太小,则将被响应体替换并返回,否则将分配一个新的切片。
该函数会自动跟随重定向。
如果 postArgs 为 nil,则发送空的 POST 请求体。
函数签名:
func (c *Client) Post(ctx context.Context, dst []byte, url string, postArgs *protocol.Args, requestOptions ...config.RequestOption) (statusCode int, body []byte, err error)
示例代码:
func main() {
// hertz server:http://localhost:8080/hello ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "hello %s", ctx.PostForm("name"))
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
var postArgs protocol.Args
postArgs.Set("name", "cloudwego") // Set post args
status, body, err := c.Post(context.Background(), nil, "http://localhost:8080/hello", &postArgs)
fmt.Printf("status=%v body=%v err=%v\n", status, string(body), err)
// status == 200 res.Body() == []byte("hello cloudwego") err == <nil>
}
请求超时
注意:Do、DoRedirects、Get、Post 等请求函数可以通过 WithRequestTimeout 设置请求超时时间,DoTimeout 和 DoDeadline 函数通过传参的形式设置请求超时时间,两者都是修改
RequestOptions.requestTimeout字段,所以在使用 DoTimeout 和 DoDeadline 函数时无需使用 WithRequestTimeout 函数,若同时使用了,请求超时时间以最后一次设置的为准。
func WithRequestTimeout(t time.Duration) RequestOption
func (c *Client) DoTimeout(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, timeout time.Duration) error
func (c *Client) DoDeadline(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, deadline time.Time) error
WithRequestTimeout
Do、DoRedirects、Get、Post
等请求函数虽然不能以传参的方式设置请求超时返回,但可以通过 Client Request 配置
中的 WithRequestTimeout 配置项来设置请求超时返回。
示例代码:
func main() {
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
// Do
req, res := &protocol.Request{}, &protocol.Response{}
req.SetOptions(config.WithRequestTimeout(5 * time.Second))
req.SetMethod(consts.MethodGet)
req.SetRequestURI("http://localhost:8888/get")
err = c.Do(context.Background(), req, res)
// DoRedirects
err = c.DoRedirects(context.Background(), req, res, 5)
// Get
_, _, err = c.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://localhost:8888/get", config.WithRequestTimeout(5*time.Second))
// Post
postArgs := &protocol.Args{}
_, _, err = c.Post(context.Background(), nil, "http://localhost:8888/post", postArgs, config.WithRequestTimeout(5*time.Second))
}
DoTimeout
DoTimeout 函数执行给定的请求并在给定的超时时间内等待响应。
该函数不会跟随重定向,请使用 Get 函数或 DoRedirects 函数或 Post 函数来跟随重定向。
如果 resp 为 nil,则会忽略响应。如果在给定的超时时间内未能收到响应,则会返回 errTimeout 错误。
函数签名:
func (c *Client) DoTimeout(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, timeout time.Duration) error
示例代码:
func main() {
// hertz server:http://localhost:8080/ping ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "pong") biz handler time: 1.5s
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
req, res := &protocol.Request{}, &protocol.Response{}
req.SetMethod(consts.MethodGet)
req.SetRequestURI("http://localhost:8080/ping")
err = c.DoTimeout(context.Background(), req, res, time.Second*3)
fmt.Printf("resp = %v,err = %+v\n", string(res.Body()), err)
// res.Body() == []byte("pong") err == <nil>
err = c.DoTimeout(context.Background(), req, res, time.Second)
fmt.Printf("resp = %v,err = %+v\n", string(res.Body()), err)
// res.Body() == []byte("") err.Error() == "timeout"
}
DoDeadline
DoDeadline 执行给定的请求并等待响应,直至给定的最后期限。
该函数不会跟随重定向,请使用 Get 函数或 DoRedirects 函数或 Post 函数来跟随重定向。
如果 resp 为 nil,则会忽略响应。如果在给定的截止日期之前未能收到响应,则会返回 errTimeout 错误。
函数签名:
func (c *Client) DoDeadline(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, deadline time.Time) error
示例代码:
func main() {
// hertz server:http://localhost:8080/ping ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "pong") biz handler time: 1.5s
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
req, res := &protocol.Request{}, &protocol.Response{}
req.SetMethod(consts.MethodGet)
req.SetRequestURI("http://localhost:8080/ping")
err = c.DoDeadline(context.Background(), req, res, time.Now().Add(3*time.Second))
fmt.Printf("resp = %v,err = %+v\n", string(res.Body()), err)
// res.Body() == []byte("pong") err == <nil>
err = c.DoDeadline(context.Background(), req, res, time.Now().Add(1*time.Second))
fmt.Printf("resp = %v,err = %+v\n", string(res.Body()), err)
// res.Body() == []byte("") err.Error() == "timeout"
}
请求重试
func (c *Client) SetRetryIfFunc(retryIf client.RetryIfFunc)
SetRetryIfFunc
SetRetryIfFunc
方法用于自定义配置重试发生的条件。(更多内容请参考 retry-条件配置)
函数签名:
func (c *Client) SetRetryIfFunc(retryIf client.RetryIfFunc)
示例代码:
func main() {
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
var customRetryIfFunc = func(req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response, err error) bool {
return true
}
c.SetRetryIfFunc(customRetryIfFunc)
status2, body2, _ := c.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://www.example.com")
fmt.Printf("status=%v body=%v\n", status2, string(body2))
}
添加请求内容
Hertz 客户端可以在 HTTP 请求中添加 query 参数、www-url-encoded、multipart/form-data、json 等多种形式的请求内容。
示例代码:
func main() {
client, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
req := &protocol.Request{}
res := &protocol.Response{}
// Use SetQueryString to set query parameters
req.Reset()
req.Header.SetMethod(consts.MethodPost)
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/bind")
req.SetQueryString("query=query&q=q1&q=q2&vd=1")
err = client.Do(context.Background(), req, res)
if err != nil {
return
}
// Send "www-url-encoded" request
req.Reset()
req.Header.SetMethod(consts.MethodPost)
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/bind?query=query&q=q1&q=q2&vd=1")
req.SetFormData(map[string]string{
"form": "test form",
})
err = client.Do(context.Background(), req, res)
if err != nil {
return
}
// Send "multipart/form-data" request
req.Reset()
req.Header.SetMethod(consts.MethodPost)
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/bind?query=query&q=q1&q=q2&vd=1")
req.SetMultipartFormData(map[string]string{
"form": "test form",
})
err = client.Do(context.Background(), req, res)
if err != nil {
return
}
// Send "Json" request
req.Reset()
req.Header.SetMethod(consts.MethodPost)
req.Header.SetContentTypeBytes([]byte("application/json"))
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1/bind?query=query&q=q1&q=q2&vd=1")
data := struct {
Json string `json:"json"`
}{
"test json",
}
jsonByte, _ := json.Marshal(data)
req.SetBody(jsonByte)
err = client.Do(context.Background(), req, res)
if err != nil {
return
}
}
上传文件
Hertz 客户端支持向服务器上传文件。
示例代码:
func main() {
client, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
req := &protocol.Request{}
res := &protocol.Response{}
req.SetMethod(consts.MethodPost)
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/singleFile")
req.SetFile("file", "your file path")
err = client.Do(context.Background(), req, res)
if err != nil {
return
}
fmt.Println(err, string(res.Body()))
}
流式读响应内容
Hertz 客户端支持流式读取 HTTP 响应内容。
client 有复用连接的问题,如果使用了流式,那连接就会交由用户处理 (resp.BodyStream() 底层是对 connection 的封装)
,这个时候对连接的管理会有一些不同:
- 如果用户不关闭连接,连接最终会被 GC 关掉,不会造成连接泄漏。但是,由于关闭连接需要等待 2RTT,在高并发情况下可能会出现 fd 被打满导致无法新建连接的情况。
- 用户可以调用相关接口回收连接,回收后,该连接会放入连接池中复用,资源使用率更好,性能更高。以下几种方式都会回收连接,注意回收只能回收一次。
- 显式调用
protocol.ReleaseResponse(), resp.Reset(), resp.ResetBody()。 - 非显式调用:server 侧也会有回收 resp 的逻辑。如果 client 与 server 使用同一个 response 的情况下就不需要显式调用回收的方法了。
- 显式调用
示例代码:
func main() {
c, _ := client.NewClient(client.WithResponseBodyStream(true))
req := &protocol.Request{}
resp := &protocol.Response{}
defer func() {
protocol.ReleaseRequest(req)
protocol.ReleaseResponse(resp)
}()
req.SetMethod(consts.MethodGet)
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/streamWrite")
err := c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
if err != nil {
return
}
bodyStream := resp.BodyStream()
p := make([]byte, resp.Header.ContentLength()/2)
_, err = bodyStream.Read(p)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
left, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(bodyStream)
fmt.Println(string(p), string(left))
}
服务发现
Hertz 客户端支持通过服务发现寻找目标服务器。
Hertz 支持自定义服务发现模块,更多内容可参考 服务发现拓展。
Hertz 目前已接入的服务发现中心相关内容可参考 服务注册与发现。
TLS
Hertz 客户端默认使用的网络库 netpoll 不支持 TLS,如果要配置 TLS 访问 https 地址,应该使用标准库。
TLS 相关的配置信息可参考 tls。
示例代码:
func main() {
clientCfg := &tls.Config{
InsecureSkipVerify: true,
}
c, err := client.NewClient(
client.WithTLSConfig(clientCfg),
client.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()),
)
if err != nil {
return
}
req, res := &protocol.Request{}, &protocol.Response{}
req.SetMethod(consts.MethodGet)
req.SetRequestURI("https://www.example.com")
err = c.Do(context.Background(), req, res)
fmt.Printf("resp = %v,err = %+v", string(res.Body()), err)
}
正向代理
func (c *Client) SetProxy(p protocol.Proxy)
SetProxy
SetProxy 用来设置客户端代理。(更多内容请参考 正向代理)
注意:同一个客户端不能设置多个代理,如果需要使用另一个代理,请创建另一个客户端并为其设置代理。
示例代码:
func (c *Client) SetProxy(p protocol.Proxy)
函数签名:
func main() {
// Proxy address
proxyURL := "http://<__user_name__>:<__password__>@<__proxy_addr__>:<__proxy_port__>"
parsedProxyURL := protocol.ParseURI(proxyURL)
client, err := client.NewClient(client.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()))
if err != nil {
return
}
client.SetProxy(protocol.ProxyURI(parsedProxyURL))
upstreamURL := "http://google.com"
_, body, _ := client.Get(context.Background(), nil, upstreamURL)
fmt.Println(string(body))
}
关闭空闲连接
func (c *Client) CloseIdleConnections()
CloseIdleConnections
CloseIdleConnections 方法用于关闭任何处于空闲状态的 keep-alive 连接。这些连接可能是之前的请求所建立的,但现在已经空闲了一段时间。该方法不会中断任何当前正在使用的连接。
函数签名:
func (c *Client) CloseIdleConnections()
示例代码:
func main() {
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
status, body, _ := c.Get(context.Background(), nil, "http://www.example.com")
fmt.Printf("status=%v body=%v\n", status, string(body))
// close idle connections
c.CloseIdleConnections()
}
获取拨号器名称
func (c *Client) GetDialerName() (dName string, err error)
GetDialerName
GetDialerName 方法用于获取客户端当前使用的拨号器的名称。如果无法获取拨号器名称,则返回 unknown。
函数签名:
func (c *Client) GetDialerName() (dName string, err error)
示例代码:
func main() {
c, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
// get dialer name
dName, err := c.GetDialerName()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("GetDialerName failed: %v", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("dialer name=%v\n", dName)
// dName == "standard"
}
中间件
func (c *Client) Use(mws ...Middleware)
func (c *Client) UseAsLast(mw Middleware) error
func (c *Client) TakeOutLastMiddleware() Middleware
Use
使用 Use 方法对当前 client
增加一个中间件。(更多内容请参考 客户端中间件)
函数签名:
func (c *Client) Use(mws ...Middleware)
UseAsLast
UseAsLast 函数将中间件添加到客户端中间件链的最后。
如果客户端中间件链在之前已经设置了最后一个中间件,UseAsLast 函数将会返回 errorLastMiddlewareExist
错误。因此,为确保客户端中间件链的最后一个中间件为空,可以先使用 TakeOutLastMiddleware
函数清空客户端中间件链的最后一个中间件。
注意:
UseAsLast函数将中间件设置在了c.lastMiddleware中,而使用 Use 函数设置的中间件链存放在c.mws中,两者相对独立,只是在执行客户端中间件链的最后才执行c.lastMiddleware,因此UseAsLast函数在 Use 函数之前或之后调用皆可。
函数签名:
func (c *Client) UseAsLast(mw Middleware) error
示例代码:
func main() {
client, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
client.Use(MyMiddleware)
client.UseAsLast(LastMiddleware)
req := &protocol.Request{}
res := &protocol.Response{}
req.SetRequestURI("http://www.example.com")
err = client.Do(context.Background(), req, res)
if err != nil {
return
}
}
TakeOutLastMiddleware
TakeOutLastMiddleware 函数返回 UseAsLast 函数中设置的最后一个中间件并将其清空,若没有设置则返回 nil。
函数签名:
func (c *Client) TakeOutLastMiddleware() Middleware
示例代码:
func main() {
client, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return
}
client.Use(MyMiddleware)
client.UseAsLast(LastMiddleware)
req := &protocol.Request{}
res := &protocol.Response{}
req.SetRequestURI("http://www.example.com")
err = client.Do(context.Background(), req, res)
if err != nil {
return
}
middleware := client.TakeOutLastMiddleware() // middleware == LastMiddleware
middleware = client.TakeOutLastMiddleware() // middleware == nil
}
title: “国际化” date: 2022-09-01 weight: 5 keywords: [“国际化”, “i18n”] description: “Hertz 提供了国际化 (i18n) 的中间件扩展 。”
Hertz 提供了国际化 (i18n) 的 中间件扩展 ,它参考了 Gin 的 实现 。
使用方法可参考如下 example
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/i18n
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
hertzI18n "github.com/hertz-contrib/i18n"
"github.com/nicksnyder/go-i18n/v2/i18n"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":3000"))
h.Use(hertzI18n.Localize())
h.GET("/:name", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, hertzI18n.MustGetMessage(&i18n.LocalizeConfig{
MessageID: "welcomeWithName",
TemplateData: map[string]string{
"name": ctx.Param("name"),
},
}))
})
h.GET("/", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, hertzI18n.MustGetMessage("welcome"))
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
Localize
用于将 i18n 扩展集成进 hertz server
函数标签如下:
func Localize(opts ...Option) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
_ "embed"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
hertzI18n "github.com/hertz-contrib/i18n"
"github.com/nicksnyder/go-i18n/v2/i18n"
"golang.org/x/text/language"
"gopkg.in/yaml.v3"
)
func main() {
h := server.New()
h.Use(hertzI18n.Localize())
h.GET("/:name", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, hertzI18n.MustGetMessage(&i18n.LocalizeConfig{
MessageID: "welcomeWithName",
TemplateData: map[string]string{
"name": ctx.Param("name"),
},
}))
})
h.GET("/", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, hertzI18n.MustGetMessage("welcome"))
})
h.Spin()
}
MustGetMessage
MustGetMessage 用于获取 i18n 信息,但不做错误处理。
函数签名如下:
func MustGetMessage(param interface{}) string
示例代码如下:
h.GET("/:name", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, hertzI18n.MustGetMessage(&i18n.LocalizeConfig{
MessageID: "welcomeWithName",
TemplateData: map[string]string{
"name": ctx.Param("name"),
},
}))
})
h.GET("/", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, hertzI18n.MustGetMessage("welcome"))
})
LocalizeConfig 配置项
该配置项移步 go-i18n 自行查看
WithBundle
WithBundle用于将自定义配置加载进入中间件
函数标签如下:
func WithBundle(cfg *BundleCfg) Option
示例代码如下:
package main
import (
"context"
_ "embed"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
hertzI18n "github.com/hertz-contrib/i18n"
"github.com/nicksnyder/go-i18n/v2/i18n"
"golang.org/x/text/language"
"gopkg.in/yaml.v3"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(
server.WithHostPorts(":3000"),
server.WithExitWaitTime(time.Second),
)
h.Use(hertzI18n.Localize(
hertzI18n.WithBundle(&hertzI18n.BundleCfg{
RootPath: "./localize",
AcceptLanguage: []language.Tag{language.Chinese, language.English},
DefaultLanguage: language.Chinese,
FormatBundleFile: "yaml",
UnmarshalFunc: yaml.Unmarshal,
}),
))
h.GET("/:name", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, hertzI18n.MustGetMessage(&i18n.LocalizeConfig{
MessageID: "welcomeWithName",
TemplateData: map[string]string{
"name": ctx.Param("name"),
},
}))
})
h.GET("/", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, hertzI18n.MustGetMessage("welcome"))
})
h.Spin()
}
配置项
| 配置项 | 类型 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DefaultLanguage | language.Tag | language.English | 默认转换语言类型 |
| FormatBundleFile | string | “yaml” | 转换文件模板类型,例如:yaml, json |
| AcceptLanguage | []language.Tag | []language.Tag{defaultLanguage,language.Chinese} | 接收转换类型 |
| RootPath | string | defaultRootPath | 模板文件目录 |
| UnmarshalFunc | i18n.UnmarshalFunc | yaml.Unmarshal | 模板文件解码函数,例如:yaml.Unmarshal |
| Loader | Loader | LoaderFunc(ioutil.ReadFile) | 文件读取函数,例如 LoaderFunc(ioutil.ReadFile) |
WithGetLangHandle
WithGetLangHandle 用于配置 i18n 模板触发条件,可以通过从参数,请求头中取出信息
函数标签如下:
func WithGetLangHandle(handler GetLangHandler)
示例代码如下:
func main() {
h := server.New()
h.Use(hertzI18n.Localize(
hertzI18n.WithGetLangHandle(
func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext, defaultLang string) string {
lang := ctx.Query("lang")
if lang == "" {
return defaultLang
}
return lang
},
),
))
// ...
h.Spin()
}
完整用法示例详见 i18n
title: “访问日志” date: 2023-03-14 weight: 10 keywords: [“HTTP”, “访问日志”] description: “访问日志可以收集所有 HTTP 请求的详细信息,包括时间、端口、请求方法等。Hertz 也提供了 access log 的实现。”
访问日志可以收集所有 HTTP 请求的详细信息,包括时间、端口、请求方法等。Hertz 也提供了 access log 的 实现 ,这里的实现参考了 fiber。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/accesslog
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/accesslog"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(":8080"),
)
h.Use(accesslog.New())
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"msg": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
用户可以通过自定义初始化配置来设置访问日志的格式以及内容。
WithFormat
使用 WithFormat 自定义日志格式,默认的日志格式为 [${time}] ${status} - ${latency} ${method} ${path}
。传入的格式方式为 ${tag},具体 tag 参数可以参考下面的 支持的标签。
函数签名:
func WithFormat(s string) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/accesslog"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(":8080"),
)
h.Use(accesslog.New(accesslog.WithFormat("[${time}] ${status} - ${latency} ${method} ${path} ${queryParams}")))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"msg": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
WithTimeFormat
使用 WithTimeFormat 自定义时间格式,默认时间格式为 15:04:05
,具体格式可以参考该 链接 或者 go
的 time 包。
函数签名:
func WithTimeFormat(s string) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/accesslog"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(":8080"),
)
h.Use(accesslog.New(
accesslog.WithTimeFormat(time.RFC822),
))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"msg": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
WithTimeInterval
使用 WithTimeInterval 配置时间戳的刷新间隔,默认值为 500ms。
函数签名:
func WithTimeInterval(t time.Duration) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/accesslog"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(":8080"),
)
h.Use(accesslog.New(
accesslog.WithTimeInterval(time.Second),
))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"msg": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
WithAccessLogFunc
使用 WithAccessLogFunc 自定义日志打印函数。
函数签名:
func WithAccessLogFunc(f func(ctx context.Context, format string, v ...interface{})) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/accesslog"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(":8080"),
)
h.Use(accesslog.New(
accesslog.WithAccessLogFunc(hlog.CtxInfof),
))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"msg": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
WithTimeZoneLocation
使用 WithTimeZoneLocation 自定义时区,默认使用当地时区。
函数签名:
func WithTimeZoneLocation(loc *time.Location) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/accesslog"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(":8080"),
)
location, err := time.LoadLocation("Asia/Shanghai")
if err != nil {
return
}
h.Use(accesslog.New(
accesslog.WithTimeZoneLocation(location),
))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"msg": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
日志格式
默认日志格式
[${time}] ${status} - ${latency} ${method} ${path}
例子:
[21:54:36] 200 - 2.906859ms GET /ping
支持的标签
| 标签 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| pid | 进程 ID |
| time | 时间 |
| referer | 当前请求的来源页面 地址 |
| protocol | 协议类型 |
| port | 端口 |
| ip | Host 中的 ip 地址 |
| ips | Header 中的 X-Forwarded-For |
| host | HTTP 中的 Host |
| method | 请求方法 |
| path | 请求路径 |
| url | 请求 url |
| ua | User-Agent 的缩写 |
| latency | 处理消息的延迟 |
| status | HTTP 返回的状态码 |
| resBody | 返回内容 |
| reqHeaders | 请求的 Header 内容 |
| resHeaders | 返回的 Header 内容 |
| queryParams | 请求的 query 参数 |
| body | 请求的消息体内容 |
| bytesSent | 返回的消息体长度 |
| bytesReceived | 请求的消息体长度 |
| route | 请求路由的路径 |
标签扩展
支持自定义标签,前提要保证是线程安全的。
代码示例:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/bytebufferpool"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/accesslog"
)
func main() {
accesslog.Tags["test_tag"] = func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, buf *bytebufferpool.ByteBuffer) (int, error) {
return buf.WriteString("test")
}
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(":8080"),
)
h.Use(accesslog.New(accesslog.WithFormat("${test_tag}")))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"msg": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
title: “基本认证” date: 2022-10-13 weight: 2 keywords: [“HTTP”, “基本认证”] description: “Hertz 提供了 basic auth 的实现。”
在 HTTP 中,基本认证(Basic access authentication)是一种用来允许网页浏览器或其他客户端程序在请求时提供用户名和密码形式的身份凭证的一种登录验证方式。
在基本认证中,请求包含一个格式为 Authorization: Basic <credentials> 的头部字段,其中 credentials 是用户名和密码的 Base64
编码,用一个冒号 : 连接。
Hertz 也提供了 basic auth 的 实现 ,参考了 gin 的 实现 。
导入
import "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/server/basic_auth"
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/server/basic_auth"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.Use(basic_auth.BasicAuth(map[string]string{
"username1": "password1",
"username2": "password2",
}))
h.GET("/basicAuth", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "hello hertz")
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
Hertz 通过使用中间件可以实现让网页浏览器或其他客户端程序在请求时提供用户名和密码形式作为身份凭证进行登录验证,Hertz 提供了两种函数帮助用户快速使用基本认证(Basic access authentication)功能,用户可以根据业务场景自行选择不同的函数进行使用。
上述示例代码中,只使用了基本配置函数 BasicAuth,扩展配置函数 BasicAuthForRealm 的参数配置项如下:
注意: BasicAuth 是对 BasicAuthForRealm 的封装并提供了默认配置项。
| 参数 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| accounts | Accounts 被定义为 map[string]string 类型,以键值对的形式存储用户名和密码 |
| realm | 安全域字符串,默认值为 Authorization Required |
| userKey | 认证通过后在上下文中设置的用户名所对应的键值,默认值为 user |
BasicAuth
basic_auth 中间件提供了 BasicAuth 用于在客户端对服务端发起请求时进行用户名密码形式的身份验证。
函数签名:
func BasicAuth(accounts Accounts) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/server/basic_auth"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.Use(basic_auth.BasicAuth(map[string]string{
"username1": "password1",
"username2": "password2",
}))
h.GET("/basicAuth", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "hello hertz")
})
h.Spin()
}
BasicAuthForRealm
basic_auth 中间件提供了 BasicAuthForRealm 用于在使用 BasicAuth 进行身份验证的基础上提供更多例如 Realm 等的扩展配置。
函数签名:
func BasicAuthForRealm(accounts Accounts, realm, userKey string) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/server/basic_auth"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
// your-realm: 安全域字符串,本例中会以 Www-Authenticate: Basic realm="your-realm" 的形式保存在响应头中
// your-userKey: 认证通过后会以 userKey 为键 username 为值的形式设置在上下文中
h.Use(basic_auth.BasicAuthForRealm(map[string]string{
"username3": "password3",
"username4": "password4",
}, "your-realm", "your-userKey"))
h.GET("/basicAuth", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "hello hertz")
})
h.Spin()
}
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example
title: “JWT 认证” date: 2022-06-09 weight: 3 keywords: [“JWT 认证”, “JSON Web Token”, “JWT”] description: “Hertz 提供了 jwt 的实现。”
JSON Web Token(JWT)是一个轻量级的认证规范,这个规范允许我们使用 JWT 在用户和服务器之间传递安全可靠的信息。其本质是一个 token,是一种紧凑的 URL 安全方法,用于在网络通信的双方之间传递。 Hertz 也提供了 jwt 的 实现 ,参考了 gin 的 实现 。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/jwt
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/jwt"
)
type login struct {
Username string `form:"username,required" json:"username,required"`
Password string `form:"password,required" json:"password,required"`
}
var identityKey = "id"
func PingHandler(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
user, _ := ctx.Get(identityKey)
ctx.JSON(200, utils.H{
"message": fmt.Sprintf("username:%v", user.(*User).UserName),
})
}
// User demo
type User struct {
UserName string
FirstName string
LastName string
}
func main() {
h := server.Default()
// the jwt middleware
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
Realm: "test zone",
Key: []byte("secret key"),
Timeout: time.Hour,
MaxRefresh: time.Hour,
IdentityKey: identityKey,
PayloadFunc: func(data interface{}) jwt.MapClaims {
if v, ok := data.(*User); ok {
return jwt.MapClaims{
identityKey: v.UserName,
}
}
return jwt.MapClaims{}
},
IdentityHandler: func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) interface{} {
claims := jwt.ExtractClaims(ctx, c)
return &User{
UserName: claims[identityKey].(string),
}
},
Authenticator: func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) (interface{}, error) {
var loginVals login
if err := c.BindAndValidate(&loginVals); err != nil {
return "", jwt.ErrMissingLoginValues
}
userID := loginVals.Username
password := loginVals.Password
if (userID == "admin" && password == "admin") || (userID == "test" && password == "test") {
return &User{
UserName: userID,
LastName: "Hertz",
FirstName: "CloudWeGo",
}, nil
}
return nil, jwt.ErrFailedAuthentication
},
Authorizator: func(data interface{}, ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) bool {
if v, ok := data.(*User); ok && v.UserName == "admin" {
return true
}
return false
},
Unauthorized: func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, code int, message string) {
c.JSON(code, map[string]interface{}{
"code": code,
"message": message,
})
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("JWT Error:" + err.Error())
}
// When you use jwt.New(), the function is already automatically called for checking,
// which means you don't need to call it again.
errInit := authMiddleware.MiddlewareInit()
if errInit != nil {
log.Fatal("authMiddleware.MiddlewareInit() Error:" + errInit.Error())
}
h.POST("/login", authMiddleware.LoginHandler)
h.NoRoute(authMiddleware.MiddlewareFunc(), func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
claims := jwt.ExtractClaims(ctx, c)
log.Printf("NoRoute claims: %#v\n", claims)
c.JSON(404, map[string]string{"code": "PAGE_NOT_FOUND", "message": "Page not found"})
})
auth := h.Group("/auth")
// Refresh time can be longer than token timeout
auth.GET("/refresh_token", authMiddleware.RefreshHandler)
auth.Use(authMiddleware.MiddlewareFunc())
{
auth.GET("/ping", PingHandler)
}
h.Spin()
}
提示
因为 JWT 的核心是认证与授权,所以在使用 Hertz 的 jwt 扩展时,不仅需要为 /login
接口绑定认证逻辑 authMiddleware.LoginHandler。
还要以中间件的方式,为需要授权访问的路由组注入授权逻辑 authMiddleware.MiddlewareFunc()。
配置
Hertz 通过使用中间件,为路由请求提供了 jwt 的校验功能。其中 HertzJWTMiddleware 结构定义了 jwt
配置信息,并提供了默认配置,用户也可以依据业务场景进行定制。
上述示例代码中,只传入了两项必要的自定义的配置。关于 HertzJWTMiddleware 的更多常用配置如下:
| 参数 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
Realm |
用于设置所属领域名称,默认为 hertz jwt |
SigningAlgorithm |
用于设置签名算法,可以是 HS256、HS384、HS512、RS256、RS384 或者 RS512 等,默认为 HS256 |
Key |
用于设置签名密钥(必要配置) |
KeyFunc |
用于设置获取签名密钥的回调函数,设置后 token 解析时将从 KeyFunc 获取 jwt 签名密钥 |
Timeout |
用于设置 token 过期时间,默认为一小时 |
MaxRefresh |
用于设置最大 token 刷新时间,允许客户端在 TokenTime + MaxRefresh 内刷新 token 的有效时间,追加一个 Timeout 的时长 |
Authenticator |
用于设置登录时认证用户信息的函数(必要配置) |
Authorizator |
用于设置授权已认证的用户路由访问权限的函数 |
PayloadFunc |
用于设置登陆成功后为向 token 中添加自定义负载信息的函数 |
Unauthorized |
用于设置 jwt 验证流程失败的响应函数 |
LoginResponse |
用于设置登录的响应函数 |
LogoutResponse |
用于设置登出的响应函数 |
RefreshResponse |
用于设置 token 有效时长刷新后的响应函数 |
IdentityHandler |
用于设置获取身份信息的函数,默认与 IdentityKey 配合使用 |
IdentityKey |
用于设置检索身份的键,默认为 identity |
TokenLookup |
用于设置 token 的获取源,可以选择 header、query、cookie、param、form,默认为 header:Authorization |
TokenHeadName |
用于设置从 header 中获取 token 时的前缀,默认为 Bearer |
WithoutDefaultTokenHeadName |
用于设置 TokenHeadName 为空,默认为 false |
TimeFunc |
用于设置获取当前时间的函数,默认为 time.Now() |
HTTPStatusMessageFunc |
用于设置 jwt 校验流程发生错误时响应所包含的错误信息 |
SendCookie |
用于设置 token 将同时以 cookie 的形式返回,下列 cookie 相关配置生效的前提是该值为 true,默认为 false |
CookieMaxAge |
用于设置 cookie 的有效期,默认为 Timeout 定义的一小时 |
SecureCookie |
用于设置允许不通过 HTTPS 传递 cookie 信息,默认为 false |
CookieHTTPOnly |
用于设置允许客户端访问 cookie 以进行开发,默认为 false |
CookieDomain |
用于设置 cookie 所属的域,默认为空 |
SendAuthorization |
用于设置为所有请求的响应头添加授权的 token 信息,默认为 false |
DisabledAbort |
用于设置在 jwt 验证流程出错时,禁止请求上下文调用 abort(),默认为 false |
CookieName |
用于设置 cookie 的 name 值 |
CookieSameSite |
用于设置使用 protocol.CookieSameSite 声明的参数设置 cookie 的 SameSite 属性值 |
ParseOptions |
用于设置使用 jwt.ParserOption 声明的函数选项式参数配置 jwt.Parser 的属性值 |
Key
用于设置 token 的签名密钥。
示例代码:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
Key: []byte("secret key"),
})
KeyFunc
程序执行时 KeyFunc 作为 jwt.Parse() 的参数,负责为 token 解析提供签名密钥,通过自定义 KeyFunc 的逻辑,可以在解析
token 之前完成一些自定义的操作,如:校验签名方法的有效性、选择对应的签名密钥、将 token 存入请求上下文等。
函数签名:
func(t *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error)
默认处理逻辑如下:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
KeyFunc: func(t *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) {
if jwt.GetSigningMethod(mw.SigningAlgorithm) != t.Method {
return nil, ErrInvalidSigningAlgorithm
}
if mw.usingPublicKeyAlgo() {
return mw.pubKey, nil
}
// save token string if valid
c.Set("JWT_TOKEN", token)
return mw.Key, nil
},
})
Authenticator
配合 HertzJWTMiddleware.LoginHandler 使用,登录时触发,用于认证用户的登录信息。
函数签名:
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) (interface{}, error)
示例代码:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
Authenticator: func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) (interface{}, error) {
var loginVals login
if err := c.BindAndValidate(&loginVals); err != nil {
return "", jwt.ErrMissingLoginValues
}
userID := loginVals.Username
password := loginVals.Password
if (userID == "admin" && password == "admin") || (userID == "test" && password == "test") {
return &User{
UserName: userID,
LastName: "Hertz",
FirstName: "CloudWeGo",
}, nil
}
return nil, jwt.ErrFailedAuthentication
},
})
Authorizator
用于设置已认证的用户路由访问权限的函数,如下函数通过验证用户名是否为 admin,从而判断是否有访问路由的权限。
如果没有访问权限,则会触发 Unauthorized 参数中声明的 jwt 流程验证失败的响应函数。
函数签名:
func(data interface{}, ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) bool
示例代码:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
Authorizator: func(data interface{}, ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) bool {
if v, ok := data.(*User); ok && v.UserName == "admin" {
return true
}
return false
}
})
PayloadFunc
用于设置登录时为 token 添加自定义负载信息的函数,如果不传入这个参数,则 token 的 payload 部分默认存储 token
的过期时间和创建时间,如下则额外存储了用户名信息。
函数签名:
func(data interface{}) jwt.MapClaims
示例代码:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
PayloadFunc: func(data interface{}) jwt.MapClaims {
if v, ok := data.(*User); ok {
return jwt.MapClaims{
identityKey: v.UserName,
}
}
return jwt.MapClaims{}
},
})
IdentityHandler
IdentityHandler 作用在登录成功后的每次请求中,用于设置从 token
提取用户信息的函数。这里提到的用户信息在用户成功登录时,触发 PayloadFunc 函数,已经存入 token 的负载部分。
具体流程:通过在 IdentityHandler 内配合使用 identityKey,将存储用户信息的 token 从请求上下文中取出并提取需要的信息,封装成
User 结构,以 identityKey 为 key,User 为 value 存入请求上下文当中以备后续使用。
函数签名:
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) interface{}
示例代码:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
IdentityHandler: func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) interface{} {
claims := jwt.ExtractClaims(ctx, c)
return &User{
UserName: claims[identityKey].(string),
}
}
})
Unauthorized
用于设置 jwt 授权失败后的响应函数,如下函数将参数列表中的错误码和错误信息封装成 json 响应返回。
函数签名:
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, code int, message string)
默认处理逻辑如下:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
Unauthorized: func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, code int, message string) {
c.JSON(code, map[string]interface{}{
"code": code,
"message": message,
})
}
})
LoginResponse
用于设置登录的响应函数,作为 LoginHandler 的响应结果。
函数签名:
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, code int, token string, expire time.Time)
默认处理逻辑如下:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
LoginResponse: func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, code int, token string, expire time.Time) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, map[string]interface{}{
"code": http.StatusOK,
"token": token,
"expire": expire.Format(time.RFC3339),
})
}
})
// 在 LoginHandler 内调用
h.POST("/login", authMiddleware.LoginHandler)
LogoutResponse
用于设置登出的响应函数,作为 LogoutHandler 的响应结果。
函数签名:
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, code int)
默认处理逻辑如下:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
LogoutResponse: func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, code int) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, map[string]interface{}{
"code": http.StatusOK,
})
}
})
// 在 LogoutHandler 内调用
h.POST("/logout", authMiddleware.LogoutHandler)
RefreshResponse
用于设置 token 有效时长刷新后的响应函数,作为 RefreshHandler 的响应结果。
函数签名:
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, code int, token string, expire time.Time)
默认处理逻辑如下:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
RefreshResponse: func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, code int, token string, expire time.Time) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, map[string]interface{}{
"code": http.StatusOK,
"token": token,
"expire": expire.Format(time.RFC3339),
})
},
})
// 在 RefreshHandler 内调用
auth.GET("/refresh_token", authMiddleware.RefreshHandler)
TokenLookup
通过键值对的形式声明 token 的获取源,有四种可选的方式,默认值为 header:Authorization,如果同时声明了多个数据源则以 ,
为分隔线,第一个满足输入格式的数据源将被选择,其余忽略。
示例代码:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
// - "header:<name>"
// - "query:<name>"
// - "cookie:<name>"
// - "param:<name>"
// - "form:<name>"
TokenLookup: "header: Authorization, query: token, cookie: jwt"
})
TimeFunc
用于设置获取当前时间的函数,默认为 time.Now(),在 jwt 校验过程中,关于 token 的有效期的验证需要以 token
创建时间为起点,TimeFunc 提供了 jwt 获取当前时间的函数,可以选择覆盖这个默认配置,应对一些时区不同的情况。
函数签名:
func() time.Time
默认处理逻辑如下:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
TimeFunc: func() time.Time {
return time.Now()
}
})
HTTPStatusMessageFunc
一旦 jwt 校验流程产生错误,如 jwt 认证失败、token 鉴权失败、刷新 token 有效时长失败等,对应 error
将以参数的形式传递给 HTTPStatusMessageFunc,由其提取出需要响应的错误信息,最终以 string 参数形式传递给 Unauthorized
声明的 jwt 验证流程失败的响应函数返回。
函数签名:
func(e error, ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) string
默认处理逻辑如下:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
HTTPStatusMessageFunc: func(e error, ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) string {
return e.Error()
}
})
Cookie
cookie 相关的配置参数有八个,将 SendCookie 设置为 true、TokenLookup 设置为 cookie: jwt 后,token 将同时以 cookie
的形式返回,并在接下来的请求中从 HTTP Cookie 获取。
示例代码:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
SendCookie: true,
TokenLookup: "cookie: jwt",
CookieMaxAge: time.Hour,
SecureCookie: false,
CookieHTTPOnly: false,
CookieDomain: ".test.com",
CookieName: "jwt-cookie",
CookieSameSite: protocol.CookieSameSiteDisabled,
})
ParseOptions
利用 ParseOptions 可以开启相关配置有三个,分别为
WithValidMethods: 用于提供解析器将检查的签名算法,只有被提供的签名算法才被认为是有效的WithJSONNumber: 用于配置底层 JSON 解析器使用UseNumber方法WithoutClaimsValidation: 用于禁用 claims 验证
示例代码:
authMiddleware, err := jwt.New(&jwt.HertzJWTMiddleware{
ParseOptions: []jwt.ParserOption{
jwt.WithValidMethods([]string{"HS256"}),
jwt.WithJSONNumber(),
jwt.WithoutClaimsValidation(),
},
})
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example
title: “Request ID”
date: 2022-10-01
weight: 9
description: >
keywords: [“Request ID”, “X-Request-ID”]
description: “Hertz 提供了可以对 X-Request-ID 进行操作的 Request ID 中间件。”
X-Request-ID 在 HTTP Headers 中是一种非标准响应字段,通常用于关联客户端和服务器之间的 HTTP 请求。
Hertz 也提供了可以对 X-Request-ID 进行操作的 Request ID 中间件,参考了
gin 的 实现。
安装
下载并安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/requestid
导入
import "github.com/hertz-contrib/requestid"
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/requestid"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(
// 自定义 request id 生成逻辑
requestid.New(
requestid.WithGenerator(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) string {
return "cloudwego.io"
}),
// 自定义 request id 响应头键值
requestid.WithCustomHeaderStrKey("Your-Customised-Key"),
),
)
// Example ping request.
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
hlog.Info(string(c.Response.Header.Header()))
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
Hertz 通过使用中间件,可以在响应头中添加一个键为 X-Request-ID 的标识符,如果在请求头中设置了 X-Request-ID
字段,则会在响应头中将 X-Request-ID 原样返回。
Request ID 中间件提供了默认配置,用户也可以依据业务场景使用 WithGenerator,WithCustomHeaderStrKey,WithHandler
函数对以下配置项进行定制。
| 配置 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| WithGenerator | 定义生成 Request ID 的函数,默认生成 UUID 标识符 |
| WithCustomHeaderStrKey | 定义 Request ID 的键值,默认为 X-Request-ID |
| WithHandler | 定义 Request ID 的处理函数 |
初始化 Request ID
requestid 中间件提供了 New 用于在响应头添加 Request ID 字段。
函数签名:
func New(opts ...Option) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/requestid"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(
requestid.New(),
)
// Example ping request.
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
自定义 Request ID 键值
requestid 中间件提供了 WithCustomHeaderStrKey 用于自定义 Request ID 键值。
注意:如果需要在请求头中设置 X-Request-ID,则需要保持和自定义响应头键值一致。
函数签名:
func WithCustomHeaderStrKey(s HeaderStrKey) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/requestid"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
// define your own header to save request id here
h.Use(
requestid.New(
requestid.WithCustomHeaderStrKey("Your-Header-StrKey"),
),
)
// Example ping request.
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
自定义 Request ID 值
requestid 中间件提供了 WithGenerator 用于自定义 Request ID 值的生成。
函数签名:
func WithGenerator(g Generator) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/requestid"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(
// define your own request id generator here
requestid.New(requestid.WithGenerator(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) string {
return "cloudwego.io"
})),
)
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
自定义 Request ID Handler
requestid 中间件提供了 WithHandler 用于自定义 Request ID 的处理函数。
函数签名:
func WithHandler(handler Handler) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/requestid"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
var bar string
h.Use(
requestid.New(
requestid.WithGenerator(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) string {
return "hello"
}),
// define your request id handler here
requestid.WithHandler(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, requestID string) {
bar = requestID + " hertz"
}),
),
)
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{
"ping": "pong",
"foo": bar, // hello hertz
})
})
h.Spin()
}
获取 Request ID
requestid 中间件提供了 Get 用于从请求头中获取 Request ID,它也支持获取使用 requestid.WithCustomHeaderStrKey 自定义
Request ID 键值。
函数签名:
func Get(c *app.RequestContext) string
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/requestid"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(
requestid.New(requestid.WithGenerator(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) string {
return "cloudwego.io"
})),
)
// You may retrieve request id from header by calling requestid.Get
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{
"ping": "pong",
"request-id": requestid.Get(c),
})
})
h.Spin()
}
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example
title: “Sentry” date: 2022-11-25 weight: 11 keywords: [“Sentry”, “实时错误监控”] description: “Hertz 通过使用中间件 hertzsentry,整合了 Sentry-Go 的 SDK。”
Sentry 是一个开源的实时错误监控项目,支持很多平台,包括 Web 前端、服务器端、移动端和游戏端等。Hertz 通过使用中间件 hertzsentry ,整合了 Sentry-Go 的 SDK。提供了一些统一的接口,帮助用户获得 sentry hub 和报告错误信息。
注意:信息上报功能的实现,依旧是以 Sentry 的 Go SDK 为载体。
这个项目参考了 fibersentry 的实现。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/hertzsentry
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/getsentry/sentry-go"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/hertzsentry"
)
var yourDsn = ""
func main() {
// set interval to 0 means using fs-watching mechanism.
h := server.Default(server.WithAutoReloadRender(true, 0))
// init sentry
if err := sentry.Init(sentry.ClientOptions{
// The DSN to use. If the DSN is not set, the client is effectively disabled.
Dsn: yourDsn,
// Before send callback.
BeforeSend: func(event *sentry.Event, hint *sentry.EventHint) *sentry.Event {
return event
},
// In debug mode, the debug information is printed to stdout to help you understand what
// sentry is doing.
Debug: true,
// Configures whether SDK should generate and attach stacktraces to pure capture message calls.
AttachStacktrace: true,
}); err != nil {
log.Fatal("sentry init failed")
}
// use sentry middleware and config with your requirements.
// attention! you should use sentry handler after recovery.Recovery()
h.Use(hertzsentry.NewSentry(
hertzsentry.WithSendRequest(true),
hertzsentry.WithRePanic(true),
))
h.GET("/hello", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// use GetHubFromContext to get the hub
if hub := hertzsentry.GetHubFromContext(ctx); hub != nil {
hub.WithScope(func(scope *sentry.Scope) {
scope.SetTag("hertz", "CloudWeGo Hertz")
scope.SetLevel(sentry.LevelDebug)
hub.CaptureMessage("Just for debug")
})
}
ctx.SetStatusCode(0)
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
Hertz 通过使用中间件,整合了 Sentry-Go 的功能。其中 hertzsentry.options 结构定义了 hertzsentry
的配置信息,并提供了默认配置,用户也可以依据业务场景进行定制。
| 参数 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| rePanic | 用于配置 Sentry 在恢复后是否要再次 panic。如果使用了 Recover 中间件,则设置为 true,默认为 false。 |
| waitForDelivery | 用于配置是否要在继续处理响应之前阻止请求并清空缓存区(只有异步传输时才真正意义上有清空缓存区的操作)。如果使用 Recover 中间件,跳过这个选项或将其设置为 false 是安全的,默认为 false。 |
| sendRequest | 用于配置在捕获 sentry 事件时是否要添加当前的请求头信息,默认为 false。 |
| sendBody | 用于配置在捕获 sentry 事件时是否要添加当前的请求正文信息,默认为 false。 |
| timeout | 用于配置 sentry 事件传递请求的超时时长,默认为 2 秒。 |
Flush(Go-Sentry)
Go-Sentry 可以选择异步或者同步发送捕获的信息,选择异步发送时,Flush 用于清空缓存区,同步发送时没有缓存的概念,直接返回 true。
触发 Flush 时等待,直到底层传输系统向 Sentry 服务器发送所有事件完毕,返回 true。但最多等待给定的超时时间,如果达到超时,则返回 false。在这种情况下,有些事件可能没有被发送。(这两种情况下缓存区都将被清空)
应该在终止程序之前调用 Flush,以避免无意中丢弃事件。
不要在每次调用 CaptureEvent、CaptureException 或 CaptureMessage 后不加区分地调用 Flush。相反,要想让 SDK 在网络上同步发送事件,请将其配置为使用 HTTPSyncTransport。
函数签名:
func (hub *Hub) Flush(timeout time.Duration) bool
Flush 调用逻辑如下:
func (hub *Hub) Flush(timeout time.Duration) bool {
client := hub.Client()
if client == nil {
return false
}
// client 的传输方式为异步或同步(需提前配置 Go-Sentry 的初始化参数)
return client.Flush(timeout)
}
title: “Recovery” date: 2022-12-15 weight: 2 keywords: [“Recovery”, “panic 恢复”] description: “Recovery 中间件是 Hertz 框架预置的中间件,为 Hertz 框架提供 panic 恢复的功能。”
Recovery 中间件是 Hertz 框架预置的中间件,使用 server.Default() 可以默认注册该中间件,为 Hertz 框架提供 panic 恢复的功能。
如果你不使用server.Default(),你也可以通过以下方式注册 Recovery 中间件:
h := server.New()
h.Use(recovery.Recovery())
Recovery 中间件会恢复 Hertz 框架运行中的任何 panic,在 panic 发生之后,Recover 中间件会默认打印出 panic
的时间、内容和堆栈信息,同时通过*app.RequestContext将返回响应的状态码设置成 500。
导入
import "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/server/recovery"
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.GET("/test", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
panic("test")
c.String(http.StatusOK, "test interface")
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
Recovery 中间件提供了默认的 panic 处理函数defaultRecoveryHandler()。
同时你也可以通过WithRecoveryHandler()函数来自定义出现 panic 后的处理函数,函数签名如下:
func WithRecoveryHandler(f func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext, err interface{}, stack []byte))
如果你在发生 panic 之后希望能够获取客户端信息,示例代码如下:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/middlewares/server/recovery"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
func MyRecoveryHandler(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext, err interface{}, stack []byte) {
hlog.SystemLogger().CtxErrorf(c, "[Recovery] err=%v\nstack=%s", err, stack)
hlog.SystemLogger().Infof("Client: %s", ctx.Request.Header.UserAgent())
ctx.AbortWithStatus(consts.StatusInternalServerError)
}
func main() {
h := server.New()
h.Use(recovery.Recovery(recovery.WithRecoveryHandler(MyRecoveryHandler)))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
panic("test")
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong "+fmt.Sprint(time.Now().Unix()))
})
h.Spin()
}
title: “Pprof” date: 2022-09-24 weight: 7 keywords: [“pprof”, “性能分析”] description: “Hertz 提供了 pprof 扩展,帮助用户对 Hertz 项目进行性能分析。”
Hertz 提供了 pprof 扩展,帮助用户对 Hertz 项目进行性能分析,pprof 扩展的实现参考了 Gin 的实现。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/pprof
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/pprof"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
pprof.Register(h)
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
PrefixOptions
pprof 的默认前缀为 debug/pprof,即用户在 Hertz 项目中注册并使用 pprof 后,用户可以通过访问
localhost:8888/debug/pprof 来查看当前项目的采样信息。
此外,用户可以在注册 pprof 时指定自定义前缀。
函数签名如下:
Register(r *server.Hertz, prefixOptions ...string)
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/pprof"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
// default is "debug/pprof"
pprof.Register(h, "dev/pprof")
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
}
RouteRegister
pprof 不仅可以注册到 Hertz 对象上,还可以注册到路由组(RouterGroup)上。
函数签名如下:
RouteRegister(rg *route.RouterGroup, prefixOptions ...string)
本方式注册后的 pprof 前缀为路由组的前缀与自定义前缀拼接后的结果。
- 用户不指定前缀,注册后的
pprof的前缀为路由组的前缀与默认前缀/debug/pprof拼接后的结果,即为/xxx/debug/pprof(xxx为路由组前缀); - 用户指定前缀,注册后的
pprof的前缀为路由组的的前缀与自定义前缀拼接后的结果,比如下文示例中注册后的pprof前缀为/admin/pprof。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/pprof"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
pprof.Register(h)
adminGroup := h.Group("/admin")
adminGroup.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
pprof.RouteRegister(adminGroup, "pprof")
h.Spin()
}
查看 pprof 采样信息
通过浏览器查看
通过浏览器访问 localhost:8888/debug/pprof
- Hertz 端口号默认为 8888
- pprof 默认地址前缀为
debug/pprof - 端口号和访问路由与用户实际端口号和
pprof前缀一致
通过 go tool pprof 查看
使用 go tool pprof 工具查看堆栈采样信息:
go tool pprof http://localhost:8888/debug/pprof/heap
使用 go tool pprof 工具查看 CPU 采样信息:
go tool pprof http://localhost:8888/debug/pprof/profile
默认采样时间为 30s,可通过查询字符串来自定义采样时间:
go tool pprof http://localhost:8888/debug/pprof/profile?seconds=10
使用 go tool pprof 工具查看 go 协程阻塞信息:
go tool pprof http://localhost:8888/debug/pprof/block
获取执行 trace 信息:
wget http://localhost:8888/debug/pprof/trace?seconds=5
通过 go tool pprof 查看火焰图
安装 graphviz
go tool pprof -http :8080 localhost:8888/debug/pprof/profile?seconds=10
完整用法示例详见 example
title: “Paseto” date: 2023-05-08 weight: 16 keywords: [“Paseto”, “JOSE”, “JWT”, “JWE”, “JWS”] description: “这是为 Hertz 实现的 PASETO 中间件。”
Paseto 拥有你喜欢 JOSE 的一切(JWT、JWE、JWS),没有困扰 JOSE 标准的 许多设计缺陷。
这是为 Hertz 实现的 PASETO 中间件。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/paseto
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/paseto"
)
func performRequest() {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
c, _ := client.NewClient()
req, resp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto")
req.SetMethod("GET")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("get token: %s\n", resp.Body())
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetHeader("Authorization", string(resp.Body()))
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response :%s", resp.Body())
}
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.GET("/paseto", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
now := time.Now()
genTokenFunc := paseto.DefaultGenTokenFunc()
token, err := genTokenFunc(&paseto.StandardClaims{
Issuer: "cwg-issuer",
ExpiredAt: now.Add(time.Hour),
NotBefore: now,
IssuedAt: now,
}, nil, nil)
if err != nil {
hlog.Error("generate token failed")
}
ctx.String(http.StatusOK, token)
})
h.POST("/paseto", paseto.New(), func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(http.StatusOK, "token is valid")
})
go performRequest()
h.Spin()
}
配置项
| 配置 | 默认值 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| Next | nil | 用于设置一个函数,当返回 true 时跳过这个中间件 |
| ErrorFunc | 输出日志并返回 401 | 用于设置一个在发生错误时执行的函数 |
| SuccessHandler | 将声明保存到 app.RequestContext | 用于设置一个函数,该函数在令牌有效时执行 |
| KeyLookup | header:Authorization | 用于设置一个“<source>:<key>”形式的字符串,用于创建从请求中提取令牌的提取器 |
| TokenPrefix | "" | 用于设置一个字符串,用于保存令牌查找的前缀 |
| ParseFunc | 解析 V4 公共令牌 | 用于设置一个解析并验证令牌的函数 |
Next
WithNext 设置一个函数来判断是否跳过这个中间件。
函数签名:
func WithNext(f NextHandler) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/paseto"
)
func performRequest() {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
c, _ := client.NewClient()
req, resp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto")
req.SetMethod("GET")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetHeader("Authorization", string(resp.Body()))
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response :%s,because I have the token\n", resp.Body())
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetHeader("skip", "yes")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response :%s,because I trigger the nextFunc\n", resp.Body())
req.SetMethod("POST")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response :%s,because I don't have token nor trigger the nextFunc\n", resp.Body())
}
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
next := func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) bool {
return string(c.GetHeader("skip")) == "yes"
}
h.GET("/paseto", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
now := time.Now()
genTokenFunc := paseto.DefaultGenTokenFunc()
token, err := genTokenFunc(&paseto.StandardClaims{
Issuer: "cwg-issuer",
ExpiredAt: now.Add(time.Hour),
NotBefore: now,
IssuedAt: now,
}, nil, nil)
if err != nil {
hlog.Error("generate token failed")
}
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, token)
})
h.POST("/paseto", paseto.New(paseto.WithNext(next)), func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "token is valid")
})
go performRequest()
h.Spin()
}
ErrorFunc
WithErrorFunc 设置 ErrorHandler。
ErrorHandler 定义一个在发生错误时执行的函数。
函数签名:
func WithErrorFunc(f app.HandlerFunc) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/paseto"
)
func performRequest() {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
c, _ := client.NewClient()
req, resp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetMethod("GET")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto/withsecret")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto")
req.SetHeader("Authorization", string(resp.Body()))
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response:%s\n", resp.Body())
req.SetMethod("GET")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto/withnosecret")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto")
req.SetHeader("Authorization", string(resp.Body()))
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response:%s", resp.Body())
}
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
handler := func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, "invalid token")
c.Abort()
}
h.GET("/paseto/withsecret", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
now := time.Now()
genTokenFunc := paseto.DefaultGenTokenFunc()
token, err := genTokenFunc(&paseto.StandardClaims{
Issuer: "cwg-issuer",
ExpiredAt: now.Add(time.Hour),
NotBefore: now,
IssuedAt: now,
}, utils.H{
"secret1": "answer1",
}, nil)
if err != nil {
hlog.Error("generate token failed")
}
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, token)
})
h.GET("/paseto/witherrorfunc", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
now := time.Now()
genTokenFunc := paseto.DefaultGenTokenFunc()
token, err := genTokenFunc(&paseto.StandardClaims{
Issuer: "cwg-issuer",
ExpiredAt: now.Add(time.Hour),
NotBefore: now,
IssuedAt: now,
}, nil, nil)
if err != nil {
hlog.Error("generate token failed")
}
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, token)
})
h.POST("/paseto", paseto.New(paseto.WithErrorFunc(handler)), func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "token is valid")
})
go performRequest()
h.Spin()
}
SuccessHandler
WithSuccessHandler 设置处理已解析令牌的逻辑。
函数签名:
func WithSuccessHandler(f SuccessHandler) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
gpaseto "aidanwoods.dev/go-paseto"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/paseto"
)
func performRequest() {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
c, _ := client.NewClient()
req, resp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetMethod("GET")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto/withsecret")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto")
req.SetHeader("Authorization", string(resp.Body()))
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response:%s\n", resp.Body())
req.SetMethod("GET")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto/withnosecret")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto")
req.SetHeader("Authorization", string(resp.Body()))
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response:%s", resp.Body())
}
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
handler := func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext, token *gpaseto.Token) {
var answer string
if err := token.Get("secret1", &answer); err != nil {
c.String(consts.StatusBadRequest, "you don't not the answer of secret1")
c.Abort()
}
}
h.GET("/paseto/withsecret", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
now := time.Now()
genTokenFunc := paseto.DefaultGenTokenFunc()
token, err := genTokenFunc(&paseto.StandardClaims{
Issuer: "cwg-issuer",
ExpiredAt: now.Add(time.Hour),
NotBefore: now,
IssuedAt: now,
}, utils.H{
"secret1": "answer1",
}, nil)
if err != nil {
hlog.Error("generate token failed")
}
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, token)
})
h.GET("/paseto/withnosecret", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
now := time.Now()
genTokenFunc := paseto.DefaultGenTokenFunc()
token, err := genTokenFunc(&paseto.StandardClaims{
Issuer: "cwg-issuer",
ExpiredAt: now.Add(time.Hour),
NotBefore: now,
IssuedAt: now,
}, nil, nil)
if err != nil {
hlog.Error("generate token failed")
}
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, token)
})
h.POST("/paseto", paseto.New(paseto.WithSuccessHandler(handler)), func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "token is valid")
})
go performRequest()
h.Spin()
}
KeyLookup
WithKeyLookUp 以“<source>:<key>”的形式设置一个字符串,用于创建从请求中提取令牌的“提取器”。
函数签名:
func WithKeyLookUp(lookup string) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/paseto"
)
func performRequest() {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
c, _ := client.NewClient()
req, resp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto")
req.SetMethod("GET")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("get token: %s\n", resp.Body())
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetBody([]byte("Authorization=" + string(resp.Body())))
req.SetHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response :%s", resp.Body())
}
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.GET("/paseto", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
now := time.Now()
genTokenFunc := paseto.DefaultGenTokenFunc()
token, err := genTokenFunc(&paseto.StandardClaims{
Issuer: "cwg-issuer",
ExpiredAt: now.Add(time.Hour),
NotBefore: now,
IssuedAt: now,
}, nil, nil)
if err != nil {
hlog.Error("generate token failed")
}
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, token)
})
h.POST("/paseto", paseto.New(paseto.WithKeyLookUp("form:Authorization")), func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "token is valid")
})
go performRequest()
h.Spin()
}
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/paseto"
)
func performRequest() {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
c, _ := client.NewClient()
req, resp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto")
req.SetMethod("GET")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("get token: %s\n", resp.Body())
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetHeader("Authorization", "Bearer "+string(resp.Body()))
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response :%s", resp.Body())
}
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.GET("/paseto", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
now := time.Now()
genTokenFunc := paseto.DefaultGenTokenFunc()
token, err := genTokenFunc(&paseto.StandardClaims{
Issuer: "cwg-issuer",
ExpiredAt: now.Add(time.Hour),
NotBefore: now,
IssuedAt: now,
}, nil, nil)
if err != nil {
hlog.Error("generate token failed")
}
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, token)
})
h.POST("/paseto", paseto.New(paseto.WithTokenPrefix("Bearer ")), func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "token is valid")
})
go performRequest()
h.Spin()
}
ParseFunc
WithParseFunc 设置 ParseFunc。
ParseFunc 解析并验证令牌。
函数签名:
func WithParseFunc(f ParseFunc) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/paseto"
)
func performRequest() {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
c, _ := client.NewClient()
req, resp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetMethod("GET")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto/correct-issuer")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto")
req.SetHeader("Authorization", string(resp.Body()))
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response:%s\n", resp.Body())
req.SetMethod("GET")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto/wrong-issuer")
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/paseto")
req.SetHeader("Authorization", string(resp.Body()))
_ = c.Do(context.Background(), req, resp)
fmt.Printf("Authorization response:%s,because issuer is wrong", resp.Body())
}
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.GET("/paseto/correct-issuer", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
now := time.Now()
token, err := paseto.DefaultGenTokenFunc()(&paseto.StandardClaims{
Issuer: "CloudWeGo-issuer",
ExpiredAt: now.Add(time.Hour),
NotBefore: now,
IssuedAt: now,
}, nil, nil)
if err != nil {
hlog.Error("generate token failed")
}
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, token)
})
h.GET("/paseto/wrong-issuer", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
now := time.Now()
token, err := paseto.DefaultGenTokenFunc()(&paseto.StandardClaims{
Issuer: "CloudWeRun-issuer",
ExpiredAt: now.Add(time.Hour),
NotBefore: now,
IssuedAt: now,
}, nil, nil)
if err != nil {
hlog.Error("generate token failed")
}
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, token)
})
parseFunc, _ := paseto.NewV4PublicParseFunc(paseto.DefaultPublicKey, []byte(paseto.DefaultImplicit), paseto.WithIssuer("CloudWeGo-issuer"))
h.POST("/paseto", paseto.New(paseto.WithParseFunc(parseFunc)), func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "token is valid")
})
go performRequest()
h.Spin()
}
版本比较
| 版本 | 本地 | 公共 |
|---|---|---|
| v1 | 使用“AES-256-CBC”加密并使用 HMAC-SHA-256 签名 | 使用RSA-SHA-256签名 |
| v2 | 使用“XSalsa20Poly-1305”加密并使用“HMAC-SHA-384”签名` | 使用EdDSA(Ed25519)签名 |
| v3 | 使用“XChaCha20Poly1305”加密并使用“HMAC-SHA-384”签名` | 使用EdDSA(Ed25519)签名 |
| v4 | 使用“XChaCha20Poly1305”加密,并使用“HMAC-SHA-512-256”签名` | 使用EdDSA(Ed448)签名 |
完整示例
完成用法示例详见 paseto/example
title: “跨源资源共享” date: 2022-05-21 weight: 1 keywords: [“跨源资源共享”] description: “hertz 提供 cors 跨域中间件的实现。”
跨源资源共享(CORS)机制允许服务器标识除了它自己的其它 origin,使得浏览器可以访问加载这些资源; 该机制也用来检查服务器是否允许浏览器发送真实的请求,通过浏览器发送"预检"请求实现,在预检请求头部中有 HTTP 方法和真实请求会用到的头。
hertz 提供 cors 跨域中间件的 实现 ,这里的实现参考了 gin 的 cors。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/cors
示例代码
package main
import (
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/cors"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
// CORS for https://foo.com and https://github.com origins, allowing:
// - PUT and PATCH methods
// - Origin header
// - Credentials share
// - Preflight requests cached for 12 hours
h.Use(cors.New(cors.Config{
AllowOrigins: []string{"https://foo.com"},
AllowMethods: []string{"PUT", "PATCH"},
AllowHeaders: []string{"Origin"},
ExposeHeaders: []string{"Content-Length"},
AllowCredentials: true,
AllowOriginFunc: func(origin string) bool {
return origin == "https://github.com"
},
MaxAge: 12 * time.Hour,
}))
h.Spin()
}
预检请求
对于跨源访问来说,如果是简单请求,本质上就是在 HTTP 请求头信息中添加一个 Origin 字段,用于描述本次请求来自哪个源,服务端可以直接响应。
而对于非简单跨源访问请求来说(比如请求方法是 PUT 或 PATCH,Content-Type 字段类型是 application/json
等),会在正式通信之前,发送一次 HTTP
预检请求(preflight),用于校验客户端是否有跨源资源访问权限,预检请求使用的方法是 OPTIONS,且这是浏览器自发的行为。
注意:部分 hertz-cors 的配置只有在预检请求发生时才会生效。
配置
Hertz 通过使用 cors 中间件,为客户端提供了跨源资源访问的能力。用户可以通过自定义 Config 结构的配置参数,精细控制服务端资源允许跨源访问的范围,亦或选择
hertz-cors 的默认配置,允许来自任意 origin 的客户端访问资源。
上述示例代码中只配置了部分可选参数,Config 的完整参数列表如下:
| 参数 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| AllowAllOrigins | 用于设置允许来自任意 origin 的客户端访问服务端资源,默认为 false |
| AllowOrigins | 用于设置允许跨源访问的 origin 列表,默认为 [] |
| AllowOriginFunc | 用于设置校验客户端 origin 的函数,当启用这个配置时,AllowOrigins 的内容将被忽略 |
| AllowMethods | 用于设置允许客户端跨源访问所使用的 HTTP 方法列表(在接收到预检请求时生效) |
| AllowHeaders | 用于设置客户端发起非简单的跨源资源访问请求时,允许使用的头信息字段列表,默认为 [](在接收到预检请求时生效) |
| AllowCredentials | 用于设置允许客户端请求携带用户凭证,如:cookies,token,SSL 凭证,默认为 false |
| ExposeHeaders | 用于设置允许暴露给客户端的响应头列表,默认为 [] |
| MaxAge | 用于设置预检请求的有效期(有效期内不会发起重复的预检请求) |
| AllowWildcard | 用于设置允许含通配符的 origin 访问资源,默认为 false |
| AllowBrowserExtensions | 用于设置允许使用流行的浏览器扩展模式,默认为 false |
| AllowWebSockets | 用于设置允许使用 WebSocket 协议,默认为 false |
| AllowFiles | 用于设置允许使用 file:// 协议(危险)除非你能确保 100% 的安全,才可以使用它,默认为 false |
AllowAllOrigins
该参数设置为 true 之后,将允许来自任意 origin 的客户端跨源访问服务端资源。
AllowAllOrigins 配置为 true 时,AllowOriginFunc 以及 AllowOrigins 配置不可以使用,否则将发生冲突。
AllowOrigins
描述了可以跨源访问的 origin 列表,如果列表中的任何 origin 携带通配符 *(每个 origin 内只允许使用一个通配符 *
),则允许任何满足匹配逻辑的 origin 访问。
与 AllowAllOrigins 配置冲突,同时只能配置一项。
与 AllowOriginFunc 配置同时使用时,AllowOriginFunc 的优先级高于 AllowOrigins。
若需要使用携带通配符的 origin,则 AllowWildcard 参数需同时设置为 true。
示例代码 1:
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/cors"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(cors.New(cors.Config{
AllowOrigins: []string{"https://foo.com"},
}))
h.Spin()
}
示例代码 2:
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/cors"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(cors.New(cors.Config{
AllowWildcard: true,
AllowOrigins: []string{"http://some-domain/*"},
}))
h.Spin()
}
AllowOriginFunc
以 origin 为形参,用于自定义 origin 的校验逻辑,返回 true 表示校验通过。
与 AllowAllOrigins 配置冲突,同时只能配置一项。
与 AllowOrigins 配置同时使用时,AllowOriginFunc 的优先级高于 AllowOrigins。
函数签名:
func(origin string) bool
示例代码:
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/cors"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(cors.New(cors.Config{
AllowOriginFunc: func(origin string) bool {
return origin == "https://github.com"
},
}))
h.Spin()
}
AllowMethods
该配置只有在接收到预检请求时才会生效,用于设置允许客户端跨源访问所使用的 HTTP 方法列表。
如果是由 GET 或者 POST 发起的简单请求,则无需额外设置。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/cors"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(cors.New(cors.Config{
AllowWildcard: true,
AllowMethods: []string{"PUT", "PATCH"},
}))
h.Spin()
}
AllowHeaders
该配置只有在接收到预检请求时才会生效,如果浏览器请求包括 Access-Control-Request-Headers
字段,则 Access-Control-Allow-Headers 字段是必需的。它是一个逗号分隔的字符串,表明服务器支持的所有头信息字段。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/cors"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(cors.New(cors.Config{
AllowHeaders: []string{"Origin"},
}))
h.Spin()
}
ExposeHeaders
用于设置允许客户端从 HTTP Response 的 Header 中获取的自定义头信息字段名称。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/cors"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(cors.New(cors.Config{
ExposeHeaders: []string{"Content-Length"},
}))
h.Spin()
}
更多用法示例详见 cors
title: “CSRF” date: 2022-12-6 weight: 12 keywords: [“CSRF”, “跨站点请求伪造攻击”] description: “Hertz 提供了 CSRF 中间件,可帮助您防止跨站点请求伪造攻击。”
Cross-site request forgery(CSRF)是一种挟制用户在当前已登录的 Web 应用程序上执行非本意的操作的攻击方法。
Hertz 提供了 CSRF 中间件,可帮助您防止跨站点请求伪造攻击。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/csrf
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/csrf"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("secret"))
h.Use(sessions.New("csrf-session", store))
h.Use(csrf.New())
h.GET("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, csrf.GetToken(ctx))
})
h.POST("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, "CSRF token is valid")
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
| 配置项 | 默认值 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
Secret |
csrfSecret |
用于生成令牌(必要配置) |
IgnoreMethods |
“GET”, “HEAD”, “OPTIONS”, “TRACE” | 被忽略的方法将将视为无需 csrf保护 |
Next |
nil |
Next 定义了一个函数,当返回真时,跳过这个 csrf 中间件。 |
KeyLookup |
header:X-CSRF-TOKEN |
KeyLookup 是一个" |
ErrorFunc |
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) { panic(c.Errors.Last()) } |
当 app.HandlerFunc返回一个错误时,ErrorFunc 被执行 |
Extractor |
基于 KeyLookup 创建 | Extractor返回csrf token。如果设置了这个,它将被用来代替基于KeyLookup的 Extractor。 |
WithSecret
csrf 中间件提供了 WithSecret 用于帮助用户设置自定义秘钥用于签发 token,默认为 csrfSecret。
函数签名:
func WithSecret(secret string) Option
默认值:csrfSecret
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/csrf"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("store"))
h.Use(sessions.New("csrf-session", store))
h.Use(csrf.New(csrf.WithSecret("your_secret")))
h.GET("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, csrf.GetToken(ctx))
})
h.POST("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, "CSRF token is valid")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithIgnoredMethods
csrf 中间件提供了 WithIgnoredMethods 用于帮助用户设置自定义无需保护的方法,默认为 GET, HEAD, OPTIONS
和 TRACE。
函数签名:
func WithIgnoredMethods(methods []string) Option
默认值:{"GET", "HEAD", "OPTIONS", "TRACE"}
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/csrf"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("secret"))
h.Use(sessions.New("csrf-session", store))
h.Use(csrf.New(csrf.WithIgnoredMethods([]string{"GET", "HEAD", "TRACE"})))
h.GET("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, csrf.GetToken(ctx))
})
h.OPTIONS("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, "success")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithErrorFunc
csrf 中间件提供了 WithErrorFunc 方便用户自定义错误处理逻辑。
函数签名:
func WithErrorFunc(f app.HandlerFunc) Option
默认实现:
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) { panic(c.Errors.Last()) }
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/csrf"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func myErrFunc(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
if ctx.Errors.Last() == nil {
err := fmt.Errorf("myErrFunc called when no error occurs")
ctx.String(400, err.Error())
ctx.Abort()
}
ctx.AbortWithMsg(ctx.Errors.Last().Error(), http.StatusBadRequest)
}
func main() {
h := server.Default()
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("store"))
h.Use(sessions.New("csrf-session", store))
h.Use(csrf.New(csrf.WithErrorFunc(myErrFunc)))
h.GET("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, csrf.GetToken(ctx))
})
h.POST("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, "CSRF token is valid")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithKeyLookUp
csrf 中间件提供了 WithKeyLookUp 帮助用户设置 keyLookup。
csrf 用于从 source(支持的 source 包括 header、param、query、form) 中提取 token。
格式为 <source>:<key>,默认值为:header:X-CSRF-TOKEN。
函数签名:
func WithKeyLookUp(lookup string) Option
默认值:header:X-CSRF-TOKEN"
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/csrf"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("store"))
h.Use(sessions.New("csrf-session", store))
h.Use(csrf.New(csrf.WithKeyLookUp("form:csrf")))
h.GET("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, csrf.GetToken(ctx))
})
h.POST("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, "CSRF token is valid")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithNext
csrf 中间件提供了 WithNext 方便用户自定义设置,以在特定条件下跳过 csrf中间件。
函数签名:
func WithNext(f CsrfNextHandler) Option
默认:nil
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/csrf"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func isPostMethod(_ context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) bool {
if string(ctx.Method()) == "POST" {
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
func main() {
h := server.Default()
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("store"))
h.Use(sessions.New("csrf-session", store))
// skip csrf middleware when request method is post
h.Use(csrf.New(csrf.WithNext(isPostMethod)))
h.POST("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, "success even no csrf-token in header")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithExtractor
csrf 中间件提供了 WithExtractor,供用户通过自定义的方法从请求中获取csrf-token。
函数签名:
func WithExtractor(f CsrfExtractorHandler) Option
默认实现:
func CsrfFromHeader(param string) func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) (string, error) {
return func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) (string, error) {
token := c.GetHeader(param)
if string(token) == "" {
return "", errMissingHeader
}
return string(token), nil
}
}
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"errors"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/csrf"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func myExtractor(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) (string, error) {
token := ctx.FormValue("csrf-token")
if token == nil {
return "", errors.New("missing token in form-data")
}
return string(token), nil
}
func main() {
h := server.Default()
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("secret"))
h.Use(sessions.New("csrf-session", store))
h.Use(csrf.New(csrf.WithExtractor(myExtractor)))
h.GET("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, csrf.GetToken(ctx))
})
h.POST("/protected", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(200, "CSRF token is valid")
})
h.Spin()
}
title: “Swagger” date: 2022-10-06 weight: 8 keywords: [“Swagger”, “RESTful API”] description: “用 Swagger 2.0 来自动生成 RESTful API 文档的 Hertz 中间件。”
这是一个用 Swagger 2.0 来自动生成 RESTful API 文档的 Hertz 中间件。
参考了 gin 的 实现,对 Hertz 进行了适配。
使用用法
-
在你的 API 源代码中添加注释,参考 Declarative Comments Format。
-
可以通过运行以下命令下载 Go 对应的 Swag 可执行文件:
但是需要注意的是,go get 安装可执行文件需要配合 GOPATH 模式工作。
go get github.com/swaggo/swag/cmd/swag
因为从 Go 1.17 开始,在 go mod 模式下通过 go get 下载对应库文件将无法自动编译并安装到 $GOPATH/bin 的路径,
所以不再推荐用 go get 来安装可执行文件的方式。可以使用 go install来代替。
go install github.com/swaggo/swag/cmd/swag@latest
- 在你的 Go 项目的根目录下运行 Swag (例如
~/root/go-project-name),Swag 会解析注释并在~/root/go-project-name/docs目录下生成必要的文件 (docs文件夹和docs/doc.go)。
swag init
使用参数运行 Swag (全部参数可以通过运行 swag init -h 查看)。
swag init --parseDependency --parseInternal --parseDepth 5 --instanceName "swagger"
| 选项 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| parseInternal | false | 解析内部依赖包。 |
| parseDependency | false | 解析外部依赖包。 |
| parseDepth | 100 | 解析依赖包深度,如果你知道解析结构的深度,推荐使用这个参数,swag 命令的执行时间会显著减少。 |
| instanceName | “swagger” | swagger 文档的实例名称。如果要在一个 Hertz 路由上部署多个不同的 swagger 实例,请确保每个实例有一个唯一的名字。 |
- 通过运行以下命令在工程中下载 hertz-swagger :
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/swagger
go get github.com/swaggo/files
并在你的代码中引用如下代码:
import "github.com/hertz-contrib/swagger" // hertz-swagger middleware
import "github.com/swaggo/files" // swagger embed files
示例代码
现在假设你已经实现了一个简单的 api,如下所示:
func PingHandler(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(200, map[string]string{
"ping": "pong",
})
}
那么如何在 api 上面使用 hertz-swagger?只要按照下面的步骤即可。
- 使用 hertz-swagger 规则为 api 和主函数添加注释,如下所示:
// PingHandler 测试 handler
// @Summary 测试 Summary
// @Description 测试 Description
// @Accept application/json
// @Produce application/json
// @Router /ping [get]
func PingHandler(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(200, map[string]string{
"ping": "pong",
})
}
-
使用
swag init命令来生成文档,生成的文档将被存储在docs/目录下。 -
将生成的 docs 包导入当前项目中:
假设你的项目名为
github.com/go-project-name/docs。
import (
docs "github.com/go-project-name/docs"
)
-
编译运行你的应用程序,之后在 http://localhost:8888/swagger/index.html,可以看到 Swagger UI 界面。
-
完整的代码和文件依赖关系,如下所示:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/swagger"
_ "github.com/hertz-contrib/swagger/example/basic/docs"
swaggerFiles "github.com/swaggo/files"
)
// PingHandler 测试 handler
// @Summary 测试 Summary
// @Description 测试 Description
// @Accept application/json
// @Produce application/json
// @Router /ping [get]
func PingHandler(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(200, map[string]string{
"ping": "pong",
})
}
// @title HertzTest
// @version 1.0
// @description This is a demo using Hertz.
// @contact.name hertz-contrib
// @contact.url https://github.com/hertz-contrib
// @license.name Apache 2.0
// @license.url http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html
// @host localhost:8888
// @BasePath /
// @schemes http
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.GET("/ping", PingHandler)
url := swagger.URL("http://localhost:8888/swagger/doc.json") // The url pointing to API definition
h.GET("/swagger/*any", swagger.WrapHandler(swaggerFiles.Handler, url))
h.Spin()
}
样例的项目目录结构树如下,swag init 运行在相对的目录 . 下。
.
├── docs
│ ├── docs.go
│ ├── swagger.json
│ └── swagger.yaml
├── go.mod
├── go.sum
└── main.go
支持多个 API
这个功能是在 swag v1.7.9 中引入的。
配置
你可以使用不同的配置选项来配置 Swagger。
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.GET("/ping", PingHandler)
url := swagger.URL("http://localhost:8888/swagger/doc.json") // The url pointing to API definition
h.GET("/swagger/*any", swagger.WrapHandler(swaggerFiles.Handler, url, swagger.DefaultModelsExpandDepth(-1)))
h.Spin()
}
| 选项 | 类型 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| URL | string | “doc.json” | 指向 API 定义的 URL |
| DocExpansion | string | “list” | 控制操作和标签的默认扩展设置。它可以是 list(只展开标签)、full(展开标签和操作)或 none(不展开)。 |
| DeepLinking | bool | true | 如果设置为 true,可以启用标签和操作的深度链接。更多信息请参见深度链接文档。 |
| DefaultModelsExpandDepth | int | 1 | 模型的默认扩展深度(设置为 -1 完全隐藏模型)。 |
| PersistAuthorization | bool | false | 如果设置为 true,则会持久化保存授权数据,在浏览器关闭/刷新时不会丢失。 |
| Oauth2DefaultClientID | string | "” | 如果设置了这个字段,它将用于预填 OAuth2 授权对话框的 client_id 字段。 |
title: “Casbin” date: 2023-02-06 weight: 13 keywords: [“Casbin”, “权限管理”, “访问控制”] description: “针对用户的使用场景,提供 Casbin 中间件,对 Hertz 进行了适配。”
Casbin
是⼀个强⼤的、⾼效的开源访问控制框架,其权限管理机制支持常用的多种 访问控制模型
,如 ACL/RBAC/ABAC 等。可以实现灵活的访问权限控制。
针对用户的使用场景,提供 Casbin 中间件,对 Hertz 进行了适配。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/casbin
导入
import "github.com/hertz-contrib/casbin"
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/casbin"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
// 使用 session 存储用户信息.
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("secret"))
h.Use(sessions.New("session", store))
auth, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddleware("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv", subjectFromSession)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
h.POST("/login", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
// 校验用户名和密码.
// ...
// 存储用户名 (casbin 访问实体)
session := sessions.Default(c)
session.Set("name", "alice")
err := session.Save()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
c.String(200, "you login successfully")
})
h.GET("/book", auth.RequiresPermissions("book:read", casbin.WithLogic(casbin.AND)), func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
})
h.POST("/book", auth.RequiresRoles("user", casbin.WithLogic(casbin.AND)), func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you posted a book successfully")
})
h.Spin()
}
// subjectFromSession 从 session 中获取访问实体.
func subjectFromSession(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) string {
// 获取访问实体
session := sessions.Default(c)
if subject, ok := session.Get("name").(string); !ok {
return ""
} else {
return subject
}
}
配置
Hertz 通过使用 casbin 中间件,为服务端提供了控制用户访问权限的能力。
使用该拓展时,需要先初始化中间件,然后使用中间件方法进行鉴权操作。
初始化中间件
NewCasbinMiddleware
通过提供 Model 和 Policy
相关配置以及 LookupHandler(用于获取访问实体)来初始化中间件,
该函数会根据提供的配置自动初始化 *casbin.Enforcer 用于鉴权操作。
函数签名如下:
func NewCasbinMiddleware(modelFile string, adapter interface{}, lookup LookupHandler) (*Middleware, error)
示例代码:
func exampleLookupHandler(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) string {
// 获取访问实体
session := sessions.Default(c)
if subject, ok := session.Get("name").(string); !ok {
return ""
} else {
return subject
}
}
func main() {
...
casbinMiddleware, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddleware("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv", exampleLookupHandler)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
...
}
NewCasbinMiddlewareFromEnforcer
通过提供 enforcer 以及 LookupHandler(用于获取访问实体)来初始化中间件。
函数签名如下:
func NewCasbinMiddlewareFromEnforcer(e casbin.IEnforcer, lookup LookupHandler) (*Middleware, error)
示例代码:
func exampleLookupHandler(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) string {
// 获取访问实体
session := sessions.Default(c)
if subject, ok := session.Get("name").(string); !ok {
return ""
} else {
return subject
}
}
func main() {
...
enforcer, err := casbinsdk.NewEnforcer("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv")
if err != nil{
log.Fatal(err)
}
casbinMiddleware, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddlewareFromEnforcer(enforcer, exampleLookupHandler)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
...
}
中间件方法
中间件方法用来判断用户的具体权限逻辑。
该中间件的方法参数格式如下:
func (m *Middleware) exampleMiddlwareMethod(expression string, opts ...Option) app.HandlerFunc
其中包含 expression 和 opts 两个参数,
参数说明如下:
-
expression
表达式含有一个或多个变量,变量之间用空格分隔,表达式的具体格式与
Logic(见后文选项说明)相关,表达式的计算最终值为 True or False,True 则代表通过鉴权中间件,False 则代表没有通过鉴权中间件,
如
Logic为 AND or OR,则格式为:"var1 var2 var3 var4",比如"book:read book:write"如
Logic为 CUSTOM,则格式为:"var1 opr1 var2 opr2 var3",比如"book:read && book:write || book:all" -
opts
选项 介绍 默认值 WithLogicLogic是在expression中的逻辑操作 (AND/OR/CUSTOM)ANDWithPermissionParserPermissionParserFunc是用于解析expression中变量得出obj和act的函数PermissionParserWithSeparator(":")WithPermissionParserSeparatorPermissionParserSeparator是用于设置expression中变量内部的分隔符:WithUnauthorizedUnauthorized用于定义未通过授权中间件时的响应体(找不到访问实体)func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) { c.AbortWithStatus(consts.StatusUnauthorized) }WithForbiddenForbidden用于定义访问到禁止访问资源的响应体(访问实体没有相应权限)func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) { c.AbortWithStatus(consts.StatusForbidden) }
RequiresPermissions
寻找访问实体(Subject)及通过方法中提供的参数 expression (表达式中变量说明见下)判断访问实体所含有的权限是否满足 expression 中的权限集合的关系。
expression 中的变量为 Model 中
[request_definition]
r = sub, xxx, xxx
sub 后面的参数集合,
如:
[request_definition]
r = sub, obj, act
使用了默认的 PermissionParser时,expression 中的变量格式应该是:"book:read"。
如:
[request_definition]
r = sub, dom, obj, act
使用了默认的 PermissionParser时,expression 中的变量格式应该是:"book1.com:book:read"。
函数签名如下:
func (m *Middleware) RequiresPermissions(expression string, opts ...Option) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码:
用户只含有 book:read 权限时,
func main(){
...
h := server.Default()
m, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddleware("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv", subjectFromSession)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book:read"), // 通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book:read book:write"), // 不通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
...
}
RequiresRoles
寻找访问实体(Subject)及通过方法中提供的参数 expression(表达式中变量说明见下)判断访问实体所属的角色是否满足 expression
中的角色集合的关系。
expression中的变量为 RBAC 中的 rule 集合
函数签名如下:
func (m *Middleware) RequiresRoles(expression string, opts ...Option) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码:
用户属于 user 和 reader 角色时,
func main(){
...
h := server.Default()
m, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddleware("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv", subjectFromSession)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
h.POST("/book",
auth.RequiresRoles("user"), // 通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you posted a book successfully")
},
)
h.POST("/book",
auth.RequiresRoles("user reader"), // 通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you posted a book successfully")
},
)
h.POST("/book",
auth.RequiresRoles("user reader admin"), // 不通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you posted a book successfully")
},
)
...
}
注意:此方法当且仅当使用了 Casbin 当中基于角色的访问控制模式(即 RBAC)时使用。
选项说明
WithLogic
Logic 是在 expression 中的逻辑操作 (AND/OR/CUSTOM) 。
函数签名:
func WithLogic(logic Logic) Option
选项:
const (
AND Logic = iota
OR
CUSTOM
)
AND
expression 中的所有变量进行逻辑与操作。
示例代码:
用户只含有 book:read 权限时,
func main(){
...
h := server.Default()
m, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddleware("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv", subjectFromSession)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book:read", casbin.WithLogic(casbin.AND)), // 通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book:read book:write", casbin.WithLogic(casbin.AND)), // 不通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
...
}
OR
expression 中的所有变量进行逻辑或操作
示例代码:
用户只含有 book:read 权限时,
func main(){
...
h := server.Default()
m, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddleware("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv", subjectFromSession)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book:read", casbin.WithLogic(casbin.OR)), // 通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book:read book:and", casbin.WithLogic(casbin.OR)), // 通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
...
}
CUSTOM
expression 为类 C 表达式。
注意:
使用该模式时,不可使用选项 WithPermissionParser
(执行鉴权逻辑时会产生不可预期的错误),如有定义解析权限字符串之类的需求,建议使用选项 WithPermissionParserSeparator。
示例代码:
用户只含有 book:read 权限时,
func main(){
...
h := server.Default()
m, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddleware("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv", subjectFromSession)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book:read", casbin.WithLogic(casbin.CUSTOM)), // 通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book:read && book:write", casbin.WithLogic(casbin.CUSTOM)), // 不通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book:read || book:write", casbin.WithLogic(casbin.CUSTOM)), // 通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("!book:read", casbin.WithLogic(casbin.CUSTOM)), // 不通过
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
...
}
WithPermissionParser
PermissionParserFunc 是用于解析 RequiresPermissions 方法中 expression 的变量的函数。
函数签名:
func WithPermissionParser(pp PermissionParserFunc) Option
示例代码:
func main(){
...
h := server.Default()
m, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddleware("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv", subjectFromSession)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book-read",
casbin.WithPermissionParser(func(str string) []string {
return strings.Split(str, "-")
}),
),
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
...
}
WithPermissionParserSeparator
PermissionParserSeparator 是用于设置 expression 中变量内部的分隔符。
函数签名:
func WithPermissionParserSeparator(sep string) Option
示例代码:
func main(){
...
h := server.Default()
m, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddleware("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv", subjectFromSession)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book-read",
casbin.WithPermissionParserSeparator("-"),
),
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
...
}
WithUnauthorized
Unauthorized 用于定义未通过授权中间件时的响应体(找不到访问实体,即 LookupHandler 返回的结果为空)。
函数签名:
func WithUnauthorized(u app.HandlerFunc) Option
示例代码:
func main(){
...
h := server.Default()
m, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddleware("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv", subjectFromSession)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book:read",
casbin.WithUnauthorized(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.AbortWithStatus(consts.StatusUnauthorized)
}),
),
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
...
}
WithForbidden
Forbidden 用于定义访问到禁止访问资源的响应体(访问实体没有相应权限)。
函数签名:
func WithForbidden(f app.HandlerFunc) Option
示例代码:
func main(){
...
h := server.Default()
m, err := casbin.NewCasbinMiddleware("example/config/model.conf", "example/config/policy.csv", subjectFromSession)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
h.GET("/book",
m.RequiresPermissions("book:read",
casbin.WithForbidden(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.AbortWithStatus(consts.StatusForbidden)
}),
),
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "you read the book successfully")
},
)
...
}
title: “Gzip 压缩” date: 2022-09-01 weight: 4 keywords: [“Gzip”, “压缩”] description: “Hertz 提供了 Gzip 的实现。”
在 HTTP 中,GNUzip(Gzip) 压缩编码是一种用来优化 Web 应用程序性能的方式,并且 Hertz 也提供了 Gzip 的 实现 。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/gzip
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/gzip"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.Use(gzip.Gzip(gzip.DefaultCompression))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong "+fmt.Sprint(time.Now().Unix()))
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
Gzip
Gzip提供了四种压缩选项:BestCompression,BestSpeed,DefaultCompression,NoCompression 用于用户自定义压缩模式
| 选项 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| BestCompression | 提供最佳的文件压缩率 |
| BestSpeed | 提供了最佳的压缩速度 |
| DefaultCompression | 默认压缩率 |
| NoCompression | 不进行压缩 |
函数签名如下:
func Gzip(level int, options ...Option) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码如下:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/gzip"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
// BestCompression option
h.Use(gzip.Gzip(gzip.BestCompression))
// BestSpeed option
h.Use(gzip.Gzip(gzip.BestSpeed))
// DefaultCompression option
h.Use(gzip.Gzip(gzip.DefaultCompression))
// NoCompression option
h.Use(gzip.Gzip(gzip.NoCompression))
h.GET("/api/book", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong "+fmt.Sprint(time.Now().Unix()))
})
h.Spin()
}
WithExcludedExtensions
gzip 提供 WithExcludeExtensions 用于帮助用户设置不需要 gzip 压缩的文件后缀,默认值为.png, .gif, .jpeg, .jpg
函数签名如下:
func WithExcludedPaths(args []string) Option
示例代码如下:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/gzip"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.Use(
gzip.Gzip(
gzip.DefaultCompression,
gzip.WithExcludedExtensions([]string{".pdf", ".mp4"}),
),
)
h.GET("/api/book", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong "+fmt.Sprint(time.Now().Unix()))
})
h.Spin()
}
WithExcludedPaths
gzip 提供了 WithExcludedPaths用于帮助用户设置其不需要进行 gzip 压缩的文件路径
函数签名如下:
func WithExcludedPaths(args []string) Option
示例代码如下:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/gzip"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.Use(
gzip.Gzip(
gzip.DefaultCompression,
// This WithExcludedPaths takes as its parameter the file path
gzip.WithExcludedPaths([]string{"/api/"}),
),
)
// This is No compression
h.GET("/api/book", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong "+fmt.Sprint(time.Now().Unix()))
})
// This is the compressed
h.GET("/book", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong "+fmt.Sprint(time.Now().Unix()))
})
h.Spin()
}
WithExcludedPathRegexes
gzip 提供了WithExcludedPathRegexes用于帮助用户设置自定义的正则表达式来过滤掉不需要 gzip 压缩的文件
函数签名如下:
func WithExcludedPathRegexes(args []string) Option
示例代码如下:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/gzip"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
h.Use(
gzip.Gzip(
gzip.DefaultCompression,
// This WithExcludedPathRegexes takes as an argument a regular expression that describes the path to be excluded
gzip.WithExcludedPathRegexes([]string{"/api.*"}),
),
)
// This is No compression
h.GET("/api/book", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong "+fmt.Sprint(time.Now().Unix()))
})
// This is the compressed
h.GET("/book", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong "+fmt.Sprint(time.Now().Unix()))
})
h.Spin()
}
更多用法示例详见 gzip
title: “Cache” date: 2023-02-25 weight: 15 keywords: [“HTTP响应”, “缓存”] description: “Hertz 提供了对 cache 的适配,支持 multi-backend。”
cache 是一个用于缓存 HTTP 响应的中间件,开启后有助于提高服务器的并发访问能力。Hertz 也提供了对 cache 的 适配,支持 multi-backend,参考了 gin-cache 的实现。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/cache
导入
import "github.com/hertz-contrib/cache"
示例代码
- memory
func main() {
h := server.New()
// 设置全局的缓存过期时间(会被更细粒度的设置覆盖)
memoryStore := persist.NewMemoryStore(1 * time.Minute)
// 设置针对以 URI 为 Key 的缓存过期时间
h.Use(cache.NewCacheByRequestURI(memoryStore, 2*time.Second))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
- redis
func main() {
h := server.New()
redisStore := persist.NewRedisStore(redis.NewClient(&redis.Options{
Network: "tcp",
Addr: "127.0.0.1:6379",
}))
h.Use(cache.NewCacheByRequestURI(redisStore, 2*time.Second))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
初始化
cache 中间件提供了三种初始化的方式。
NewCacheByRequestURI
用于创建以 URI 为 Key 的缓存响应结果的中间件。
函数签名:
func NewCacheByRequestURI(defaultCacheStore persist.CacheStore, defaultExpire time.Duration, opts ...Option) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
memoryStore := persist.NewMemoryStore(1 * time.Minute)
h.Use(cache.NewCacheByRequestURI(memoryStore, 2*time.Second))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
NewCacheByRequestPath
用于创建以 URL 为 Key 的缓存响应结果的中间件,丢弃 query 参数。
函数签名:
func NewCacheByRequestPath(defaultCacheStore persist.CacheStore, defaultExpire time.Duration, opts ...Option) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
memoryStore := persist.NewMemoryStore(1 * time.Minute)
h.Use(cache.NewCacheByRequestPath(memoryStore, 2*time.Second))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
NewCache
用于创建自定义缓存逻辑的中间件,必须手动声明缓存的 Key(需要使用 WithCacheStrategyByRequest 配置参数)。
函数签名:
func NewCache(
defaultCacheStore persist.CacheStore,
defaultExpire time.Duration,
opts ...Option,
) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
memoryStore := persist.NewMemoryStore(1 * time.Minute)
h.Use(cache.NewCache(
memoryStore,
2*time.Second,
cache.WithCacheStrategyByRequest(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) (bool, cache.Strategy) {
return true, cache.Strategy{
CacheKey: c.Request.URI().String(),
}
}),
))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
| 配置 | 默认值 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| WithCacheStrategyByRequest | nil | 用于设置自定义的缓存策略 |
| WithOnHitCache | nil | 用于设置缓存命中的回调函数 |
| WithOnMissCache | nil | 用于设置缓存未命中的回调函数 |
| WithBeforeReplyWithCache | nil | 用于设置返回缓存响应前的回调函数 |
| WithOnShareSingleFlight | nil | 用于设置请求共享 SingleFlight 结果时的回调函数 |
| WithSingleFlightForgetTimeout | 0 | 用于设置 SingleFlight 的超时时间 |
| WithIgnoreQueryOrder | false | 用于设置当使用 URI 为缓存的 Key 时,忽略 query 参数的顺序 |
| WithPrefixKey | "" | 用于设置缓存响应 Key 的前缀 |
| WithoutHeader | false | 用于设置是否需要缓存响应头 |
WithCacheStrategyByRequest
通过使用 WithCacheStrategyByRequest 自定义缓存策略,包括缓存的 Key、存储介质,以及过期时间。
该配置生效的前提是,通过 cache.NewCache 方法初始化 cache 中间件。
函数签名:
func WithCacheStrategyByRequest(getGetCacheStrategyByRequest GetCacheStrategyByRequest) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
memoryStore := persist.NewMemoryStore(1 * time.Minute)
h.Use(cache.NewCache(
memoryStore,
2*time.Second,
cache.WithCacheStrategyByRequest(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) (bool, cache.Strategy) {
return true, cache.Strategy{
CacheKey: c.Request.URI().String(),
}
}),
))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithOnHitCache & WithOnMissCache
通过使用 WithOnHitCache 设置缓存命中的回调函数。
通过使用 WithOnMissCache 设置缓存未命中的回调函数。
函数签名:
func WithOnHitCache(cb OnHitCacheCallback) Option
func WithOnMissCache(cb OnMissCacheCallback) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
memoryStore := persist.NewMemoryStore(1 * time.Minute)
var cacheHitCount, cacheMissCount int32
h.Use(cache.NewCacheByRequestURI(
memoryStore,
2*time.Second,
cache.WithOnHitCache(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
atomic.AddInt32(&cacheHitCount, 1)
}),
cache.WithOnMissCache(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
atomic.AddInt32(&cacheMissCount, 1)
}),
))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.GET("/get_hit_count", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, fmt.Sprintf("total hit count: %d", cacheHitCount))
})
h.GET("/get_miss_count", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, fmt.Sprintf("total miss count: %d", cacheMissCount))
})
h.Spin()
}
WithBeforeReplyWithCache
通过使用 WithBeforeReplyWithCache 设置返回缓存响应前的回调函数。
函数签名:
func WithBeforeReplyWithCache(cb BeforeReplyWithCacheCallback) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
memoryStore := persist.NewMemoryStore(1 * time.Minute)
h.Use(cache.NewCacheByRequestURI(
memoryStore,
2*time.Second,
cache.WithBeforeReplyWithCache(func(c *app.RequestContext, cache *cache.ResponseCache) {
cache.Data = append([]byte{'p', 'r', 'e', 'f', 'i', 'x', '-'}, cache.Data...)
}),
))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithOnShareSingleFlight & WithSingleFlightForgetTimeout
通过使用 WithOnShareSingleFlight 设置请求共享 SingleFlight 结果时的回调函数。
通过使用 WithSingleFlightForgetTimeout 设置 SingleFlight 的超时时间。
函数签名:
func WithOnShareSingleFlight(cb OnShareSingleFlightCallback) Option
func WithSingleFlightForgetTimeout(forgetTimeout time.Duration) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
memoryStore := persist.NewMemoryStore(1 * time.Minute)
h.Use(cache.NewCacheByRequestPath(
memoryStore,
10*time.Second,
cache.WithOnShareSingleFlight(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
hlog.Info("share the singleFlight result " + string(c.Response.Body()))
}),
cache.WithSingleFlightForgetTimeout(1*time.Second),
))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
time.Sleep(3 * time.Second)
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithIgnoreQueryOrder
通过使用 WithIgnoreQueryOrder 设置当使用 NewCacheByRequestURI 方法创建缓存中间件时,忽略 URI 的 query 参数顺序(为
true 触发参数排序)。
函数签名:
func WithIgnoreQueryOrder(b bool) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
memoryStore := persist.NewMemoryStore(1 * time.Minute)
h.Use(cache.NewCacheByRequestPath(
memoryStore,
60*time.Second,
cache.WithIgnoreQueryOrder(true),
cache.WithOnHitCache(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
hlog.Infof("hit cache IgnoreQueryOrder")
}),
cache.WithOnMissCache(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
hlog.Infof("miss cache IgnoreQueryOrder")
}),
))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithPrefixKey
通过使用 WithPrefixKey 设置响应 Key 的前缀。
函数签名:
func WithPrefixKey(prefix string) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
memoryStore := persist.NewMemoryStore(1 * time.Minute)
h.Use(cache.NewCache(
memoryStore,
60*time.Second,
cache.WithPrefixKey("prefix-"),
cache.WithOnHitCache(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
resp := &cache.ResponseCache{}
memoryStore.Get(c, "prefix-test", &resp)
hlog.Info("data = " + string(resp.Data))
}),
cache.WithCacheStrategyByRequest(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) (bool, cache.Strategy) {
return true, cache.Strategy{
CacheKey: "test",
}
}),
))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithoutHeader
通过使用 WithoutHeader 设置是否需要缓存响应头,为 false 则缓存响应头。
函数签名:
func WithoutHeader(b bool) Option
示例代码:
func main() {
h := server.New()
memoryStore := persist.NewMemoryStore(1 * time.Minute)
h.Use(cache.NewCache(
memoryStore,
60*time.Second,
cache.WithoutHeader(true),
cache.WithCacheStrategyByRequest(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) (bool, cache.Strategy) {
return true, cache.Strategy{
CacheKey: "test-key",
}
}),
cache.WithOnHitCache(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
resp := &cache.ResponseCache{}
memoryStore.Get(c, "test-key", &resp)
hlog.Info("header = " + string(resp.Header.Get("head")))
hlog.Info("data = " + string(resp.Data))
}),
))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")
})
h.Spin()
}
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 cache/example
title: “Session 扩展” date: 2022-10-07 weight: 6 keywords: [“Session”] description: “Hertz 提供了 Session 的实现。”
Session 是服务器为了保存用户状态而创建的一种特殊的对象。
Hertz 也提供了 Session 的 实现,它参考了 Gin 的 实现。
安装
下载并安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions
导入
import "github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8000"))
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("secret"))
h.Use(sessions.New("mysession", store))
h.GET("/incr", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
session := sessions.Default(c)
var count int
v := session.Get("count")
if v != nil {
count = v.(int)
count++
}
session.Set("count", count)
_ = session.Save()
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"count": count})
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
Hertz 通过使用中间件,可以对 Session 进行一系列的操作配置。其中 Session 接口定义了对 Session 操作配置的主要方法,接口方法的介绍如下:
注意: Session 接口对 gorilla-session 的方法进行了简单封装。
| 方法 | 函数签名 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| ID | ID() string |
用于获取存储时生成的 Session ID,它不应该作为用户信息的一部分去使用 |
| Get | Get(key interface{}) interface{} |
用于根据给定的键值参数获取 Session 值 |
| Set | Set(key, val interface{}) |
用于设置与给定键值相关联的 Session 值 |
| Delete | Delete(key interface{}) |
用于根据给定的键值删除相关联的 Session 值 |
| Clear | Clear() |
用于删除 Session 中存储的所有值 |
| AddFlash | AddFlash(value interface{}, vars ...string) |
用于向 Session 添加一条 flash message |
| Flashes | Flashes(vars ...string) []interface{} |
用于获取 Session 中的 flash message |
| Options | Options(Options) |
用于设置 Session 的配置 |
| Save | Save() error |
用于保存当前请求期间使用的所有会话 |
NewStore
sessions 中间件提供了 NewStore 用于将 Session 存储在 Cookie 或者 Redis 中。
Cookie
函数签名:
func NewStore(keyPairs ...[]byte) Store
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8000"))
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("secret"))
h.Use(sessions.New("mysession", store))
h.GET("/incr", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
session := sessions.Default(c)
var count int
v := session.Get("count")
if v == nil {
count = 0
} else {
count = v.(int)
count++
}
session.Set("count", count)
_ = session.Save()
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"count": count})
})
h.Spin()
}
Redis
函数签名:
func NewStore(size int, network, addr, passwd string, keyPairs ...[]byte) (Store, error)
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/redis"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8000"))
store, _ := redis.NewStore(10, "tcp", "localhost:6379", "", []byte("secret"))
h.Use(sessions.New("mysession", store))
h.GET("/incr", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
session := sessions.Default(c)
var count int
v := session.Get("count")
if v == nil {
count = 0
} else {
count = v.(int)
count++
}
session.Set("count", count)
session.Save()
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"count": count})
})
h.Spin()
}
New
sessions 中间件提供了 New 用于创建单个 Session。
函数签名:
func New(name string, store Store) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8000"))
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("secret"))
h.Use(sessions.New("mysession", store))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
session := sessions.Default(c)
if session.Get("hello") != "world" {
session.Set("hello", "world")
_ = session.Save()
}
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"hello": session.Get("hello")})
})
h.Spin()
}
Many
sessions 中间件提供了 Many 用于创建多个 Session。
函数签名:
func Many(names []string, store Store) app.HandlerFunc
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8000"))
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("secret"))
sessionNames := []string{"a", "b"}
h.Use(sessions.Many(sessionNames, store))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
sessionA := sessions.DefaultMany(c, "a")
sessionB := sessions.DefaultMany(c, "b")
if sessionA.Get("hello") != "world!" {
sessionA.Set("hello", "world!")
_ = sessionA.Save()
}
if sessionB.Get("hello") != "world?" {
sessionB.Set("hello", "world?")
_ = sessionB.Save()
}
c.JSON(200, utils.H{
"a": sessionA.Get("hello"),
"b": sessionB.Get("hello"),
})
})
h.Spin()
}
Default
sessions 中间件提供了 Default 用于获取单个 Session 对象。
函数签名:
func Default(c *app.RequestContext) Session
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8000"))
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("secret"))
h.Use(sessions.New("mysession", store))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
session := sessions.Default(c)
if session.Get("hello") != "world" {
session.Set("hello", "world")
_ = session.Save()
}
c.JSON(200, utils.H{"hello": session.Get("hello")})
})
h.Spin()
}
DefaultMany
sessions 中间件提供了 DefaultMany 用于根据 Session 名获取对应的 Session 对象。
函数签名:
func DefaultMany(c *app.RequestContext, name string) Session
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sessions/cookie"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8000"))
store := cookie.NewStore([]byte("secret"))
sessionNames := []string{"a", "b"}
h.Use(sessions.Many(sessionNames, store))
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
sessionA := sessions.DefaultMany(c, "a")
sessionB := sessions.DefaultMany(c, "b")
if sessionA.Get("hello") != "world!" {
sessionA.Set("hello", "world!")
_ = sessionA.Save()
}
if sessionB.Get("hello") != "world?" {
sessionB.Set("hello", "world?")
_ = sessionB.Save()
}
c.JSON(200, utils.H{
"a": sessionA.Get("hello"),
"b": sessionB.Get("hello"),
})
})
h.Spin()
}
分布式 Session
Hertz 也提供了基于 Redis 的分布式 Session 解决方案的 bizdemo。
注意:这只是对分布式 Session 功能的简单演示,具体业务代码需用户结合对应的业务逻辑做出相应修改
基于 Redis 的分布式 Session 解决方案是指将不同服务器的 Session 统一存储在 Redis 或 Redis 集群中,旨在解决分布式系统下多个服务器的 Session 不同步的问题。
核心代码展示
- Session 中间件初始化:
// biz/mw/session.go
func InitSession(h *server.Hertz) {
store, err := redis.NewStore(consts.MaxIdleNum, consts.TCP, consts.RedisAddr, consts.RedisPasswd, []byte(consts.SessionSecretKey))
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
h.Use(sessions.New(consts.HertzSession, store))
}
- 用户登录后存储 Session:
// biz/handler/user/user_service.go/Login
// ...
session := sessions.Default(c)
session.Set(consts.Username, req.Username)
_ = session.Save()
// ...
- 用户直接访问主页时判断是否存在对应 Session,不存在则重定向到登录页面(本例)或者限制登录后才可以进行浏览或使用的资源:
// pkg/render/render.go
// ...
session := sessions.Default(c)
username := session.Get(consts.Username)
if username == nil {
// ...
c.Redirect(http.StatusMovedPermanently, []byte("/login.html"))
return
}
// ...
- 用户登出后清理 Session:
// biz/handler/user/user_service.go/Logout
// ...
session := sessions.Default(c)
session.Delete(consts.Username)
_ = session.Save()
// ...
Session 中间件对大多数复杂的逻辑进行了封装,用户只需要调用简单的接口即可完成对应的业务流程。
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 example 以及 hertz_session
title: “KeyAuth”
date: 2022-09-22
weight: 7
keywords: [“KeyAuth”, “token 鉴权”]
description: “Hertz 提供了 keyauth 扩展用于帮助用户实现 token 鉴权。”
Hertz 提供了 keyauth 扩展用于帮助用户实现 token
鉴权。 keyauth 扩展的实现参考了 Fiber
和 Echo 的实现。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/keyauth
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/keyauth"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(keyauth.New(
keyauth.WithContextKey("token"),
keyauth.WithKeyLookUp("query:token", ""),
))
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
value, _ := ctx.Get("token")
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": value})
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
WithFilter
keyauth 扩展提供了 WithFilter 用于帮助用户设置自定义过滤逻辑用于跳过 keyauth扩展,默认为 nil,不跳过。
Filter 函数签名如下:
type KeyAuthFilterHandler func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) bool
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/keyauth"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(keyauth.New(
keyauth.WithFilter(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) bool {
return string(ctx.GetHeader("admin")) == "test"
}),
))
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
value, _ := ctx.Get("token")
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": value})
})
h.Spin()
}
WithValidator
keyauth 扩展提供了 WithValidator 用于帮助用户设置自定义的校验逻辑用于 token 校验,默认返回 true 和 nil。
Validator 函数签名如下:
type KeyAuthValidatorHandler func(context.Context, *app.RequestContext, string) (bool, error)
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/keyauth"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(keyauth.New(
keyauth.WithValidator(func(ctx context.Context, requestContext *app.RequestContext, s string) (bool, error) {
if s == "test_admin" {
return true, nil
}
return false, nil
}),
))
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
value, _ := ctx.Get("token")
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": value})
})
h.Spin()
}
WithSuccessHandler
keyauth 扩展提供了 WithSuccessHandler 用于帮助用户设置校验 token 通过的自定义处理逻辑。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/keyauth"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(keyauth.New(
keyauth.WithSuccessHandler(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Next(c)
}),
))
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
value, _ := ctx.Get("token")
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": value})
})
h.Spin()
}
WithErrorHandler
keyauth 扩展提供了 WithErrorHandler 用于帮助用户设置校验 token 失败的自定义处理逻辑。
ErrorHandler 函数签名如下:
type KeyAuthErrorHandler func(context.Context, *app.RequestContext, error)
默认处理逻辑如下:
func errHandler(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext, err error) {
if err == ErrMissingOrMalformedAPIKey {
ctx.AbortWithMsg(err.Error(), http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
ctx.AbortWithMsg(err.Error(), http.StatusUnauthorized)
}
WithKeyLookUp
keyauth 扩展提供了 WithKeyLookUp 帮助用户设置 keyLookup。
keyLookup 用于从 source(支持的 source 包括 cookie、header、param、query、form) 中提取 token。
格式为 <source>:<token_name>,默认值为:header:Authorization。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/keyauth"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(keyauth.New(
keyauth.WithKeyLookUp("header:token", "Bearer"),
))
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
value, _ := ctx.Get("token")
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": value})
})
h.Spin()
}
WithContextKey
keyauth 扩展提供了 WithContextKey 用于帮助用户设置存储在请求上下文的 token 对应的 key。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/keyauth"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(keyauth.New(
keyauth.WithContextKey("token"),
))
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
value, _ := ctx.Get("token")
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": value})
})
h.Spin()
}
title: “ETag”
date: 2023-02-11
weight: 14
keywords: [“ETag”]
description: “Hertz 提供了可以对 ETag 进行操作的 ETag 中间件。”
ETag HTTP 响应头是资源的特定版本的标识符。这可以让缓存更高效,并节省带宽,因为如果内容没有改变,Web
服务器不需要发送完整的响应。而如果内容发生了变化,使用 ETag 有助于防止资源的同时更新相互覆盖(“空中碰撞”)。
Hertz 也提供了可以对 ETag 进行操作的 ETag 中间件,参考了 fiber
的 实现。
安装
下载并安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/etag
导入
import "github.com/hertz-contrib/etag"
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"net/http"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/etag"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(etag.New())
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong")
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
| 配置 | 默认值 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| WithWeak | false | 使用弱验证器 |
| WithNext | nil | 定义一个 Next 函数,当返回值为 true 时跳过 etag 中间件 |
| WithGenerator | nil | 自定义 ETag 生成逻辑 |
WithWeak
etag 中间件提供了 WithWeak,用于使用弱验证器。
函数签名:
func WithWeak() Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"net/http"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/etag"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(etag.New(etag.WithWeak()))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithNext
etag 中间件提供了 WithNext,当定义的 Next 函数返回值为 true 时,跳过 etag 中间件。
函数签名:
func WithNext(next NextFunc) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"net/http"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/etag"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(etag.New(etag.WithNext(
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) bool {
if string(c.Method()) == http.MethodPost {
return true
} else {
return false
}
},
)))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithGenerator
etag 中间件提供 WithGenerator,以供用户自定义 ETag 的生成逻辑。
注意:当与 WithWeak 一起使用时,不应该在你的自定义 ETag 前添加 W/ 前缀。
函数签名:
func WithGenerator(gen Generator) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"net/http"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/etag"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.Use(etag.New(etag.WithGenerator(
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) []byte {
return []byte("my-custom-etag")
},
)))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "pong")
})
h.Spin()
}
完整示例
完整用法示例详见 etag/example
title: “Secure” date: 2022-11-06 weight: 10 keywords: [“Secure”, “访问请求安全”] description: “Secure 是 Hertz 的一个 HTTP 中间件 , 它可以通过检查 HTTP 请求以达到快速的保证访问请求安全。”
Secure 是 Hertz 的一个 HTTP 中间件 , 它可以通过检查 HTTP 请求以达到快速的保证访问请求安全 (secure), 并且 Secure 中间件不仅提供了默认的基础配置,还提供了大量的自定义配置选项可供选择。
本 中间件 参考了 gin-contrib/secure 的实现。
安装
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/secure
在工程中引入
import "github.com/hertz-contrib/secure"
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/secure"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
// use default config
h.Use(secure.New())
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "pong")
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
使用须知
Secure 所提供的配置项是为了简化一些常见的 HTTP headers 的配置,如对配置项配置 HTTP headers 的作用感到困惑,可以自行在 MDN Docs 中进行查询它们的作用
New
Secure 提供 New() 函数用于将 Secure 集成进入 Hertz。默认配置如下所示
| 配置函数 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| WithSSLRedirect | WithSSLRedirect 设置为 true, 则将只允许 https 请求访问 |
true |
| WithIsDevelopment | 如果 WithIsDevelopment 设置为 true, 则中间件应用的整个安全策略将被完全禁用 |
false |
| WithSTSSecond | WithSTSSecond 用于设置 Strict-Transport-Security 的 max-age 的秒数 (second) |
315360000 |
| WithFrameDeny | WithFrameDeny 用于设置 X-Frame-Options 中的值,为 true 则设置值为 DENY |
true |
| WithContentTypeNosniff | 如果 WithContentTypeNosniff 设置为 true, 则在 X-Content-Type-Options 中 添加 nosniff 值 |
true |
| WithBrowserXssFilter | 如果 WithBrowserXssFilter 设置为 true, 则添加在 X-XSS-Protection 头中添加 1; mode=block 的值 |
true |
| WithContentSecurityPolicy | WithContentSecurityPolicy 用于配置 Content-Security-Policy 中的策略 |
“default-src ‘self’” |
| WithIENoOpen | WithIENoOpen 用于防止 Internet Explorer 在网站的中执行下载任务,默认设置为 true, 即阻止下载 |
true |
| WIthSSLProxyHeaders | WIthSSLProxyHeaders 用于设置 request headers map。若请求是不安全的,就将请求头的信息和 request headers map 中的信息进行匹配。如果匹配到了相应的值,就把该请求视为安全的请求 |
map[string]string{“X-Forwarded-Proto”: “https”} |
当然,除了这些默认的配置项,我们还有其他的配置项在后续介绍
WithAllowHosts
WithAllowHosts 用于设置一个允许访问的完全合格域名的白名单,该名单默认为默认为空列表,允许任何和所有的主机名称
函数签名:
func WithAllowedHosts(ss []string) Option
WithSSLTemporaryRedirect
WithSSLTemporaryRedirect 在设置为 true 时,在重定向时将使用 302 状态码 (StatusFound)。否则使用 301 (
StatusMovedPermanently)
函数签名:
func WithSSLTemporaryRedirect(b bool) Option
WithSSLHost
WithSSLHost 用于设置将 http 请求重定向到 https 的主机名,默认为 "" 表示使用同一个主机名
函数签名:
func WithSSLHost(s string) Option
WithSTSIncludeSubdomains
WithSTSIncludeSubdomains 设置为 true 时,将会在 Strict-Transport-Security 中填入 includeSubdomains 的值,默认值为
false
函数签名:
func WithSTSIncludeSubdomains(b bool) Option
WithCustomFrameOptionsValue
使用 WithCustomFrameOptionsValue 可以在 X-Frame-Options 中填入自定义的值
注意:
这一设置将会覆盖上文提到的 WithFrameDeny 的设置
函数签名:
func WithCustomFrameOptionsValue(s string) Option
WithReferrerPolicy
WithReferrerPolicy 用于设置 Referrer-Policy 中的策略,Referrer-Policy 监管的访问来源信息应当包含在生成的请求之中
函数签名:
func WithReferrerPolicy(s string) Option
WithBadHostHandler
WithBadHostHandler 用于设置在请求发生错误时的处理逻辑,默认返回 403 (StatusForbidden) 状态码
函数签名:
func WithBadHostHandler(handler app.HandlerFunc) Option
示例:
package main
import (
"context"
"net/http"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/secure"
)
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.Use(secure.New(
secure.WithAllowedHosts([]string{"example.com"}),
secure.WithSSLHost("example.com"),
// 如果在启动服务器后访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/ping, 就可以看到效果
secure.WithBadHostHandler(func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(http.StatusForbidden, utils.H{
"message": "this is a custom Bad Host Handler!",
})
}),
))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(200, "pong")
})
h.Spin()
}
WithFeaturePolicy
WithFeaturePolicy 用于设置 Feature-Policy 的策略
函数签名:
func WithFeaturePolicy(s string) Option
WithDontRedirectIPV4Hostnames
WithDontRedirectIPV4Hostnames 设置为 true 时,那么对 IPV4 地址的主机名的请求就不会被重定向。这项配置为了让类似
Loadbalancer 的设置健康检查成功。
函数签名:
func WithDontRedirectIPV4Hostnames(b bool) Option
title: “中间件概览” date: 2022-05-20 weight: 6 keywords: [“中间件”, “服务端中间件”, “客户端中间件”, “路由级别”] description: “中间件概览。”
Hertz中间件的种类是多种多样的,简单分为两大类:
- 服务端中间件
- 客户端中间件
服务端中间件
Hertz 服务端中间件是 HTTP 请求-响应周期中的一个函数,提供了一种方便的机制来检查和过滤进入应用程序的 HTTP 请求, 例如记录每个请求或者启用CORS。
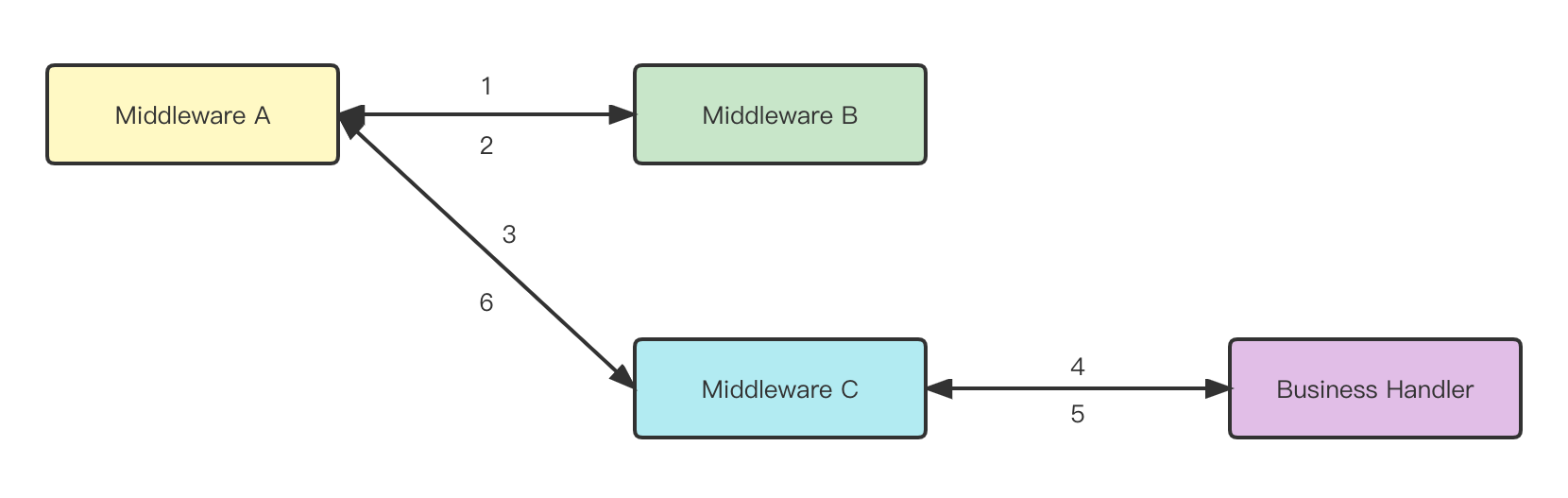 |
|---|
| 图1:中间件调用链 |
中间件可以在请求更深入地传递到业务逻辑之前或之后执行:
- 中间件可以在请求到达业务逻辑之前执行,比如执行身份认证和权限认证,当中间件只有初始化(pre-handle)相关逻辑,且没有和 real
handler 在一个函数调用栈中的需求时,中间件中可以省略掉最后的
.Next,如图1的中间件 B。 - 中间件也可以在执行过业务逻辑之后执行,比如记录响应时间和从异常中恢复。如果在业务 handler 处理之后有其它处理逻辑(
post-handle ),或对函数调用链(栈)有强需求,则必须显式调用
.Next,如图1的中间件 C。
实现一个中间件
// 方式一
func MyMiddleware() app.HandlerFunc {
return func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
// pre-handle
// ...
c.Next(ctx)
}
}
// 方式二
func MyMiddleware() app.HandlerFunc {
return func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.Next(ctx) // call the next middleware(handler)
// post-handle
// ...
}
}
Server 级别中间件
Server 级别中间件会对整个server的路由生效
h := server.Default()
h.Use(GlobalMiddleware())
路由组级别中间件
路由组级别中间件对当前路由组下的路径生效
h := server.Default()
group := h.Group("/group")
group.Use(GroupMiddleware())
或者
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
func GroupMiddleware() []app.HandlerFunc {
return []app.HandlerFunc{func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
fmt.Println("group middleware")
c.Next(ctx)
}}
}
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8888"))
group := h.Group("/group", append(GroupMiddleware(),
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
fmt.Println("group middleware 2")
c.Next(ctx)
})...)
// ...
h.Spin()
}
单一路由级别中间件
单一路由级别中间件只对当前路径生效
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
func PathMiddleware() []app.HandlerFunc {
return []app.HandlerFunc{func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
fmt.Println("path middleware")
c.Next(ctx)
}}
}
func main() {
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8888"))
h.GET("/path", append(PathMiddleware(),
func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "path")
})...)
h.Spin()
}
如果你使用hz工具和IDL开发项目、router文件夹下会自动根据服务和方法生成路由组中间件和单一方法中间件模板,你可以在其中添加相应的逻辑,定制自己的个性化中间件。
使用默认中间件
Hertz 框架已经预置了常用的 recover 中间件,使用 server.Default() 默认可以注册该中间件。
常用中间件
Hertz 提供了常用的 BasicAuth、CORS、JWT等中间件,更多实现可以在 hertz-contrib 查找,其他中间件如有需求,可提 issue 告诉我们。
客户端中间件
客户端中间件可以在请求发出之前或获取响应之后执行:
- 中间件可以在请求发出之前执行,比如统一为请求添加签名或其他字段。
- 中间件也可以在收到响应之后执行,比如统一修改响应结果适配业务逻辑。
实现一个中间件
客户端中间件实现和服务端中间件不同。Client 侧无法拿到中间件 index 实现递增,因此 Client 中间件采用提前构建嵌套函数的形式实现,在实现一个中间件时,可以参考下面的代码。
func MyMiddleware(next client.Endpoint) client.Endpoint {
return func(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response) (err error) {
// pre-handle
// ...
err = next(ctx, req, resp)
if err != nil {
return
}
// post-handle
// ...
}
}
注意:必须执行
next方法才能继续调用后续中间件。如果想停止中间件调用,在next之前返回就可以了。
注册一个中间件
注册中间件的方式和 Server 相同
c, err := client.NewClient()
c.Use(MyMiddleware)
完整示例
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
)
func MyMiddleware(next client.Endpoint) client.Endpoint {
return func(ctx context.Context, req *protocol.Request, resp *protocol.Response) (err error) {
// pre-handle
// ...
fmt.Println("before request")
req.AppendBodyString("k1=v1&")
err = next(ctx, req, resp)
if err != nil {
return
}
// post-handle
// ...
fmt.Println("after request")
return nil
}
}
func main() {
client, _ := client.NewClient()
client.Use(MyMiddleware)
statusCode, body, err := client.Post(context.Background(),
[]byte{},
"http://httpbin.org/redirect-to?url=http%3A%2F%2Fhttpbin.org%2Fpost&status_code=302",
&protocol.Args{})
fmt.Printf("%d, %s, %s", statusCode, body, err)
}
中间件可能执行不止一次,比如发生跳转等,需要考虑幂等性
注意
RequestContext 相关操作
在实现服务端中间件的时候通常会用到 RequestContext
相关操作,见 请求上下文。
Handler 相关操作
一个服务端中间件即为一个 Handler,Handler 相关操作见 Handler。
快速中止服务端中间件
服务端中间件会按定义的先后顺序依次执行,如果想快速终止中间件调用,可以使用以下方法,注意当前中间件仍将执行。
c.Abort():终止后续调用c.AbortWithMsg(msg string, statusCode int):终止后续调用,并设置 response 中 body 和状态码c.AbortWithStatus(code int):终止后续调用,并设置状态码
title: “响应” date: 2023-04-14 weight: 2 keywords: [“RequestContext”, “渲染”, “Header”, “Body”, “文件操作”, “响应”, “Flush”] description: “RequestContext 中与响应相关的功能。”
Header
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetContentType(contentType string)
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetContentTypeBytes(contentType []byte)
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetConnectionClose()
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetStatusCode(statusCode int)
func (ctx *RequestContext) Status(code int)
func (ctx *RequestContext) NotFound()
func (ctx *RequestContext) NotModified()
func (ctx *RequestContext) Redirect(statusCode int, uri []byte)
func (ctx *RequestContext) Header(key, value string)
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetCookie(name, value string, maxAge int, path, domain string, sameSite protocol.CookieSameSite, secure, httpOnly bool)
func (ctx *RequestContext) AbortWithStatus(code int)
func (ctx *RequestContext) AbortWithError(code int, err error) *errors.Error
SetContentType
设置 Content-Type。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetContentType(contentType string)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Write([]byte(`{"foo":"bar"}`))
ctx.SetContentType("application/json; charset=utf-8")
// Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
})
SetContentTypeBytes
以 []byte 方式设置 Content-Type。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetContentTypeBytes(contentType []byte)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Write([]byte(`{"foo":"bar"}`))
ctx.SetContentType([]byte("application/json; charset=utf-8"))
// Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
})
SetConnectionClose
设置 Connection: close,告知客户端服务器想关闭连接。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetConnectionClose()
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.SetConnectionClose()
})
SetStatusCode
设置 Status Code。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetStatusCode(statusCode int)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.SetStatusCode(consts.StatusOK)
// Status Code: 200
})
Status
设置 Status Code,SetStatusCode 的别名。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Status(code int)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Status(consts.StatusOK)
// Status Code: 200
})
NotFound
设置 Status Code 代码为 404。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) NotFound()
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.NotFound()
// Status Code: 404
})
NotModified
设置 Status Code 代码为 304。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) NotModified()
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.NotModified()
// Status Code: 304
})
Redirect
设置 Status Code 代码以及要跳转的地址。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Redirect(statusCode int, uri []byte)
示例:
// internal redirection
// GET http://www.example.com:8888/user
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Redirect(consts.StatusFound, []byte("/pet"))
})
// GET http://www.example.com:8888/pet
h.GET("/pet", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "cat")
})
// external redirection
// GET http://www.example.com:8888/user
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Redirect(consts.StatusFound, []byte("http://www.example1.com:8888/pet"))
})
// GET http://www.example1.com:8888/pet
h.GET("/pet", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, "cat")
})
Header
设置或删除指定 Header。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Header(key, value string)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Header("My-Name", "tom")
ctx.Header("My-Name", "")
ctx.Header("My-Name-Not-Exists", "yes")
})
SetCookie
设置 Cookie。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetCookie(name, value string, maxAge int, path, domain string, sameSite protocol.CookieSameSite, secure, httpOnly bool)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.SetCookie("user", "hertz", 1, "/", "localhost", protocol.CookieSameSiteLaxMode, true, true)
cookie := ctx.Response.Header.Get("Set-Cookie")
// cookie == "user=hertz; max-age=1; domain=localhost; path=/; HttpOnly; secure; SameSite=Lax"
})
AbortWithStatus
设置 Status Code 并终止后续的 Handler。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) AbortWithStatus(code int)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.AbortWithStatus(consts.StatusOK)
}, func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// will not execute
})
AbortWithError
设置 Status Code 收集 Error 并终止后续的 Handler,返回 Error。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) AbortWithError(code int, err error) *errors.Error
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.AbortWithError(consts.StatusOK, errors.New("hertz error"))
err := ctx.Errors.String()
// err == "Error #01: hertz error"
}, func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// will not execute
})
ResponseHeader 对象
使用 RequestContext.Response.Header 获取 ResponseHeader 对象,该对象提供了以下方法获取/设置响应头部。
| 函数签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
func (h *ResponseHeader) IsHTTP11() bool |
判断是否是 HTTP/1.1 协议,true 表示是 HTTP/1.1 协议 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetHeaderLength(length int) |
设置响应头的大小 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) GetHeaderLength() |
获取响应头的大小 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetContentRange(startPos, endPos, contentLength int) |
在响应头中设置 Content-Range: bytes startPos-endPos/contentLength,如 Content-Range: bytes 1-5/10 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) NoDefaultContentType() bool |
获取未指定 Content-Type 时的默认发送行为,false 表示发送默认 Content-Type 的值,true 表示不发送,默认 Content-Type 的值为 text/plain; charset=utf-8 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetNoDefaultContentType(b bool) |
设置未指定 Content-Type 时的默认发送行为,false 表示发送默认 Content-Type 的值,true 表示不发送,默认 Content-Type 的值为 text/plain; charset=utf-8 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetContentType(contentType string) |
设置 Content-Type |
func (h *ResponseHeader) ContentType() []byte |
获取 Content-Type |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetContentTypeBytes(contentType []byte) |
设置 Content-Type |
func (h *ResponseHeader) ContentLength() int |
获取 Content-Length,可以是负值,-1 表示 Transfer-Encoding: chunked,-2 表示 Transfer-Encoding: identity |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetContentLength(contentLength int) |
设置 Content-Length,可以是负值,-1 表示 Transfer-Encoding: chunked,-2 表示 Transfer-Encoding: identity |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetContentLengthBytes(contentLength []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型的 Content-Length,可以是负值,-1 表示 Transfer-Encoding: chunked,-2 表示 Transfer-Encoding: identity |
func (h *ResponseHeader) CopyTo(dst *ResponseHeader) |
返回响应头的副本,在对响应头存在竞争访问时可以使用 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) GetHeaders() []argsKV |
以键值对的形式返回所有响应头 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) VisitAll(f func(key, value []byte)) |
遍历所有 Header 的键值并执行 f 函数 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) Get(key string) string |
获取键为 key 的值,并发安全 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) GetAll(key string) []string |
获取 []byte 类型的键为 key 的所有值(用于获取存在相同 key 的多个值),并发安全 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) Peek(key string) []byte |
获取 []byte 类型的键为 key 的值,并发不安全,竞争访问时使用 Get |
func (h *ResponseHeader) PeekAll(key string) [][]byte |
获取 []byte 类型的键为 key 的所有值(用于获取存在相同 key 的多个值),并发不安全,竞争访问时使用 GetAll |
func (h *ResponseHeader) Set(key, value string) |
设置 Header 键值,用于为同一个 Key 设置单个 Header |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetBytesV(key string, value []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型的 Header 键值,用于为同一个 Key 设置单个 Header |
func (h *ResponseHeader) Add(key, value string) |
设置 Header 键值,用于为同一个 Key 设置多个 Header,但 key 会覆盖以下 Header: Content-Type, Content-Length, Connection, Cookie, Transfer-Encoding, Host, User-Agent |
func (h *ResponseHeader) AddArgBytes(key, value []byte, noValue bool) |
添加 Header 键值(与 Add 不同,key 一定不会被规范化且 key 为 Content-Type, Content-Length, Content-Encoding, Connection, Server, Set-Cookie, Transfer-Encoding 时不会做特殊处理) |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetArgBytes(key, value []byte, noValue bool) |
设置 Header 键值(与 Set 不同,key 一定不会被规范化且 key 为 Content-Type, Content-Length, Content-Encoding, Connection, Server, Set-Cookie, Transfer-Encoding 时不会做特殊处理) |
func (h *ResponseHeader) Del(key string) |
删除 Header 中键为 key 的键值对 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) DelBytes(key []byte) |
删除 Header 中键为 key 的键值对 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) AppendBytes(dst []byte) []byte |
将完整的 Header 附加到 dst 中并返回 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) Header() []byte |
获取 []byte 类型的完整的 Header |
func (h *ResponseHeader) PeekLocation() []byte |
返回 Header 中 key 为 Location 的值 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) Cookie(cookie *Cookie) bool |
填充给定 cookie.Key 的 cookie,如果 cookie.Key 不存在则返回 false |
func (h *RequestHeader) FullCookie() []byte |
以字节数组形式返回完整的 cookie |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetCookie(cookie *Cookie) |
设置 Cookie 的键值 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) VisitAllCookie(f func(key, value []byte)) |
遍历所有 Cookie 的键值并执行 f 函数 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) DelAllCookies() |
删除所有 Cookie |
func (h *ResponseHeader) DelCookie(key string) |
删除响应头中键为 key 的 Cookie,若要删除来自客户端的 Cookie,请使用 DelClientCookie 函数 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) DelCookieBytes(key []byte) |
删除响应头中键为 key 的 Cookie,若要删除来自客户端的 Cookie,请使用 DelClientCookieBytes 函数 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) DelClientCookie(key string) |
删除来自客户端键为 key 的 Cookie |
func (h *ResponseHeader) DelClientCookieBytes(key []byte) |
删除来自客户端键为 key 的 Cookie |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetConnectionClose(close bool) |
在响应头中设置 Connection: close 标志 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) ConnectionClose() bool |
判断是否包含 Connection: close |
func (h *ResponseHeader) ContentEncoding() []byte |
获取 Content-Encoding |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetContentEncoding(contentEncoding string) |
设置 Content-Encoding |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetContentEncodingBytes(contentEncoding []byte) |
设置 Content-Encoding |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetCanonical(key, value []byte) |
设置 Header 键值,假设该键是规范形式 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) Server() []byte |
返回 Header 中 key 为 Server 的值 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetServerBytes(server []byte) |
设置 Header 中 key 为 Server 的值 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) MustSkipContentLength() bool |
判断是否有响应 body(HTTP/1.1 协议规定,响应状态码为 1xx、204、304 时没有响应 body) |
func (h *ResponseHeader) StatusCode() int |
获取响应状态码 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetStatusCode(statusCode int) |
设置响应状态码 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) Len() int |
返回 Header 的数量 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) DisableNormalizing() |
禁用 Header 名字的规范化 (首字母和破折号后第一个字母大写) |
func (h *ResponseHeader) IsDisableNormalizing() bool |
是否禁用 Header 名字的规范化,默认不禁用 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) Trailer() *Trailer |
获取 Trailer |
func (h *ResponseHeader) SetProtocol(p string) |
设置协议名 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) GetProtocol() string |
获取协议名 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) Reset() |
重置响应头 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) ResetSkipNormalize() |
重置响应头,除了 disableNormalizing 状态 |
func (h *ResponseHeader) ResetConnectionClose() |
重置 connectionClose 标志为 false 并删除 Connection Header |
渲染
支持对 JSON,HTML,Protobuf 等的渲染。(更多内容请参考 渲染)
func (ctx *RequestContext) Render(code int, r render.Render)
func (ctx *RequestContext) String(code int, format string, values ...interface{})
func (ctx *RequestContext) ProtoBuf(code int, obj interface{})
func (ctx *RequestContext) JSON(code int, obj interface{})
func (ctx *RequestContext) PureJSON(code int, obj interface{})
func (ctx *RequestContext) IndentedJSON(code int, obj interface{})
func (ctx *RequestContext) HTML(code int, name string, obj interface{})
func (ctx *RequestContext) Data(code int, contentType string, data []byte)
func (ctx *RequestContext) XML(code int, obj interface{})
Body
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetBodyStream(bodyStream io.Reader, bodySize int)
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetBodyString(body string)
func (ctx *RequestContext) Write(p []byte) (int, error)
func (ctx *RequestContext) WriteString(s string) (int, error)
func (ctx *RequestContext) AbortWithMsg(msg string, statusCode int)
func (ctx *RequestContext) AbortWithStatusJSON(code int, jsonObj interface{})
SetBodyStream
设置 Body Stream 和可选的 Body 大小。该函数用于 Hertz Server 的流式处理,详情可见 流式处理。
注意:bodySize 小于 0 时数据全部写入,大于等于 0 时根据设置的 bodySize 大小写入数据。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetBodyStream(bodyStream io.Reader, bodySize int)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
data := "hello world"
r := strings.NewReader(data)
ctx.SetBodyStream(r, -1) // Body: "hello world"
})
h.GET("/user1", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
data := "hello world"
r1 := strings.NewReader(data)
ctx.SetBodyStream(r1, 5) // Body: "hello"
})
SetBodyString
设置 Body。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetBodyString(body string)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.SetBodyString("hello world") // Body: "hello world"
})
Write
将字节数组 p 添加到 Body 中。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Write(p []byte) (int, error)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Write([]byte("hello"))
ctx.Write([]byte(" "))
ctx.Write([]byte("world"))
// Body: "hello world"
})
WriteString
设置 Body 并返回大小。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) WriteString(s string) (int, error)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
size, _ := ctx.WriteString("hello world")// Body: "hello world", size == 11
})
AbortWithMsg
设置 Status Code 和 Body 并终止后续的 Handler。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) AbortWithMsg(msg string, statusCode int)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.AbortWithMsg("abort", consts.StatusOK)
}, func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// will not execute
})
AbortWithStatusJSON
设置 Status Code 和 Json 格式 Body 并终止后续的 Handler。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) AbortWithStatusJSON(code int, jsonObj interface{})
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.AbortWithStatusJSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{
"foo": "bar",
"html": "<b>",
})
}, func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// will not execute
})
文件操作
func (ctx *RequestContext) File(filepath string)
func (ctx *RequestContext) FileAttachment(filepath, filename string)
func (ctx *RequestContext) FileFromFS(filepath string, fs *FS)
File
将指定文件写入到 Body Stream。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) File(filepath string)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.File("./main.go")
})
FileAttachment
将指定文件写入到 Body Stream 并通过 Content-Disposition 指定为下载。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) FileAttachment(filepath, filename string)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.FileAttachment("./main.go")
})
FileFromFS
将指定文件写入到 Body Stream。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) FileFromFS(filepath string, fs *FS)
示例:
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.FileFromFS("./main.go", &app.FS{
Root: ".",
IndexNames: nil,
GenerateIndexPages: false,
AcceptByteRange: true,
})
})
其他
func (ctx *RequestContext) Flush() error
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetResponse() (dst *protocol.Response)
Flush
把数据刷入被劫持的 Response Writer 中。( 更多内容请参考 response_writer)
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Flush() error
GetResponse
获取 Response 对象。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetResponse() (dst *protocol.Response)
title: “请求” date: 2023-04-14 weight: 1 keywords: [“RequestContext”, “URI”, “Header”, “Body”, “文件操作”, “元数据存储”, “Handler”, “请求”, “参数绑定与校验”, “ClientIP”, “并发安全”] description: “RequestContext 中与请求相关的功能。”
URI
func (ctx *RequestContext) Host() []byte
func (ctx *RequestContext) FullPath() string
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetFullPath(p string)
func (ctx *RequestContext) Path() []byte
func (ctx *RequestContext) Param(key string) string
func (ctx *RequestContext) Query(key string) string
func (ctx *RequestContext) DefaultQuery(key, defaultValue string) string
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetQuery(key string) (string, bool)
func (ctx *RequestContext) QueryArgs() *protocol.Args
func (ctx *RequestContext) URI() *protocol.URI
Host
获取请求的主机地址。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Host() []byte
示例:
// GET http://example.com
h.GET("/", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
host := ctx.Host() // host == []byte("example.com")
})
FullPath
获取匹配的路由完整路径,对于未匹配的路由返回空字符串。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) FullPath() string
示例:
h := server.Default(server.WithHandleMethodNotAllowed(true))
// GET http://example.com/user/bar
h.GET("/user/:name", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
fpath := ctx.FullPath() // fpath == "/user/:name"
})
// GET http://example.com/bar
h.NoRoute(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
fpath := ctx.FullPath() // fpath == ""
})
// POST http://example.com/user/bar
h.NoMethod(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
fpath := ctx.FullPath() // fpath == ""
})
SetFullPath
设置 FullPath 的值。
注意:FullPath 由路由查找时分配,通常你不需要使用 SetFullPath 去覆盖它。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetFullPath(p string)
示例:
h.GET("/user/:name", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.SetFullPath("/v1/user/:name")
fpath := ctx.FullPath() // fpath == "/v1/user/:name"
})
Path
获取请求的路径。
注意:出现参数路由时 Path 给出命名参数匹配后的路径,而 FullPath 给出原始路径。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Path() []byte
示例:
// GET http://example.com/user/bar
h.GET("/user/:name", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
path := ctx.Path() // path == []byte("/user/bar")
})
Param
获取路由参数的值。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Param(key string) string
示例:
// GET http://example.com/user/bar
h.GET("/user/:name", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
name := ctx.Param("name") // name == "bar"
id := ctx.Param("id") // id == ""
})
Query
获取路由 Query String 参数中指定属性的值,如果没有返回空字符串。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Query(key string) string
示例:
// GET http://example.com/user?name=bar
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
name := ctx.Query("name") // name == "bar"
id := ctx.Query("id") // id == ""
})
DefaultQuery
获取路由 Query String 参数中指定属性的值,如果没有返回设置的默认值。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) DefaultQuery(key, defaultValue string) string
示例:
// GET http://example.com/user?name=bar&&age=
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
name := ctx.DefaultQuery("name", "tom") // name == "bar"
id := ctx.DefaultQuery("id", "123") // id == "123"
age := ctx.DefaultQuery("age", "45") // age == ""
})
GetQuery
获取路由 Query String 参数中指定属性的值以及属性是否存在。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetQuery(key string) (string, bool)
示例:
// GET http://example.com/user?name=bar&&age=
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
name, hasName := ctx.GetQuery("name") // name == "bar", hasName == true
id, hasId := ctx.GetQuery("id") // id == "", hasId == false
age, hasAge := ctx.GetQuery("age") // age == "", hasAge == true
})
QueryArgs
获取路由 Query String 参数对象。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) QueryArgs() *protocol.Args
Args 对象
Args 对象提供了以下方法获取/设置 Query String 参数。
| 函数签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
func (a *Args) Set(key, value string) |
设置 Args 对象 key 的值 |
func (a *Args) Reset() |
重置 Args 对象 |
func (a *Args) CopyTo(dst *Args) |
将 Args 对象拷贝到 dst |
func (a *Args) Del(key string) |
删除 Args 对象 key 的键值对 |
func (a *Args) DelBytes(key []byte) |
删除 Args 对象字节数组类型 key 的键值对 |
func (a *Args) Has(key string) bool |
获取 Args 对象是否存在 key 的键值对 |
func (a *Args) String() string |
将 Args 对象转换为字符串类型的 Query String |
func (a *Args) QueryString() []byte |
将 Args 对象转换为字节数组类型的 Query String |
func (a *Args) ParseBytes(b []byte) |
解析字节数组并将键值对存入 Args 对象 |
func (a *Args) Peek(key string) []byte |
获取 Args 对象 key 的值 |
func (a *Args) PeekExists(key string) (string, bool) |
获取 Args 对象 key 的值以及是否存在 |
func (a *Args) Len() int |
获取 Args 对象键值对数量 |
func (a *Args) AppendBytes(dst []byte) []byte |
将 Args 对象 Query String 附加到 dst 中并返回 |
func (a *Args) VisitAll(f func(key, value []byte)) |
遍历 Args 对象所有的键值对 |
func (a *Args) WriteTo(w io.Writer) (int64, error) |
将 Args 对象 Query String 写入 io.Writer 中 |
func (a *Args) Add(key, value string) |
添加 Args 对象键为 key 的值 |
示例:
// GET http://example.com/user?name=bar&&age=&&pets=dog&&pets=cat
h.GET("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
args := ctx.QueryArgs()
// get information from args
s := args.String() // s == "name=bar&age=&pets=dog&pets=cat"
qs := args.QueryString() // qs == []byte("name=bar&age=&pets=dog&pets=cat")
cpqs := args.AppendBytes([]byte(nil)) // cpqs == []byte("name=bar&age=&pets=dog&pets=cat")
name := args.Peek("name") // name == []byte("bar")
hasName := args.Has("name") // hasName == true
age, hasAge := args.PeekExists("age") // age == "", hasAge == true
len := args.Len() // len == 4
args.VisitAll(func(key, value []byte) {
// 1. key == []byte("name"), value == []byte("bar")
// 2. key == []byte("age"), value == nil
// 3. key == []byte("pets"), value == []byte("dog")
// 4. key == []byte("pets"), value == []byte("cat")
})
// send information to io.Writer
req := protocol.AcquireRequest()
n, err := args.WriteTo(req.BodyWriter())
// n == 31 err == nil
s := req.BodyBuffer().String()
// s == "name=bar&age=&pets=dog&pets=cat"
// change args
var newArgs protocol.Args
args.CopyTo(&newArgs)
newArgs.Set("version", "v1")
version := newArgs.Peek("version") //version == []byte("v1")
newArgs.Del("age")
hasAgeAfterDel := newArgs.Has("age") // hasAgeAfterDel == false
newArgs.DelBytes([]byte("name"))
hasNameAfterDel := newArgs.Has("name") // hasNameAfterDel == false
newArgs.Add("name", "foo")
newName := newArgs.Peek("name") //newName == []byte("foo")
newArgs.Reset()
empty := newArgs.String() // empty == ""
// parse args
var newArgs2 protocol.Args
newArgs2.ParseBytes([]byte("name=bar&age=20"))
nqs2 := newArgs2.String() // nqs2 == "name=bar&age=20"
})
URI
返回请求的 URI 对象。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) URI() *protocol.URI
URI 对象
URI 对象提供了以下方法获取/设置 URI。
| 函数签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
func (u *URI) CopyTo(dst *URI) |
拷贝 URI 对象的副本到 dst |
func (u *URI) QueryArgs() *Args |
获取 Args 对象 |
func (u *URI) Hash() []byte |
获取 Hash 值,比如 http://example.com/user?baz=123#qwe 的 Hash 是 qwe |
func (u *URI) SetHash(hash string) |
设置 Hash |
func (u *URI) SetHashBytes(hash []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型 Hash |
func (u *URI) Username() []byte |
获取 Username |
func (u *URI) SetUsername(username string) |
设置 Username |
func (u *URI) SetUsernameBytes(username []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型 Username |
func (u *URI) Password() []byte |
获取 Password |
func (u *URI) SetPassword(password string) |
设置 Password |
func (u *URI) SetPasswordBytes(password []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型 Password |
func (u *URI) QueryString() []byte |
获取 Query String,比如 http://example.com/user?baz=123 的 Query String 是 baz=123 |
func (u *URI) SetQueryString(queryString string) |
设置 Query String |
func (u *URI) SetQueryStringBytes(queryString []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型的 Query String |
func (u *URI) Path() []byte |
获取 Path,比如 http://example.com/user/he%20rtz 的 Path 是 /user/he rtz |
func (u *URI) PathOriginal() []byte |
获取未转义的 Path,比如 http://example.com/user/he%20rtz 的 Path 是 /user/he%20rtz |
func (u *URI) SetPath(path string) |
设置 Path |
func (u *URI) SetPathBytes(path []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型 Path |
func (u *URI) String() string |
获取完整 URI 比如 http://example.com/user?baz=123 的完整 URI 是 http://example.com/user?baz=123 |
func (u *URI) FullURI() []byte |
获取 []byte 类型的完整 URI |
func (u *URI) Scheme() []byte |
获取协议,如 http |
func (u *URI) SetScheme(scheme string) |
设置协议 |
func (u *URI) SetSchemeBytes(scheme []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型的协议 |
func (u *URI) Host() []byte |
获取 Host,比如 http://example.com/user 的 Host 是 example.com |
func (u *URI) SetHost(host string) |
设置 Host |
func (u *URI) SetHostBytes(host []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型 Host |
func (u *URI) LastPathSegment() []byte |
获取 Path 的最后一部分,比如 Path /foo/bar/baz.html 的最后一部分是 baz.html |
func (u *URI) Update(newURI string) |
更新 URI |
func (u *URI) UpdateBytes(newURI []byte) |
更新 []byte 类型的 URI |
func (u *URI) Parse(host, uri []byte) |
初始化 URI |
func (u *URI) AppendBytes(dst []byte) []byte |
将完整的 URI 赋值到 dst 中并返回 dst |
func (u *URI) RequestURI() []byte |
获取 RequestURI,比如 http://example.com/user?baz=123 的 RequestURI 是 /user?baz=123 |
func (u *URI) Reset() |
重置 URI |
Header
// RequestHeader
func (h *RequestHeader) Add(key, value string)
func (h *RequestHeader) Set(key, value string)
func (h *RequestHeader) Header() []byte
func (h *RequestHeader) String() string
func (h *RequestHeader) VisitAll(f func(key, value []byte))
// RequestContext
func (ctx *RequestContext) IsGet() bool
func (ctx *RequestContext) IsHead() bool
func (ctx *RequestContext) IsPost() bool
func (ctx *RequestContext) Method() []byte
func (ctx *RequestContext) ContentType() []byte
func (ctx *RequestContext) IfModifiedSince(lastModified time.Time) bool
func (ctx *RequestContext) Cookie(key string) []byte
func (ctx *RequestContext) UserAgent() []byte
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetHeader(key string) []byte
Add
添加或设置键为 key 的 Header。
注意:Add 通常用于为同一个 Key 设置多个 Header,若要为同一个 Key 设置单个 Header 请使用 Set。当作用于 Content-Type, Content-Length, Connection, Cookie, Transfer-Encoding, Host, User-Agent 这些 Header 时,使用多个 Add 会覆盖掉旧值。
函数签名:
func (h *RequestHeader) Add(key, value string)
示例:
hertz.GET("/example", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Request.Header.Add("hertz1", "value1")
ctx.Request.Header.Add("hertz1", "value2")
ctx.Request.Header.SetContentTypeBytes([]byte("application/x-www-form-urlencoded"))
contentType1 := ctx.Request.Header.ContentType()
// contentType1 == []byte("application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
ctx.Request.Header.Add("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=utf-8")
hertz1 := ctx.Request.Header.GetAll("hertz1")
// hertz1 == []string{"value1", "value2"}
contentType2 := ctx.Request.Header.ContentType()
// contentType2 == []byte("application/json; charset=utf-8")
})
Set
设置 Header 键值。
注意:Set 通常用于为同一个 Key 设置单个 Header,若要为同一个 Key 设置多个 Header 请使用 Add。
函数签名:
func (h *RequestHeader) Set(key, value string)
示例:
hertz.GET("/example", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Request.Header.Set("hertz1", "value1")
ctx.Request.Header.Set("hertz1", "value2")
ctx.Request.Header.SetContentTypeBytes([]byte("application/x-www-form-urlencoded"))
contentType1 := ctx.Request.Header.ContentType()
// contentType1 == []byte("application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
ctx.Request.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=utf-8")
hertz1 := ctx.Request.Header.GetAll("hertz1")
// hertz1 == []string{"value2"}
contentType2 := ctx.Request.Header.ContentType()
// contentType2 == []byte("application/json; charset=utf-8")
})
Header
获取 []byte 类型的完整的 Header。
函数签名:
func (h *RequestHeader) Header() []byte
示例:
hertz.GET("/example", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Request.Header.Set("hertz1", "value1")
header := ctx.Request.Header.Header()
// header == []byte("GET /example HTTP/1.1
//User-Agent: PostmanRuntime-ApipostRuntime/1.1.0
//Host: localhost:8888
//Cache-Control: no-cache
//Accept: */*
//Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
//Connection: keep-alive
//Hertz1: value1")
})
String
获取完整的 Header。
函数签名:
func (h *RequestHeader) String() string
示例:
hertz.GET("/example", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Request.Header.Set("hertz1", "value1")
header := ctx.Request.Header.String()
// header == "GET /example HTTP/1.1
//User-Agent: PostmanRuntime-ApipostRuntime/1.1.0
//Host: localhost:8888
//Cache-Control: no-cache
//Accept: */*
//Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
//Connection: keep-alive
//Hertz1: value1"
})
遍历 Header
遍历所有 Header 的键值并执行 f 函数。
函数签名:
func (h *RequestHeader) VisitAll(f func(key, value []byte))
示例:
hertz.GET("/example", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Request.Header.Add("Hertz1", "value1")
ctx.Request.Header.Add("Hertz1", "value2")
var hertzString []string
ctx.Request.Header.VisitAll(func(key, value []byte) {
if string(key) == "Hertz1" {
hertzString = append(hertzString, string(value))
}
})
// hertzString == []string{"value1", "value2"}
})
Method
获取请求方法的类型。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Method() []byte
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
h.Any("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
method := ctx.Method() // method == []byte("POST")
})
ContentType
获取请求头 Content-Type 的值。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) ContentType() []byte
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// Content-Type: application/json
h.Post("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
contentType := ctx.ContentType() // contentType == []byte("application/json")
})
IfModifiedSince
判断时间是否超过请求头 If-Modified-Since 的值。
注意:如果请求头不包含 If-Modified-Since 也返回 true。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) IfModifiedSince(lastModified time.Time) bool
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// If-Modified-Since: Wed, 21 Oct 2023 07:28:00 GMT
h.Post("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
t2022, _ := time.Parse(time.RFC1123, "Wed, 21 Oct 2022 07:28:00 GMT")
ifModifiedSince := ctx.IfModifiedSince(t2022) // ifModifiedSince == false
t2024, _ := time.Parse(time.RFC1123, "Wed, 21 Oct 2024 07:28:00 GMT")
ifModifiedSince = ctx.IfModifiedSince(t2024) // ifModifiedSince == true
})
Cookie
获取请求头 Cookie 中 key 的值。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Cookie(key string) []byte
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// Cookie: foo_cookie=choco; bar_cookie=strawberry
h.Post("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
fCookie := ctx.Cookie("foo_cookie") // fCookie == []byte("choco")
bCookie := ctx.Cookie("bar_cookie") // bCookie == []byte("strawberry")
noneCookie := ctx.Cookie("none_cookie") // noneCookie == nil
})
UserAgent
获取请求头 User-Agent 的值。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) UserAgent() []byte
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// User-Agent: Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36
h.Post("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ua := ctx.UserAgent() // ua == []byte("Chrome/51.0.2704.103 Safari/537.36")
})
GetHeader
获取请求头中 key 的值。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetHeader(key string) []byte
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// Say-Hello: hello
h.Post("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
customHeader := ctx.GetHeader("Say-Hello") // customHeader == []byte("hello")
})
RequestHeader 对象
使用 RequestContext.Request.Header 获取 RequestHeader 对象,该对象提供了以下方法获取/设置请求头部。
| 函数签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
func (h *RequestHeader) Method() []byte |
获取 Method |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetMethod(method string) |
设置 Method |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetMethodBytes(method []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型的 Method |
func (h *RequestHeader) IsGet() bool |
判断 Method 是否是 GET |
func (h *RequestHeader) IsHead() bool |
判断 Method 是否是 HEAD |
func (h *RequestHeader) IsPost() bool |
判断 Method 是否是 POST |
func (h *RequestHeader) IsPut() bool |
判断 Method 是否是 PUT |
func (h *RequestHeader) IsDelete() bool |
判断 Method 是否是 DELETE |
func (h *RequestHeader) IsConnect() bool |
判断 Method 是否是 CONNECT |
func (h *RequestHeader) IsOptions() bool |
判断 Method 是否是 OPTIONS |
func (h *RequestHeader) IsTrace() bool |
判断 Method 是否是 TRACE |
func (h *RequestHeader) IgnoreBody() bool |
判断是否忽略 Body (Method GET/HEAD 忽略 Body) |
func (h *RequestHeader) RequestURI() []byte |
获取 RequestURI |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetRequestURI(requestURI string) |
设置 RequestURI |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetRequestURIBytes(requestURI []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型的 RequestURI |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetProtocol(p string) |
设置协议类型,比如 HTTP/1.0 |
func (h *RequestHeader) GetProtocol() string |
获取协议类型,比如 HTTP/1.1 |
func (h *RequestHeader) IsHTTP11() bool |
判断是否是 HTTP/1.1 |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetNoHTTP11(b bool) |
设置是否不是 HTTP/1.1 |
func (h *RequestHeader) Host() []byte |
获取 Host |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetHost(host string) |
设置 Host |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetHostBytes(host []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型的 Host |
func (h *RequestHeader) ContentLength() int |
获取 Content-Length |
func (h *RequestHeader) ContentLengthBytes() []byte |
获取 []byte 类型的 Content-Length |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetContentLength(contentLength int) |
设置 Content-Length |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetContentLengthBytes(contentLength []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型的 Content-Length |
func (h *RequestHeader) InitContentLengthWithValue(contentLength int) |
初始化 Content-Length |
func (h *RequestHeader) ContentType() []byte |
获取 Content-Type |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetContentTypeBytes(contentType []byte) |
设置 Content-Type |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetNoDefaultContentType(b bool) |
控制未指定 Content-Type 时的默认发送行为,false 发送默认 Content-Type 的值,true 不发送 Content-Type |
func (h *RequestHeader) UserAgent() []byte |
获取 User-Agent |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetUserAgentBytes(userAgent []byte) |
设置 User-Agent |
func (h *RequestHeader) ConnectionClose() bool |
判断是否包含 Connection: close |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetConnectionClose(close bool) |
设置 connectionClose 标志 |
func (h *RequestHeader) ResetConnectionClose() |
重置 connectionClose 标志为 false 并删除 Connection Header |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetByteRange(startPos, endPos int) |
设置 Range (Range: bytes=startPos-endPos) |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetMultipartFormBoundary(boundary string) |
当 Content-Type=multipart/form-data 时为其设置 boundary |
func (h *RequestHeader) MultipartFormBoundary() []byte |
获取 boundary 的值 |
func (h *RequestHeader) Trailer() *Trailer |
获取 Trailer |
func (h *RequestHeader) Cookie(key string) []byte |
获取 Cookie 键为 key 的值 |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetCookie(key, value string) |
设置 Cookie 的键值 |
func (h *RequestHeader) DelCookie(key string) |
删除键为 key 的 Cookie |
func (h *RequestHeader) DelAllCookies() |
删除所有 Cookie |
func (h *RequestHeader) FullCookie() []byte |
获取所有 Cookie |
func (h *RequestHeader) Cookies() []*Cookie |
获取所有 Cookie 对象 |
func (h *RequestHeader) VisitAllCookie(f func(key, value []byte)) |
遍历所有 Cookie 的键值并执行 f 函数 |
func (h *RequestHeader) Peek(key string) []byte |
获取 []byte 类型的键为 key 的值 |
func (h *RequestHeader) Get(key string) string |
获取键为 key 的值 |
func (h *RequestHeader) PeekArgBytes(key []byte) []byte |
获取键为 key 的值 |
func (h *RequestHeader) PeekAll(key string) [][]byte |
获取 []byte 类型的键为 key 的所有值(用于获取存在相同 key 的多个值) |
func (h *RequestHeader) GetAll(key string) []string |
获取键为 key 的所有值 |
func (h *RequestHeader) PeekIfModifiedSinceBytes() []byte |
获取 If-Modified-Since |
func (h *RequestHeader) PeekContentEncoding() []byte |
获取 Content-Encoding |
func (h *RequestHeader) PeekRange() []byte |
获取 Range |
func (h *RequestHeader) HasAcceptEncodingBytes(acceptEncoding []byte) bool |
判断是否存在 Accept-Encoding 以及 Accept-Encoding 是否包含 acceptEncoding |
func (h *RequestHeader) RawHeaders() []byte |
获取原始 Header |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetRawHeaders(r []byte) |
设置原始 Header |
func (h *RequestHeader) Add(key, value string) |
添加或设置键为 key 的 Header,用于为同一个 Key 设置多个 Header,但 key 会覆盖以下 Header: Content-Type, Content-Length, Connection, Cookie, Transfer-Encoding, Host, User-Agent |
func (h *RequestHeader) InitBufValue(size int) |
初始化缓冲区大小 |
func (h *RequestHeader) GetBufValue() []byte |
获取缓冲区的值 |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetCanonical(key, value []byte) |
设置 Header 键值,假设该键是规范形式 |
func (h *RequestHeader) Set(key, value string) |
设置 Header 键值,用于为同一个 Key 设置单个 Header |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetBytesKV(key, value []byte) |
设置 []byte 类型的 Header 键值,用于为同一个 Key 设置单个 Header |
func (h *RequestHeader) DelBytes(key []byte) |
删除 Header 中键为 key 的键值对 |
func (h *RequestHeader) AddArgBytes(key, value []byte, noValue bool) |
添加 Header 键值(与 Add 不同,key 一定不会被规范化且 key 为 Content-Type, Content-Length, Connection, Cookie, Transfer-Encoding, Host, User-Agent 时不会做特殊处理) |
func (h *RequestHeader) SetArgBytes(key, value []byte, noValue bool) |
设置 Header 键值(与 Set 不同,key 一定不会被规范化且 key 为 Content-Type, Content-Length, Connection, Cookie, Transfer-Encoding, Host, User-Agent 时不会做特殊处理) |
func (h *RequestHeader) AppendBytes(dst []byte) []byte |
将完整的 Header 附加到 dst 中并返回 |
func (h *RequestHeader) Header() []byte |
获取 []byte 类型的完整的 Header |
func (h *RequestHeader) String() string |
获取完整的 Header |
func (h *RequestHeader) CopyTo(dst *RequestHeader) |
获取 RequestHeader 的副本 |
func (h *RequestHeader) VisitAll(f func(key, value []byte)) |
遍历所有 Header 的键值并执行 f 函数 |
func (h *RequestHeader) VisitAllCustomHeader(f func(key, value []byte)) |
遍历所有 Header 的键值并执行 f 函数,以下 key 除外:Content-Type, Content-Length, Cookie, Host, User-Agent) |
func (h *RequestHeader) Len() int |
返回 Header 的数量 |
func (h *RequestHeader) DisableNormalizing() |
禁用 Header 名字的规范化 (首字母和破折号后第一个字母大写) |
func (h *RequestHeader) IsDisableNormalizing() bool |
是否禁用 Header 名字的规范化,默认不禁用 |
func (h *RequestHeader) ResetSkipNormalize() |
重置 Headers,除了 disableNormalizing 状态 |
func (h *RequestHeader) Reset() |
重置 Headers |
Body
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetRawData() []byte
func (ctx *RequestContext) Body() ([]byte, error)
func (ctx *RequestContext) RequestBodyStream() io.Reader
func (ctx *RequestContext) MultipartForm() (*multipart.Form, error)
func (ctx *RequestContext) PostForm(key string) string
func (ctx *RequestContext) DefaultPostForm(key, defaultValue string) string
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetPostForm(key string) (string, bool)
func (ctx *RequestContext) PostArgs() *protocol.Args
func (ctx *RequestContext) FormValue(key string) []byte
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetFormValueFunc(f FormValueFunc)
Body
获取请求的 body 数据,如果发生错误返回 error。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Body() ([]byte, error)
示例:
// POST http://example.com/pet
// Content-Type: application/json
// {"pet":"cat"}
h.Post("/pet", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
data, err := ctx.Body() // data == []byte("{\"pet\":\"cat\"}") , err == nil
})
RequestBodyStream
获取请求的 BodyStream。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) RequestBodyStream() io.Reader
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// Content-Type: text/plain
// abcdefg
h := server.Default(server.WithStreamBody(true))
h.Post("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
sr := ctx.RequestBodyStream()
data, _ := io.ReadAll(sr) // data == []byte("abcdefg")
})
MultipartForm
获取 multipart.Form 对象,(详情请参考 multipart#Form)
注意:此函数既可以获取普通值也可以获取文件,此处给出了获取普通值的示例代码,获取文件的示例代码可参考 MultipartForm。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) MultipartForm() (*multipart.Form, error)
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// Content-Type: multipart/form-data;
// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="name"
// tom
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
form, err := ctx.MultipartForm()
name := form.Value["name"][0] // name == "tom"
})
PostForm
按名称检索 multipart.Form.Value,返回给定 name 的第一个值。
注意:该函数支持从 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 和 multipart/form-data 这两种类型的 content-type 中获取 value 值,且不支持获取文件值。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) PostForm(key string) string
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// Content-Type: multipart/form-data;
// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="name"
// tom
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
name := ctx.PostForm("name") // name == "tom"
})
DefaultPostForm
按名称检索 multipart.Form.Value,返回给定 name 的第一个值,如果不存在返回 defaultValue。
注意:该函数支持从 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 和 multipart/form-data 这两种类型的 content-type 中获取 value 值,且不支持获取文件值。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) DefaultPostForm(key, defaultValue string) string
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// Content-Type: multipart/form-data;
// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="name"
// tom
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
name := ctx.PostForm("name", "jack") // name == "tom"
age := ctx.PostForm("age", "10") // age == "10"
})
PostArgs
获取 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 参数对象。(详情请参考 Args 对象)
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) PostArgs() *protocol.Args
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
// name=tom&pet=cat&pet=dog
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
args := ctx.PostArgs()
name := args.Peek("name") // name == "tom"
var pets []string
args.VisitAll(func(key, value []byte) {
if string(key) == "pet" {
pets = append(pets, string(value))
}
})
// pets == []string{"cat", "dog"}
})
FormValue
按照以下顺序获取 key 的值。
- 从 QueryArgs 中获取值。
- 从 PostArgs 中获取值。
- 从 MultipartForm 中获取值。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) FormValue(key string) []byte
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user?name=tom
// Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
// age=10
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
name := ctx.FormValue("name") // name == []byte("tom"), get by QueryArgs
age := ctx.FormValue("age") // age == []byte("10"), get by PostArgs
})
// POST http://example.com/user
// Content-Type: multipart/form-data;
// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="name"
// tom
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
name := ctx.FormValue("name") // name == []byte("tom"), get by MultipartForm
})
SetFormValueFunc
若 FormValue 函数提供的默认获取 key 的值的方式不满足需求,用户可以使用该函数自定义获取 key 的值的方式。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetFormValueFunc(f FormValueFunc)
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user?name=tom
// Content-Type: multipart/form-data;
// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="age"
// 10
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// only return multipart form value
ctx.SetFormValueFunc(func(rc *app.RequestContext, s string) []byte {
mf, err := rc.MultipartForm()
if err == nil && mf.Value != nil {
vv := mf.Value[s]
if len(vv) > 0 {
return []byte(vv[0])
}
}
return nil
})
name := ctx.FormValue("name") // name == nil
age := ctx.FormValue("age") // age == []byte("10")
})
文件操作
func (ctx *RequestContext) MultipartForm() (*multipart.Form, error)
func (ctx *RequestContext) FormFile(name string) (*multipart.FileHeader, error)
func (ctx *RequestContext) SaveUploadedFile(file *multipart.FileHeader, dst string) error
MultipartForm
获取 multipart.Form 对象。(详情请参考 multipart#Form)
注意:此函数既可以获取普通值也可以获取文件,此处给出了获取文件值的示例代码,获取普通值的示例代码可参考 MultipartForm。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) MultipartForm() (*multipart.Form, error)
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// Content-Type: multipart/form-data;
// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="avatar"; filename="abc.jpg"
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
form, err := ctx.MultipartForm()
avatarFile := form.File["avatar"][0] // avatarFile.Filename == "abc.jpg"
})
FormFile
按名称检索 multipart.Form.File,返回给定 name 的第一个 multipart.FileHeader。(
详情请参考 multipart#FileHeader)
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) FormFile(name string) (*multipart.FileHeader, error)
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// Content-Type: multipart/form-data;
// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="avatar"; filename="abc.jpg"
h.Post("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
avatarFile, err := ctx.FormFile("avatar") // avatarFile.Filename == "abc.jpg", err == nil
})
SaveUploadedFile
保存 multipart 文件到磁盘。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SaveUploadedFile(file *multipart.FileHeader, dst string) error
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// Content-Type: multipart/form-data;
// Content-Disposition: form-data; name="avatar"; filename="abc.jpg"
h.Post("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
avatarFile, err := ctx.FormFile("avatar") // avatarFile.Filename == "abc.jpg", err == nil
// save file
ctx.SaveUploadedFile(avatarFile, avatarFile.Filename) // save file "abc.jpg"
})
RequestContext 元数据存储
注意:RequestContext 在请求结束后会被回收,元数据会被置为 nil。如需异步使用,请使用 Copy 方法。
| 函数签名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
func (ctx *RequestContext) Set(key string, value interface{}) |
在上下文中存储键值对 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) Value(key interface{}) interface{} |
获取上下文键为 key 的值 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) Get(key string) (value interface{}, exists bool) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值以及 key 是否存在 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) MustGet(key string) interface{} |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,如果不存在会发生 panic |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetString(key string) (s string) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 string 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetBool(key string) (b bool) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 bool 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetInt(key string) (i int) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 int 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetInt32(key string) (i32 int32) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 int32 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetInt64(key string) (i64 int64) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 int64 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetUint(key string) (ui uint) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 uint 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetUint32(key string) (ui32 uint32) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 uint32 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetUint64(key string) (ui64 uint64) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 uint64 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetFloat32(key string) (f32 float32) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 float32 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetFloat64(key string) (f64 float64) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 float64 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetTime(key string) (t time.Time) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 time.Time 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetDuration(key string) (d time.Duration) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 time.Duration 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetStringSlice(key string) (ss []string) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 []string 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetStringMap(key string) (sm map[string]interface{}) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 map[string]interface{} 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetStringMapString(key string) (sms map[string]string) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 map[string]string 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetStringMapStringSlice(key string) (smss map[string][]string) |
获取上下文键为 key 的值,并转换为 map[string][]string 类型 |
func (ctx *RequestContext) ForEachKey(fn func(k string, v interface{})) |
为上下文中的每个键值对调用 fn |
示例:
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Set("version1", "v1")
v := ctx.Value("version1") // v == interface{}(string) "v1"
ctx.Set("version2", "v2")
v, exists := ctx.Get("version2") // v == interface{}(string) "v2", exists == true
v, exists = ctx.Get("pet") // v == interface{} nil, exists == false
ctx.Set("version3", "v3")
v := ctx.MustGet("version3") // v == interface{}(string) "v3"
ctx.Set("version4", "v4")
vString := ctx.GetString("version4") // vString == "v4"
ctx.Set("isAdmin", true)
vBool := ctx.GetBool("isAdmin") // vBool == true
ctx.Set("age1", 20)
vInt := ctx.GetInt("age1") // vInt == 20
ctx.Set("age2", int32(20))
vInt32 := ctx.GetInt32("age2") // vInt32 == 20
ctx.Set("age3", int64(20))
vInt64 := ctx.GetInt64("age3") // vInt64 == 20
ctx.Set("age4", uint(20))
vUInt := ctx.GetUint("age4") // vUInt == 20
ctx.Set("age5", uint32(20))
vUInt32 := ctx.GetUint32("age5") // vUInt32 == 20
ctx.Set("age6", uint64(20))
vUInt64 := ctx.GetUint64("age6") // vUInt64 == 20
ctx.Set("age7", float32(20.1))
vFloat32 := ctx.GetFloat32("age7") // vFloat32 == 20.1
ctx.Set("age8", 20.1)
vFloat64 := ctx.GetFloat64("age8") // vFloat64 == 20.1
t2022, _ := time.Parse(time.RFC1123, "Wed, 21 Oct 2022 07:28:00 GMT")
ctx.Set("birthday", t2022)
vTime := ctx.GetTime("birthday") // vTime == t2022
ctx.Set("duration", time.Minute)
vDuration := ctx.GetDuration("duration") // vDuration == time.Minute
ctx.Set("pet", []string{"cat", "dog"})
vStringSlice := ctx.GetStringSlice("pet") // vStringSlice == []string{"cat", "dog"}
ctx.Set("info1", map[string]interface{}{"name": "tom"})
vStringMap := ctx.GetStringMap("info1") // vStringMap == map[string]interface{}{"name": "tom"}
ctx.Set("info2", map[string]string{"name": "tom"})
vStringMapString := ctx.GetStringMapString("info2")
// vStringMapString == map[string]string{}{"name": "tom"}
ctx.Set("smss", map[string][]string{"pets": {"cat", "dog"}})
vStringMapStringSlice := ctx.GetStringMapStringSlice("smss")
// vStringMapStringSlice == map[string][]string{"pets": {"cat", "dog"}}
ctx.Set("duration", time.Minute)
ctx.Set("version", "v1")
ctx.ForEachKey(func(k string, v interface{}) {
// 1. k == "duration", v == interface{}(time.Duration) time.Minute
// 2. k == "version", v == interface{}(string) "v1"
})
})
Handler
func (ctx *RequestContext) Next(c context.Context)
func (ctx *RequestContext) Handlers() HandlersChain
func (ctx *RequestContext) Handler() HandlerFunc
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetHandlers(hc HandlersChain)
func (ctx *RequestContext) HandlerName() string
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetIndex() int8
func (ctx *RequestContext) Abort()
func (ctx *RequestContext) IsAborted() bool
Next
执行下一个 handler,该函数通常用于中间件 handler 中。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Next(c context.Context)
示例:
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Next(c)
v := ctx.GetString("version") // v == "v1"
}, func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Set("version", "v1")
})
Handlers
获取 handlers chain。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Handlers() HandlersChain
示例:
middleware1 := func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
}
handler1 := func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
handlers := ctx.Handlers() // []Handler{middleware1, handler1}
}
h.POST("/user", middleware1, handler1)
Handler
获取 handlers chain 的最后一个 handler,一般来说,最后一个 handler 是 main handler。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Handler() HandlerFunc
示例:
middleware1 := func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
lastHandler := ctx.Handler() // lastHandler == handler1
}
handler1 := func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
}
h.POST("/user", middleware1, handler1)
SetHandlers
设置 handlers chain。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetHandlers(hc HandlersChain)
示例:
handler1 := func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Set("current", "handler1")
}
handler := func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
hc := app.HandlersChain{ctx.Handlers()[0], handler1} // append handler1 into handlers chain
ctx.SetHandlers(hc)
ctx.Next(c)
current := ctx.GetString("current") // current == "handler1"
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, current)
}
h.POST("/user", handler)
HandlerName
获取最后一个 handler 的函数名称。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) HandlerName() string
示例:
package main
func main() {
h := server.New()
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
hn := ctx.HandlerName() // hn == "main.main.func1"
})
}
GetIndex
获取当前执行的 handler 在 handlers chain 中的 index。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) GetIndex() int8
示例:
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
index := ctx.GetIndex() // index == 0
}, func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
index := ctx.GetIndex() // index == 1
})
Abort
终止后续的 handler 执行。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Abort()
示例:
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Abort()
}, func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// will not execute
})
IsAborted
获取后续的 handler 执行状态是否被终止。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) IsAborted() bool
示例:
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.Abort()
isAborted := ctx.IsAborted() // isAborted == true
}, func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// will not execute
})
参数绑定与校验
(更多内容请参考 binding-and-validate)
func (ctx *RequestContext) Bind(obj interface{}) error
func (ctx *RequestContext) Validate(obj interface{}) error
func (ctx *RequestContext) BindAndValidate(obj interface{}) error
获取 ClientIP
func (ctx *RequestContext) ClientIP() string
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetClientIPFunc(f ClientIP)
ClientIP
获取客户端 IP 的地址。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) ClientIP() string
示例:
h.Use(func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ip := ctx.ClientIP() // example: 127.0.0.1
})
SetClientIPFunc
若 ClientIP 函数提供的默认方式不满足需求,用户可以使用该函数自定义获取客户端 ip 的方式。
该函数可用于即使 remote ip 存在,也希望从 X-Forwarded-For 或 X-Real-IP Header 获取 ip
的场景(多重代理,想从 X-Forwarded-For 或 X-Real-IP Header 获得最初的 ip)。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) SetClientIPFunc(f ClientIP)
示例:
// POST http://example.com/user
// X-Forwarded-For: 203.0.113.195
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ip := ctx.ClientIP() // ip == "127.0.0.1"
opts := app.ClientIPOptions{
RemoteIPHeaders: []string{"X-Forwarded-For", "X-Real-IP"},
TrustedProxies: map[string]bool{ip: true},
}
ctx.SetClientIPFunc(app.ClientIPWithOption(opts))
ip = ctx.ClientIP() // ip == "203.0.113.195"
ctx.String(consts.StatusOK, ip)
})
并发安全
func (ctx *RequestContext) Copy() *RequestContext
Copy
拷贝 RequestContext 副本,提供协程安全的访问方式。
函数签名:
func (ctx *RequestContext) Copy() *RequestContext
示例:
h.POST("/user", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx1 := ctx.Copy()
go func(context *app.RequestContext) {
// safely
}(ctx1)
})
title: “请求上下文” date: 2023-04-12 weight: 5 keywords: [“RequestContext”, “HTTP”, “上下文传递”, “元数据存储”, “并发安全”] description: “请求上下文相关功能。”
请求上下文 RequestContext 是用于保存 HTTP 请求和设置 HTTP 响应的上下文,它提供了许多方便的 API 接口帮助用户开发。
Hertz 在 HandlerFunc 设计上,同时提供了一个标准 context.Context 和一个 RequestContext 作为函数的入参。
handler/middleware 函数签名为:
type HandlerFunc func(c context.Context, ctx *RequestContext)
上下文传递与并发安全
元数据存储
context.Context 与 RequestContext 都有存储值的能力,具体选择使用哪一个上下文有个简单依据:所储存值的生命周期和所选择的上下文要匹配。
ctx 主要用来存储请求级别的变量,请求结束就回收了,特点是查询效率高(底层是 map),协程不安全,且未实现 context.Context
接口。
c 作为上下文在中间件 /handler 之间传递,协程安全。所有需要 context.Context 接口作为入参的地方,直接传递 c 即可。
协程安全
除此之外,如果存在异步传递 ctx 或并发使用 ctx 的场景,hertz 也提供了 ctx.Copy() 接口,方便业务能够获取到一个协程安全的副本。
title: “TLS” date: 2022-11-06 weight: 5 keywords: [“TLS”, “HTTP”] description: “Hertz 支持 TLS 安全传输,帮助用户实现数据的保密性和完整性。”
Hertz 支持 TLS 安全传输,帮助用户实现了数据的保密性和完整性。
如果有 TLS 的需求,请使用 go net 网络库。netpoll 正在实现对 TLS 的支持。
在 tls.Config中,服务端和客户端都可使用的参数如下:
| 参数名 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| Certificates | 用于添加证书,可以配置多个证书。 两端自动选择第一个证书进行验证。 |
| VerifyPeerCertificate | 用于验证对端证书。 在任意一端证书验证后调用。 |
| VerifyConnection | 在两端证书均验证后,进行 TLS 连接验证。 |
| NextProtos | 用于设置支持的应用层协议。 |
| CipherSuites | 用于协商加密策略,支持 TLS 1.0-1.2。 |
| MaxVersion | 用于设置 TLS 支持的最大版本,目前是 1.3。 |
服务端
Hertz 在 server 包提供了 WithTLS Option 用于配置 TLS 服务。但是目前 Hertz 只有 标准网络库 支持
TLS,Netpoll 网络库的支持还在路上。
WithTLS 的 Transporter 默认设置为标准库的 Transporter。
// WithTLS sets TLS config to start a tls server.
// NOTE: If a tls server is started, it won't accept non-tls request.
func WithTLS(cfg *tls.Config) config.Option {
return config.Option{F: func(o *config.Options) {
route.SetTransporter(standard.NewTransporter)
o.TLS = cfg
}}
}
参数
在 tls.Config 中,除了上述基本参数,服务端可以配置的参数如下:
| 参数名 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| GetCertificate | 基于客户端 SNI 信息或证书集为空时,返回证书。 |
| GetClientCertificate | 用于服务端要求验证客户端证书时,返回客户端证书。 |
| GetConfigForClient | 当服务端从客户端接收了 ClientHello 后,返回配置信息。 如果返回的是非空的配置信息,将会被用于这次 TLS 连接。 |
| ClientAuth | 用于客户端验证策略设置,默认为 NoClientCert。 |
| ClientCAs | 当启用了 ClientAuth, 用于验证客户端证书的真实性。 |
服务器端 TLS 主要流程:
- 载入根证书,用于验证客户端的真实性。
- 载入服务器证书,用于发送给客户端以验证服务器真实性。
- 配置
tls.Config。 - 使用
WithTLS配置服务端 TLS,默认使用标准库的 Transporter。
示例代码
本次示例中的 ca.key、ca.crt、server.key 和 server.crt 均通过 openssl 生成。
首先生成 CA 的私钥和证书,命令如下:
openssl ecparam -genkey -name prime256v1 -out ca.key
openssl req -new -key ca.key -out ca.req
# country=cn, common name=ca.example.com
openssl x509 -req -in ca.req -signkey ca.key -out ca.crt -days 365
通过 CA 签名,生成服务端的私钥和证书,命令如下:
openssl ecparam -genkey -name prime256v1 -out server.key
openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.req
# country=cn, common name=server.example.com
openssl x509 -req -in server.req -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -out server.crt -CAcreateserial -days 365
服务端示例代码:
package main
// ...
func main() {
// load server certificate
cert, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair("./tls/server.crt", "./tls/server.key")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
// load root certificate
certBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile("./tls/ca.crt")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
caCertPool := x509.NewCertPool()
ok := caCertPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(certBytes)
if !ok {
panic("Failed to parse root certificate.")
}
// set server tls.Config
cfg := &tls.Config{
// add certificate
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{cert},
MaxVersion: tls.VersionTLS13,
// enable client authentication
ClientAuth: tls.RequireAndVerifyClientCert,
ClientCAs: caCertPool,
// cipher suites supported
CipherSuites: []uint16{
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,
},
// set application protocol http2
NextProtos: []string{http2.NextProtoTLS},
}
// set TLS server
// default is standard.NewTransporter
h := server.Default(server.WithTLS(cfg), server.WithHostPorts(":8443"))
h.GET("/ping", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "TLS test\n")
})
h.Spin()
}
完整用法示例详见 example 。
客户端
参数
在 tls.Config 中,除了上述基本参数,客户端可以配置的参数如下:
| 参数名 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| ServerName | 根据返回的证书信息验证主机名。 |
| InsecureSkipVerify | 用于客户端是否开启服务端的证书验证。 |
| RootCAs | 用于客户端验证服务端的证书。 |
客户端 TLS 主要流程:
- 载入根证书,用于验证服务器端的真实性。
- 载入客户证书,用于发送给服务器端以验证客户端的真实性。
- 配置
tls.Config。 - 使用
WithTLS配置客户端 TLS,默认使用标准库的 Dialer。
示例代码
通过 CA 签名,生成客户端的私钥和证书,命令如下:
openssl ecparam -genkey -name prime256v1 -out client.key
openssl req -new -key client.key -out client.req
# country=cn, common name=client.example.com
openssl x509 -req -in client.req -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -out client.crt -CAcreateserial -days 365
客户端示例代码:
package main
// ...
func main() {
// load root certificate to verify the client validity
certBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile("./tls/ca.crt")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
caCertPool := x509.NewCertPool()
ok := caCertPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(certBytes)
if !ok {
panic("Failed to parse root certificate.")
}
// load client certificate to send to server
cert, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair("./tls/client.crt", "./tls/client.key")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
// set TLS configuration
cfg := &tls.Config{
MaxVersion: tls.VersionTLS13,
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{cert},
// verify the server certificate
RootCAs: caCertPool,
// ignored the server certificate
InsecureSkipVerify: true,
}
c, err := client.NewClient(
// default dialer is standard
client.WithTLSConfig(cfg),
client.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()),
)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
// ...
}
完整用法示例详见 example 。
Autotls 中间件
Hertz 提供了 autotls 扩展适配 Let’s Encrypt ,方便用户进行 TLS 服务自动配置。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/autotls
配置
NewTlsConfig
autotls 扩展提供了 NewTlsConfig 用于帮助用户使用一行代码支持 LetsEncrypt HTTPS servers。
NewTlsConfig 函数签名如下:
func NewTlsConfig(domains ...string) *tls.Config
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/autotls"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default(
server.WithTLS(autotls.NewTlsConfig("example1.com", "example2.com")),
server.WithHostPorts(":https"),
)
// Ping handler
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(200, map[string]interface{}{
"ping": "pong",
})
})
hlog.Fatal(autotls.Run(h))
}
RunWithContext
autotls 扩展提供了 RunWithContext 用于帮助用户使用一行代码支持 LetsEncrypt HTTPS servers 的同时能够让服务优雅关机。
RunWithContext 函数签名如下:
func RunWithContext(ctx context.Context, h *server.Hertz) error
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"os/signal"
"syscall"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/autotls"
)
func main() {
// Create context that listens for the interrupt signal from the OS.
ctx, stop := signal.NotifyContext(
context.Background(),
syscall.SIGINT,
syscall.SIGTERM,
)
defer stop()
h := server.Default(
server.WithTLS(autotls.NewTlsConfig("example1.com", "example2.com")),
server.WithHostPorts(":https"),
)
// Ping handler
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(200, map[string]interface{}{
"ping": "pong",
})
})
hlog.Fatal(autotls.RunWithContext(ctx, h))
}
NewServerWithManagerAndTlsConfig
autotls 扩展提供了 NewServerWithManagerAndTlsConfig 用于帮助用户自动证书管理和 TLS 配置。
NewServerWithManagerAndTlsConfig 函数签名如下:
func NewServerWithManagerAndTlsConfig(m *autocert.Manager, tlsc *tls.Config, opts ...config.Option) *server.Hertz
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/autotls"
"golang.org/x/crypto/acme/autocert"
)
func main() {
m := autocert.Manager{
Prompt: autocert.AcceptTOS,
HostPolicy: autocert.HostWhitelist("example1.com", "example2.com"),
Cache: autocert.DirCache("/var/www/.cache"),
}
h := autotls.NewServerWithManagerAndTlsConfig(&m, nil)
// Ping handler
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(200, map[string]interface{}{
"ping": "pong",
})
})
hlog.Fatal(autotls.Run(h))
}
完整用法示例详见 example 。
注意
Client 报错 not support tls
Hertz 默认使用了 netpoll 作为网络库并且目前 netpoll 不支持 TLS。使用 TLS 需要切换到标准网络库,代码如下:
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/network/standard"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
)
func main() {
clientCfg := &tls.Config{
InsecureSkipVerify: true,
}
c, err := client.NewClient(
client.WithTLSConfig(clientCfg),
client.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()),
)
}
title: “Websocket” date: 2022-09-13 weight: 4 keywords: [“WebSocket”, “HTTP”, “hijack”, “TCP”] description: “Hertz 基于 hijack 的方式实现了对 WebSocket 的支持。”
WebSocket 是一种可以在单个 TCP 连接上进行全双工通信,位于 OSI 模型的应用层。WebSocket 使得客户端和服务器之间的数据交换变得更加简单,允许服务端主动向客户端推送数据。在 WebSocket API 中,浏览器和服务器只需要完成一次握手,两者之间就可以创建持久性的连接,并进行双向数据传输。
Hertz 提供了 WebSocket 的支持,参考 gorilla/websocket 库使用 hijack 的方式在
Hertz 进行了适配,用法和参数基本保持一致。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/websocket
示例代码
package main
import (
"context"
"flag"
"html/template"
"log"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/websocket"
)
var addr = flag.String("addr", "localhost:8080", "http service address")
var upgrader = websocket.HertzUpgrader{} // use default options
func echo(_ context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
err := upgrader.Upgrade(c, func(conn *websocket.Conn) {
for {
mt, message, err := conn.ReadMessage()
if err != nil {
log.Println("read:", err)
break
}
log.Printf("recv: %s", message)
err = conn.WriteMessage(mt, message)
if err != nil {
log.Println("write:", err)
break
}
}
})
if err != nil {
log.Print("upgrade:", err)
return
}
}
func home(_ context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.SetContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8")
homeTemplate.Execute(c, "ws://"+string(c.Host())+"/echo")
}
func main() {
flag.Parse()
h := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(*addr))
// https://github.com/cloudwego/hertz/issues/121
h.NoHijackConnPool = true
h.GET("/", home)
h.GET("/echo", echo)
h.Spin()
}
// 网络客户端代码详见:https://github.com/hertz-contrib/websocket/blob/main/examples/echo/server.go#L64,此处省略
var homeTemplate = ""
运行 server:
go run server.go
上述示例代码中,服务器包括一个简单的网络客户端。要使用该客户端,在浏览器中打开 http://127.0.0.1:8080,并按照页面上的指示操作。
配置
以下是 Hertz WebSocket 使用过程中可选的配置参数。
这部分将围绕 websocket.HertzUpgrader 结构展开说明。
| 参数 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
ReadBufferSize |
用于设置输入缓冲区的大小,单位为字节。如果缓冲区大小为零,那么就使用 HTTP 服务器分配的大小。输入缓冲区大小并不限制可以接收的信息的大小。 |
WriteBufferSize |
用于设置输出缓冲区的大小,单位为字节。如果缓冲区大小为零,那么就使用 HTTP 服务器分配的大小。输出缓冲区大小并不限制可以发送的信息的大小。 |
WriteBufferPool |
用于设置写操作的缓冲池。 |
Subprotocols |
用于按优先顺序设置服务器支持的协议。如果这个字段不是 nil,那么 Upgrade 方法通过选择这个列表中与客户端请求的协议的第一个匹配来协商一个子协议。如果没有匹配,那么就不协商协议(Sec-Websocket-Protocol 头不包括在握手响应中)。 |
Error |
用于设置生成 HTTP 错误响应的函数。 |
CheckOrigin |
用于设置针对请求的 Origin 头的校验函数,如果请求的 Origin 头是可接受的,CheckOrigin 返回 true。 |
EnableCompression |
用于设置服务器是否应该尝试协商每个消息的压缩(RFC 7692)。将此值设置为 true 并不能保证压缩会被支持。 |
WriteBufferPool
如果该值没有被设置,则额外初始化写缓冲区,并在当前生命周期内分配给该连接。当应用程序在大量的连接上有适度的写入量时,缓冲池是最有用的。
应用程序应该使用一个单一的缓冲池来为不同的连接分配缓冲区。
接口描述:
// BufferPool represents a pool of buffers. The *sync.Pool type satisfies this
// interface. The type of the value stored in a pool is not specified.
type BufferPool interface {
// Get gets a value from the pool or returns nil if the pool is empty.
Get() interface{}
// Put adds a value to the pool.
Put(interface{})
}
示例代码:
type simpleBufferPool struct {
v interface{}
}
func (p *simpleBufferPool) Get() interface{} {
v := p.v
p.v = nil
return v
}
func (p *simpleBufferPool) Put(v interface{}) {
p.v = v
}
var upgrader = websocket.HertzUpgrader{
WriteBufferPool: &simpleBufferPool{},
}
Subprotocols
WebSocket 只是定义了一种交换任意消息的机制。这些消息是什么意思,客户端在任何特定的时间点可以期待什么样的消息,或者他们被允许发送什么样的消息,完全取决于实现应用程序。
所以你需要在服务器和客户端之间就这些事情达成协议。子协议参数只是让客户端和服务端正式地交换这些信息。你可以为你想要的任何协议编造任何名字。服务器可以简单地检查客户在握手过程中是否遵守了该协议。
Error
如果 Error 为 nil,则使用 Hertz 提供的 API 来生成 HTTP 错误响应。
函数签名:
func(ctx *app.RequestContext, status int, reason error)
示例代码:
var upgrader = websocket.HertzUpgrader{
Error: func(ctx *app.RequestContext, status int, reason error) {
ctx.Response.Header.Set("Sec-Websocket-Version", "13")
ctx.AbortWithMsg(reason.Error(), status)
},
}
CheckOrigin
如果 CheckOrigin 为 nil,则使用一个安全的默认值:如果 Origin 请求头存在,并且源主机不等于请求主机头,则返回 false。CheckOrigin 函数应该仔细验证请求的来源,以防止跨站请求伪造。
函数签名:
func(ctx *app.RequestContext) bool
默认实现:
func fastHTTPCheckSameOrigin(ctx *app.RequestContext) bool {
origin := ctx.Request.Header.Peek("Origin")
if len(origin) == 0 {
return true
}
u, err := url.Parse(b2s(origin))
if err != nil {
return false
}
return equalASCIIFold(u.Host, b2s(ctx.Host()))
}
EnableCompression
服务端接受一个或者多个扩展字段,这些扩展字段是包含客户端请求的 Sec-WebSocket-Extensions 头字段扩展中的。当
EnableCompression 为 true 时,服务端根据当前自身支持的扩展与其进行匹配,如果匹配成功则支持压缩。
目前仅支持“无上下文接管”模式,详见 HertzUpgrader.Upgrade 的实现。
SetReadTimeout/SetWriteTimeout
当使用 websocket 进行读写的时候,可以通过类似如下方式设置读超时或写超时的时间。
示例代码:
func echo(_ context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
err := upgrader.Upgrade(c, func(conn *websocket.Conn) {
defer conn.Close()
// "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/network"
conn.NetConn().(network.Conn).SetReadTimeout(1 * time.Second)
conn.NetConn().(network.Conn).SetWriteTimeout(1 * time.Second)
...
})
if err != nil {
log.Print("upgrade:", err)
return
}
}
NoHijackConnPool
Hertz 连接劫持时所使用的 hijack conn 是池化管理的,因此被劫持的连接在 websocket 中使用的时候,不支持异步操作。
劫持的连接仅能被关闭一次,第二次关闭会导致空指针异常。
NoHijackConnPool 将控制是否使用缓存池来获取/释放劫持连接。如果使用池,将提升内存资源分配的性能,但无法避免二次关闭连接导致的异常。
如果很难保证 hijackConn 不会被反复关闭,可以将其设置为 true。
示例代码:
func main() {
...
// https://github.com/cloudwego/hertz/issues/121
h.NoHijackConnPool = true
...
}
更多用法示例详见 examples 。
title: “HTTP2” date: 2022-12-15 weight: 2 keywords: [“HTTP/2”, “HTTP”, “h2”, “h2c”] description: “Hertz 同时支持 h2 和 h2c。参考了 net/http2 的实现。”
HTTP/2 是对 HTTP “在线” 表达方式的一种替代。它并不是对协议的彻底重写;HTTP 方法、状态码和语义都是一样的,而且应该可以使用与 HTTP/1.x 相同的 API(可能会有一些小的补充)来表示协议。
协议的侧重点是性能:缩短用户感知的延迟、减少网络和服务器资源的使用。一个主要目标是允许使用从浏览器到网站的单一连接。
Hertz 同时支持 h2 和 h2c。参考了 net/http2 的实现。
示例代码
h2
package main
import (
"context"
"crypto/tls"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/network/standard"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/http2/config"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/http2/factory"
)
const (
keyPEM = `<your key PEM>`
certPEM = `<your cert PEM>`
)
func runClient() {
cli, _ := client.NewClient()
cli.SetClientFactory(factory.NewClientFactory(
config.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()),
config.WithTLSConfig(&tls.Config{InsecureSkipVerify: true})))
v, _ := json.Marshal(map[string]string{
"hello": "world",
"protocol": "h2",
})
for {
time.Sleep(time.Second * 1)
req, rsp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetRequestURI("https://127.0.0.1:8888")
req.SetBody(v)
err := cli.Do(context.Background(), req, rsp)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("[client]: received body: %s\n", string(rsp.Body()))
}
}
func main() {
cfg := &tls.Config{
MinVersion: tls.VersionTLS12,
CurvePreferences: []tls.CurveID{tls.X25519, tls.CurveP256},
CipherSuites: []uint16{
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,
},
}
cert, err := tls.X509KeyPair([]byte(certPEM), []byte(keyPEM))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
cfg.Certificates = append(cfg.Certificates, cert)
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8888"), server.WithALPN(true), server.WithTLS(cfg))
// register http2 server factory
h.AddProtocol("h2", factory.NewServerFactory(
config.WithReadTimeout(time.Minute),
config.WithDisableKeepAlive(false)))
cfg.NextProtos = append(cfg.NextProtos, "h2")
h.POST("/", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
var j map[string]string
_ = json.Unmarshal(ctx.Request.Body(), &j)
fmt.Printf("[server]: received request: %+v\n", j)
r := map[string]string{
"msg": "hello world",
}
for k, v := range j {
r[k] = v
}
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, r)
})
go runClient()
h.Spin()
}
h2c
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/http2/config"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/http2/factory"
)
func runClient() {
c, _ := client.NewClient()
c.SetClientFactory(factory.NewClientFactory(config.WithAllowHTTP(true)))
v, _ := json.Marshal(map[string]string{
"hello": "world",
"protocol": "h2c",
})
for {
time.Sleep(time.Second * 1)
req, rsp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetRequestURI("http://127.0.0.1:8888")
req.SetBody(v)
err := c.Do(context.Background(), req, rsp)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("client received body: %s\n", string(rsp.Body()))
}
}
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8888"), server.WithH2C(true))
// register http2 server factory
h.AddProtocol("h2", factory.NewServerFactory())
h.POST("/", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
var j map[string]string
_ = json.Unmarshal(ctx.Request.Body(), &j)
fmt.Printf("server received request: %+v\n", j)
r := map[string]string{
"msg": "hello world",
}
for k, v := range j {
r[k] = v
}
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, r)
})
go runClient()
h.Spin()
}
配置
服务端
| 配置 | 默认值 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
ReadTimeout |
0 |
建立连接后,从服务器读取到可用资源的超时时间 |
DisableKeepAlive |
false |
是否关闭 Keep-Alive模式 |
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"crypto/tls"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/network/standard"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/http2/config"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/http2/factory"
)
const (
keyPEM = `<your key PEM>`
certPEM = `<your cert PEM>`
)
func runClient() {
cli, _ := client.NewClient()
cli.SetClientFactory(factory.NewClientFactory(
config.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()),
config.WithTLSConfig(&tls.Config{InsecureSkipVerify: true})))
v, _ := json.Marshal(map[string]string{
"hello": "world",
"protocol": "h2",
})
for {
time.Sleep(time.Second * 1)
req, rsp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetRequestURI("https://127.0.0.1:8888")
req.SetBody(v)
err := cli.Do(context.Background(), req, rsp)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("[client]: received body: %s\n", string(rsp.Body()))
}
}
func main() {
cfg := &tls.Config{
MinVersion: tls.VersionTLS12,
CurvePreferences: []tls.CurveID{tls.X25519, tls.CurveP256},
CipherSuites: []uint16{
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,
},
}
cert, err := tls.X509KeyPair([]byte(certPEM), []byte(keyPEM))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
cfg.Certificates = append(cfg.Certificates, cert)
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8888"), server.WithALPN(true), server.WithTLS(cfg))
// register http2 server factory
h.AddProtocol("h2", factory.NewServerFactory(
config.WithReadTimeout(time.Minute),
config.WithDisableKeepAlive(false)))
cfg.NextProtos = append(cfg.NextProtos, "h2")
h.POST("/", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
var j map[string]string
_ = json.Unmarshal(ctx.Request.Body(), &j)
fmt.Printf("[server]: received request: %+v\n", j)
r := map[string]string{
"msg": "hello world",
}
for k, v := range j {
r[k] = v
}
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, r)
})
go runClient()
h.Spin()
}
WithReadTimeout
用于设置 ReadTimeout,默认值为 0。
函数签名:
func WithReadTimeout(t time.Duration) Option
WithDisableKeepAlive
用于设置是否禁用 keep-alive,默认不禁用。
函数签名:
func WithDisableKeepAlive(disableKeepAlive bool) Option
客户端
| 配置 | 默认值 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
MaxHeaderListSize |
0,指使用默认的限制(10MB) |
指 http2 规范中的SETTINGS_MAX_HEADER_LIST_SIZE。 |
AllowHTTP |
false |
设置是否允许 http,h2c 模式的开关 |
ReadIdleTimeout |
0,即不进行健康检查 |
若连接在该段时间间隔内未接收到任何帧,将使用ping帧进行健康检查。 |
PingTimeout |
15s |
超时时间,如果未收到对 Ping的响应,连接将在该超时时间后关闭。 |
WriteByteTimeout |
0 |
若在该段时间间隔内未写入任何数据,将关闭连接。 |
StrictMaxConcurrentStreams |
false |
设置服务器的SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS是否应该被全局使用。 |
DialTimeout |
1s |
与主机建立新连接的超时时间。 |
MaxIdleConnDuration |
0 |
闲置的长连接在该段时间后关闭。 |
DisableKeepAlive |
false |
是否在每次请求后关闭连接。 |
Dialer |
netpoll.NewDialer() |
用于设置拨号器。 |
TLSConfig |
nil |
TLS配置 |
RetryConfig |
nil |
所有与重试有关的配置 |
示例代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"crypto/tls"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client/retry"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/network/standard"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/http2/config"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/http2/factory"
)
const (
keyPEM = `<your key PEM>`
certPEM = `<your cert PEM>`
)
func runClient() {
cli, _ := client.NewClient()
cli.SetClientFactory(factory.NewClientFactory(
config.WithDialTimeout(3*time.Second),
config.WithReadIdleTimeout(1*time.Second),
config.WithWriteByteTimeout(time.Second),
config.WithPingTimeout(time.Minute),
config.WithMaxIdleConnDuration(2*time.Second),
config.WithClientDisableKeepAlive(true), //Close Connection after each request
config.WithStrictMaxConcurrentStreams(true), // Set the server's SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS to be respected globally.
config.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()), // You can customize dialer here
config.WithMaxHeaderListSize(0xffffffff), // Set SETTINGS_MAX_HEADER_LIST_SIZE to unlimited.
config.WithMaxIdempotentCallAttempts(3),
config.WithRetryConfig(
retry.WithMaxAttemptTimes(3),
retry.WithInitDelay(2*time.Millisecond),
retry.WithMaxDelay(200*time.Millisecond),
retry.WithMaxJitter(30*time.Millisecond),
retry.WithDelayPolicy(retry.FixedDelayPolicy),
),
config.WithStrictMaxConcurrentStreams(true), // Set the server's SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS to be respected globally.
config.WithTLSConfig(&tls.Config{
SessionTicketsDisabled: false,
InsecureSkipVerify: true,
}),
))
v, _ := json.Marshal(map[string]string{
"hello": "world",
"protocol": "h2",
})
for {
time.Sleep(time.Second * 1)
req, rsp := protocol.AcquireRequest(), protocol.AcquireResponse()
req.SetMethod("POST")
req.SetRequestURI("https://127.0.0.1:8888")
req.SetBody(v)
err := cli.Do(context.Background(), req, rsp)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("[client]: received body: %s\n", string(rsp.Body()))
}
}
func main() {
cfg := &tls.Config{
MinVersion: tls.VersionTLS12,
CurvePreferences: []tls.CurveID{tls.X25519, tls.CurveP256},
CipherSuites: []uint16{
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305,
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,
tls.TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,
},
}
cert, err := tls.X509KeyPair([]byte(certPEM), []byte(keyPEM))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
}
cfg.Certificates = append(cfg.Certificates, cert)
h := server.New(server.WithHostPorts(":8888"), server.WithALPN(true), server.WithTLS(cfg))
// register http2 server factory
h.AddProtocol("h2", factory.NewServerFactory(
config.WithReadTimeout(time.Minute),
config.WithDisableKeepAlive(false)))
cfg.NextProtos = append(cfg.NextProtos, "h2")
h.POST("/", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
var j map[string]string
_ = json.Unmarshal(ctx.Request.Body(), &j)
fmt.Printf("[server]: received request: %+v\n", j)
r := map[string]string{
"msg": "hello world",
}
for k, v := range j {
r[k] = v
}
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, r)
})
go runClient()
h.Spin()
}
WithMaxHeaderListSize
用于设置 SETTINGS_MAX_HEADER_LIST_SIZE。
与 HTTP2 规范不同,这里的0表示使用默认限制(目前是 10MB)。如果想表示无限,可以设置为一个尽可能大的值(0xffffffff
或 1<<32-1)。
函数签名:
func WithMaxHeaderListSize(maxHeaderListSize uint32) ClientOption
WithReadIdleTimeout
用于设置读取超时时间,超时后将使用ping帧进行健康检查。
注意,一个ping响应将被视为一个接收帧,所以如果连接上没有其他流量,健康检查将在每一个读取超时时间间隔内进行。
默认值为 0 表示不执行健康检查。
函数签名:
func WithReadIdleTimeout(readIdleTimeout time.Duration) ClientOption
WithWriteByteTimeout
用于设置写入超时时间,超时后连接将被关闭。当数据可以写入时开始计时,并随数据的写入不断延长。
函数签名:
func WithWriteByteTimeout(writeByteTimeout time.Duration) ClientOption
WithStrictMaxConcurrentStreams
用来设置服务器的SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS是否应该被全局使用。
函数签名:
func WithStrictMaxConcurrentStreams(strictMaxConcurrentStreams bool) ClientOption
WithPingTimeout
设置ping响应的超时时间,如果未收到对 Ping的响应,连接将在该超时时间后关闭。
默认为 15s
函数签名:
func WithPingTimeout(pt time.Duration) ClientOption
WithAllowHTTP
用于设置是否允许 http。如果启用,客户端将使用 h2c 模式。默认不启用。
函数签名:
func WithAllowHTTP(allow bool) ClientOption
WithDialer
支持自定义拨号器,默认为netpoll.NewDialer()。
函数签名:
func WithDialer(d network.Dialer) ClientOption
接口定义:
type Dialer interface {
// DialConnection is used to dial the peer end.
DialConnection(network, address string, timeout time.Duration, tlsConfig *tls.Config) (conn Conn, err error)
// DialTimeout is used to dial the peer end with a timeout.
//
// NOTE: Not recommended to use this function. Just for compatibility.
DialTimeout(network, address string, timeout time.Duration, tlsConfig *tls.Config) (conn net.Conn, err error)
// AddTLS will transfer a common connection to a tls connection.
AddTLS(conn Conn, tlsConfig *tls.Config) (Conn, error)
}
WithDialTimeout
用于设置与主机建立新连接的超时时间,默认为 1s。
函数签名:
func WithDialTimeout(timeout time.Duration) ClientOption
WithTLSConfig
用于自定义 TLS配置。
函数签名:
func WithTLSConfig(tlsConfig *tls.Config) ClientOption
WithMaxIdleConnDuration
用于设置长连接的最长闲置时间,超过该时间后连接关闭。默认为0。
函数签名:
func WithMaxIdleConnDuration(d time.Duration) ClientOption
WithMaxIdempotentCallAttempts
设置idempotent calls的最大尝试次数。
函数签名:
func WithMaxIdempotentCallAttempts(n int) ClientOption
WithRetryConfig
用于设置与重试有关的配置。
函数签名:
func WithRetryConfig(opts ...retry.Option) ClientOption
WithClientDisableKeepAlive
用于设置是否在每次请求后关闭连接。默认为false。
函数签名:
func WithClientDisableKeepAlive(disable bool) ClientOption
更多用法示例详见 hertz-contrib/http2。
title: “SSE” date: 2023-05-12 weight: 6 keywords: [“SSE”, “HTTP”, “Server-Sent Events”] description: “Hertz 支持 SSE,允许服务器端通过简单的 HTTP 响应向客户端发送事件。”
SSE 是 Server-Sent Events 的缩写,是一种服务器推送技术,它允许服务器端通过简单的 HTTP 响应向客户端发送事件。
hertz 的实现见 这里。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/sse
示例代码
在下面的示例中,在访问 /sse 时,服务端将每秒向客户端推送一个时间戳。
package main
import (
"context"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/sse"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.GET("/sse", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
// 客户端可以通过 Last-Event-ID 告知服务器收到的最后一个事件
lastEventID := sse.GetLastEventID(c)
hlog.CtxInfof(ctx, "last event ID: %s", lastEventID)
// 在第一次渲染调用之前必须先行设置状态代码和响应头文件
c.SetStatusCode(http.StatusOK)
s := sse.NewStream(c)
for t := range time.NewTicker(1 * time.Second).C {
event := &sse.Event{
Event: "timestamp",
Data: []byte(t.Format(time.RFC3339)),
}
err := s.Publish(event)
if err != nil {
return
}
}
})
h.Spin()
}
配置
NewStream
NewStream 用于创建一个流用于发送事件。在默认情况下,会设置 Content-Type 为 text/event-stream (
最好不要修改 Content-Type),Cache-Control 为 no-cache。
如果服务器和客户端之间有任何代理,那将建议设置响应头 X-Accel-Buffering 为 no。
函数签名:
func NewStream(c *app.RequestContext) *Stream
示例代码
package main
func main() {
h := server.Default()
h.GET("/sse", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.SetStatusCode(http.StatusOK)
c.Response.Header.Set("X-Accel-Buffering", "no")
s := sse.NewStream(c)
// ...
})
}
Publish
Publish 用于向客户端发送事件,事件的格式如下:
type Event struct {
// 事件名称
Event string
// 事件数据
Data []byte
// 事件标识符
ID string
// 事件重试时间
Retry time.Duration
}
函数签名:
func (c *Stream) Publish(event *Event) error
GetLastEventID
GetLastEventID 用于获取客户端发送的最后一个事件标识符。
函数签名:
func GetLastEventID(c *app.RequestContext) string
title: “协议” date: 2022-05-23 weight: 7 keywords: [“TLS”, “ALPN”, “Websocket”, “HTTP2”, “HTTP3”, “SSE”] description: “Hertz 支持的协议。”
TLS
Hertz Server & Client 目前只有 标准网络库 支持 TLS,Netpoll 网络库的支持还在路上。 使用参考: 示例
ALPN
开启 TLS 之后,可以通过开关控制 ALPN 是否开启(依赖当前是否通过 Protocol Suite 注册了所需要的所有协议 Servers)。
Websocket
Hertz 基于 hijack 的方式实现了对 WebSocket 的支持。
HTTP2
Hertz 参考 net/http2 实现了对 HTTP2 的支持,同时支持 h2 和 h2c。
HTTP3
Hertz 参考 quic-go 实现了对 HTTP3 的支持。
SSE
Hertz 支持 SSE,允许服务器端通过简单的 HTTP 响应向客户端发送事件。
title: “HTTP3” date: 2023-07-29 weight: 3 keywords: [“QUIC”, “HTTP”, “HTTP3”] description: “Hertz-HTTP3 基于 quic-go 实现。”
QUIC 协议是一种传输层网络协议,提供与 TLS/SSL 相当的安全性,同时具有更低的连接和传输延迟。QUIC 目前主要应用于 HTTP 协议,HTTP-over-QUIC 协议即为 HTTP/3,是 HTTP 协议的第三个正式版本。
Hertz-HTTP3 基于 quic-go 实现,实现链接。
关于 Hertz 为支持 Hertz-HTTP3 在网络传输层和协议层提供的接口设计方案可参考 Hertz 支持 QUIC & HTTP/3。
安装
go get github.com/hertz-contrib/http3
注意:go 版本需大于等于 1.19。
网络层与协议层注册
网络层注册
server.New(server.WithTransport(quic.NewTransporter))
协议层注册
server.New(server.WithTransport(quic.NewTransporter))
h.AddProtocol(suite.HTTP3, factory.NewServerFactory(&http3.Option{}))
配置说明
服务端
| 配置 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| WithTransport | 设置 HTTP3 实现的网络库 quic.NewTransporter |
| WithAltTransport | 设置备用网络库 netpoll 或 go net,适用于同时在 TCP 和 QUIC 监听的场景 |
| WithALPN | 设置是否启用 ALPN |
| WithTLS | 设置 TLS 配置 |
| WithHostPorts | 设置开启服务的域名和端口号 |
示例代码
服务端
注意:QUIC 协议依赖于 TLS 协议,因此需要提供 TLS 配置。
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/network/netpoll"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/suite"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/http3/network/quic-go"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/http3/network/quic-go/testdata"
http3 "github.com/hertz-contrib/http3/server/quic-go"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/http3/server/quic-go/factory"
)
type Test struct {
A string
B string
}
func main() {
run()
}
func run() {
h := server.New(server.WithALPN(true), server.WithTLS(testdata.GetTLSConfig()), server.WithTransport(quic.NewTransporter), server.WithAltTransport(netpoll.NewTransporter), server.WithHostPorts("127.0.0.1:8080"))
h.AddProtocol(suite.HTTP3, factory.NewServerFactory(&http3.Option{}))
h.GET("/demo/tile", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// Small 40x40 png
ctx.Write([]byte{
0x89, 0x50, 0x4e, 0x47, 0x0d, 0x0a, 0x1a, 0x0a, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0d,
0x49, 0x48, 0x44, 0x52, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x28, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x28,
0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xb6, 0x30, 0x2a, 0x2e, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x03, 0x50, 0x4c, 0x54, 0x45, 0x5a, 0xc3, 0x5a, 0xad, 0x38, 0xaa, 0xdb,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0b, 0x49, 0x44, 0x41, 0x54, 0x78, 0x01, 0x63, 0x18,
0x61, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xf0, 0x00, 0x01, 0xe2, 0xb8, 0x75, 0x22, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x49, 0x45, 0x4e, 0x44, 0xae, 0x42, 0x60, 0x82,
})
})
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.GET("/struct", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(consts.StatusOK, &Test{
A: "aaa",
B: "bbb",
})
})
v1 := h.Group("/v1")
{
v1.GET("/hello/:name", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx, "Hi %s, this is the response from Hertz.\n", ctx.Param("name"))
})
}
h.Spin()
}
客户端
Hertz-HTTP3 目前没有提供客户端的实现,但 服务端 示例代码的 TLS 配置直接拷贝于 quic-go ,因此可以直接使用 quic-go 中的 客户端示例代码 。
package main
import (
"bufio"
"bytes"
"context"
"crypto/tls"
"crypto/x509"
"flag"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"sync"
"github.com/quic-go/quic-go"
"github.com/quic-go/quic-go/http3"
"github.com/quic-go/quic-go/internal/testdata"
"github.com/quic-go/quic-go/internal/utils"
"github.com/quic-go/quic-go/logging"
"github.com/quic-go/quic-go/qlog"
)
func main() {
verbose := flag.Bool("v", false, "verbose")
quiet := flag.Bool("q", false, "don't print the data")
keyLogFile := flag.String("keylog", "", "key log file")
insecure := flag.Bool("insecure", false, "skip certificate verification")
enableQlog := flag.Bool("qlog", false, "output a qlog (in the same directory)")
flag.Parse()
urls := flag.Args()
logger := utils.DefaultLogger
if *verbose {
logger.SetLogLevel(utils.LogLevelDebug)
} else {
logger.SetLogLevel(utils.LogLevelInfo)
}
logger.SetLogTimeFormat("")
var keyLog io.Writer
if len(*keyLogFile) > 0 {
f, err := os.Create(*keyLogFile)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer f.Close()
keyLog = f
}
pool, err := x509.SystemCertPool()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
testdata.AddRootCA(pool)
var qconf quic.Config
if *enableQlog {
qconf.Tracer = func(ctx context.Context, p logging.Perspective, connID quic.ConnectionID) logging.ConnectionTracer {
filename := fmt.Sprintf("client_%x.qlog", connID)
f, err := os.Create(filename)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
log.Printf("Creating qlog file %s.\n", filename)
return qlog.NewConnectionTracer(utils.NewBufferedWriteCloser(bufio.NewWriter(f), f), p, connID)
}
}
roundTripper := &http3.RoundTripper{
TLSClientConfig: &tls.Config{
RootCAs: pool,
InsecureSkipVerify: *insecure,
KeyLogWriter: keyLog,
},
QuicConfig: &qconf,
}
defer roundTripper.Close()
hclient := &http.Client{
Transport: roundTripper,
}
var wg sync.WaitGroup
wg.Add(len(urls))
for _, addr := range urls {
logger.Infof("GET %s", addr)
go func(addr string) {
rsp, err := hclient.Get(addr)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
logger.Infof("Got response for %s: %#v", addr, rsp)
body := &bytes.Buffer{}
_, err = io.Copy(body, rsp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
if *quiet {
logger.Infof("Response Body: %d bytes", body.Len())
} else {
logger.Infof("Response Body:")
logger.Infof("%s", body.Bytes())
}
wg.Done()
}(addr)
}
wg.Wait()
}
title: “Response 的 Writer 扩展” linkTitle: “Response 的 Writer 扩展” date: 2023-03-10 weight: 6 keywords: [ “Response 的 Writer 扩展”, “Response.HijackWriter” ] description: “Hertz 提供的 Response 的 Writer 扩展。”
Hertz 提供了 response 的 writer 扩展,用户可以根据自己的需要实现相应的接口去劫持 response 的 writer。
接口定义
接口定义在 pkg/network/writer.
type ExtWriter interface {
io.Writer
Flush() error
// Finalize will be called by framework before the writer is released.
// Implementations must guarantee that Finalize is safe for multiple calls.
Finalize() error
}
劫持 Response 的 Writer
Hertz 在 app.RequestContext 中提供了 Response.HijackWriter 方法让用户劫持 response 的 writer.
用法示例:
h.GET("/hijack", func (c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// Hijack the writer of response
ctx.Response.HijackWriter(yourResponseWriter)
})
已支持 Response 的 Writer 扩展
Hertz 在 pkg/protocol/http1/resp/writer 下提供了 NewChunkedBodyWriter 方法来创建一个 response 的 writer,它允许用户在
handler 中立即刷新分块,用户也可以实现自己的 response 的 writer。
ChunkedBodyWriter
用法示例:
h.GET("/flush/chunk", func (c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// Hijack the writer of response
ctx.Response.HijackWriter(resp.NewChunkedBodyWriter(&ctx.Response, ctx.GetWriter()))
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
ctx.Write([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("chunk %d: %s", i, strings.Repeat("hi~", i)))) // nolint: errcheck
ctx.Flush() // nolint: errcheck
time.Sleep(200 * time.Millisecond)
}
})
title: “网络库扩展” linkTitle: “网络库扩展” weight: 4 keywords: [“网络库扩展”, “network.Conn”, “network.StreamConn”, “network.Dialer”] description: “Hertz 提供的网络库扩展。”
Hertz 提供了网络库扩展的能力。用户如果需要更换其他的网络库,可以根据需求实现对应的接口。Server 需要实现 network.Conn
或 network.StreamConn 接口,Client 需要实现 network.Dialer 接口。
Server 接口定义
network.Conn
该接口通常用于实现基于字节流的连接,如 TCP 连接。
type Conn interface {
net.Conn
Reader
Writer
SetReadTimeout(t time.Duration) error
}
// Reader is for buffered Reader
type Reader interface {
// Peek returns the next n bytes without advancing the reader.
Peek(n int) ([]byte, error)
// Skip discards the next n bytes.
Skip(n int) error
// Release the memory space occupied by all read slices. This method needs to be executed actively to
// recycle the memory after confirming that the previously read data is no longer in use.
// After invoking Release, the slices obtained by the method such as Peek will
// become an invalid address and cannot be used anymore.
Release() error
// Len returns the total length of the readable data in the reader.
Len() int
// ReadByte is used to read one byte with advancing the read pointer.
ReadByte() (byte, error)
// ReadBinary is used to read next n byte with copy, and the read pointer will be advanced.
ReadBinary(n int) (p []byte, err error)
}
type Writer interface {
// Malloc will provide a n bytes buffer to send data.
Malloc(n int) (buf []byte, err error)
// WriteBinary will use the user buffer to flush.
// NOTE: Before flush successfully, the buffer b should be valid.
WriteBinary(b []byte) (n int, err error)
// Flush will send data to the peer end.
Flush() error
}
network.StreamConn
该接口通常用于实现基于流的连接,如 QUIC 连接。
// StreamConn is interface for stream-based connection abstraction.
type StreamConn interface {
GetRawConnection() interface{}
// HandshakeComplete blocks until the handshake completes (or fails).
HandshakeComplete() context.Context
// CloseWithError closes the connection with an error.
// The error string will be sent to the peer.
CloseWithError(err ApplicationError, errMsg string) error
// LocalAddr returns the local address.
LocalAddr() net.Addr
// RemoteAddr returns the address of the peer.
RemoteAddr() net.Addr
// The context is cancelled when the connection is closed.
Context() context.Context
// Streamer is the interface for stream operations.
Streamer
}
type Streamer interface {
// AcceptStream returns the next stream opened by the peer, blocking until one is available.
// If the connection was closed due to a timeout, the error satisfies
// the net.Error interface, and Timeout() will be true.
AcceptStream(context.Context) (Stream, error)
// AcceptUniStream returns the next unidirectional stream opened by the peer, blocking until one is available.
// If the connection was closed due to a timeout, the error satisfies
// the net.Error interface, and Timeout() will be true.
AcceptUniStream(context.Context) (ReceiveStream, error)
// OpenStream opens a new bidirectional QUIC stream.
// There is no signaling to the peer about new streams:
// The peer can only accept the stream after data has been sent on the stream.
// If the error is non-nil, it satisfies the net.Error interface.
// When reaching the peer's stream limit, err.Temporary() will be true.
// If the connection was closed due to a timeout, Timeout() will be true.
OpenStream() (Stream, error)
// OpenStreamSync opens a new bidirectional QUIC stream.
// It blocks until a new stream can be opened.
// If the error is non-nil, it satisfies the net.Error interface.
// If the connection was closed due to a timeout, Timeout() will be true.
OpenStreamSync(context.Context) (Stream, error)
// OpenUniStream opens a new outgoing unidirectional QUIC stream.
// If the error is non-nil, it satisfies the net.Error interface.
// When reaching the peer's stream limit, Temporary() will be true.
// If the connection was closed due to a timeout, Timeout() will be true.
OpenUniStream() (SendStream, error)
// OpenUniStreamSync opens a new outgoing unidirectional QUIC stream.
// It blocks until a new stream can be opened.
// If the error is non-nil, it satisfies the net.Error interface.
// If the connection was closed due to a timeout, Timeout() will be true.
OpenUniStreamSync(context.Context) (SendStream, error)
}
type Stream interface {
ReceiveStream
SendStream
}
type ReceiveStream interface {
StreamID() int64
io.Reader
// CancelRead aborts receiving on this stream.
// It will ask the peer to stop transmitting stream data.
// Read will unblock immediately, and future Read calls will fail.
// When called multiple times or after reading the io.EOF it is a no-op.
CancelRead(err ApplicationError)
// SetReadDeadline sets the deadline for future Read calls and
// any currently-blocked Read call.
// A zero value for t means Read will not time out.
SetReadDeadline(t time.Time) error
}
type SendStream interface {
StreamID() int64
// Writer writes data to the stream.
// Write can be made to time out and return a net.Error with Timeout() == true
// after a fixed time limit; see SetDeadline and SetWriteDeadline.
// If the stream was canceled by the peer, the error implements the StreamError
// interface, and Canceled() == true.
// If the connection was closed due to a timeout, the error satisfies
// the net.Error interface, and Timeout() will be true.
io.Writer
// CancelWrite aborts sending on this stream.
// Data already written, but not yet delivered to the peer is not guaranteed to be delivered reliably.
// Write will unblock immediately, and future calls to Write will fail.
// When called multiple times or after closing the stream it is a no-op.
CancelWrite(err ApplicationError)
// Closer closes the write-direction of the stream.
// Future calls to Write are not permitted after calling Close.
// It must not be called concurrently with Write.
// It must not be called after calling CancelWrite.
io.Closer
// The Context is canceled as soon as the write-side of the stream is closed.
// This happens when Close() or CancelWrite() is called, or when the peer
// cancels the read-side of their stream.
Context() context.Context
// SetWriteDeadline sets the deadline for future Write calls
// and any currently-blocked Write call.
// Even if write times out, it may return n > 0, indicating that
// some data was successfully written.
// A zero value for t means Write will not time out.
SetWriteDeadline(t time.Time) error
}
type ApplicationError interface {
ErrCode() uint64
fmt.Stringer
}
Client 接口定义
实现以下接口就可以替换 Client 侧的网络库。
type Dialer interface {
DialConnection(network, address string, timeout time.Duration, tlsConfig *tls.Config) (conn Conn, err error)
DialTimeout(network, address string, timeout time.Duration, tlsConfig *tls.Config) (conn net.Conn, err error)
AddTLS(conn Conn, tlsConfig *tls.Config) (Conn, error)
}
自定义网络库
Hertz 的 Server 和 Client 分别提供了初始化配置项用于注册自定义的网络库。
Server
server.New(server.WithTransport(YOUR_TRANSPORT))
Client
client.NewClient(client.WithDialer(YOUR_DIALER))
title: “服务注册与发现扩展” date: 2022-08-14 weight: 3 keywords: [“服务注册与发现扩展”, “服务注册扩展”, “服务发现扩展”, “负载均衡扩展”] description: “Hertz 提供的服务注册与发现扩展。”
服务注册扩展
Hertz 支持自定义注册模块,使用者可自行扩展集成其他注册中心,该扩展定义在 pkg/app/server/registry 下。
接口定义与 Info 定义
- 接口定义
// Registry is extension interface of service registry.
type Registry interface {
Register(info *Info) error
Deregister(info *Info) error
}
- Info 定义
// Info is used for registry.
// The fields are just suggested, which is used depends on design.
type Info struct {
ServiceName string
Addr net.Addr
Weight int
// extend other infos with Tags.
Tags map[string]string
}
集成到 Hertz
- 通过
server.WithRegistry指定自己的注册模块和自定义的注册信息。
h := server.Default(
server.WithHostPorts(addr),
server.WithRegistry(r, ®istry.Info{
ServiceName: "hertz.test.demo",
Addr: utils.NewNetAddr("tcp", addr),
Weight: 10,
Tags: nil,
}))
服务发现扩展
接口定义
Hertz 支持自定义发现模块,使用者可自行扩展集成其他注册中心,该扩展定义在 pkg/app/client/discovery 下。
type Resolver interface {
// Target should return a description for the given target that is suitable for being a key for cache.
Target(ctx context.Context, target *TargetInfo) string
// Resolve returns a list of instances for the given description of a target.
Resolve(ctx context.Context, desc string) (Result, error)
// Name returns the name of the resolver.
Name() string
}
type TargetInfo struct {
Host string
Tags map[string]string
}
type Result struct {
CacheKey string // 缓存的唯一 key
Instances []Instance // 服务发现结果
}
Resolver 接口定义如下:
Resolve:作为Resolver的核心方法,从 target key 中获取我们需要的服务发现结果Result。Target:从 Hertz 提供的对端 TargetInfo 中解析出Resolve需要使用的唯一 target, 同时这个 target 将作为缓存的唯一 key。Name:用于指定 Resolver 的唯一名称,同时 Hertz 会用它来缓存和复用 Resolver。
集成到 Hertz
通过使用 Hertz 提供的 Discovery 中间件,指定自定义的服务发现扩展。
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r := nacos_demo.NewNacosResolver()
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r))
注意事项
- 我们通过复用 Resolver 的方式来提高性能,要求 Resolver 的方法实现需要是并发安全的。
负载均衡扩展
Hertz 默认提供了 WeightedRandom 负载均衡实现,同时也支持自定义负载均衡实现,该扩展定义在 pkg/app/client/loadbalance 下
接口定义
// Loadbalancer picks instance for the given service discovery result.
type Loadbalancer interface {
// Pick is used to select an instance according to discovery result
Pick(discovery.Result) discovery.Instance
// Rebalance is used to refresh the cache of load balance's information
Rebalance(discovery.Result)
// Delete is used to delete the cache of load balance's information when it is expired
Delete(string)
// Name returns the name of the Loadbalancer.
Name() string
}
集成到 Hertz
通过使用 Hertz 提供的 Discovery 中间件,指定自定义的服务发现扩展的同时也可以使用 sd.WithLoadBalanceOptions 指定自定义负载均衡扩展。
cli, err := client.NewClient()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
r := nacos_demo.NewNacosResolver()
cli.Use(sd.Discovery(r, sd.WithLoadBalanceOptions(***,***)))
title: “监控扩展” linkTitle: “监控扩展” weight: 1 keywords: [“监控扩展”] description: “Hertz 提供的监控扩展。”
用户如果需要更详细的打点,例如包大小,或者想要更换其他数据源,例如 influxDB,用户可以根据自己的需求实现 Tracer
接口,并通过 WithTracer Option 来注入。
// Tracer is executed at the start and finish of an HTTP.
type Tracer interface {
Start(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) context.Context
Finish(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext)
}
从 ctx 中可以获得 TraceInfo,进一步的从 TraceInfo 中获取请求耗时、包大小和请求返回的错误信息等,举例:
type ServerTracer struct{
// contain entities which recording metric
}
// Start record the beginning of an RPC invocation.
func (s *ServerTracer) Start(ctx context.Context, _ *app.RequestContext) context.Context {
// do nothing
return ctx
}
// Finish record after receiving the response of server.
func (s *ServerTracer) Finish(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
ti := c.GetTraceInfo()
rpcStart := ti.Stats().GetEvent(stats.HTTPStart)
rpcFinish := ti.Stats().GetEvent(stats.HTTPFinish)
cost := rpcFinish.Time().Sub(rpcStart.Time())
// TODO: record the cost of request
}
title: “框架扩展” linkTitle: “框架扩展” weight: 5 keywords: [“框架扩展”, “日志扩展”, “监控扩展”, “服务注册与发现扩展”, “网络库扩展”, “协议扩展”, “Response 的 Writer 扩展”] description: “Hertz 为用户提供的框架扩展能力。”
title: “协议扩展” linkTitle: “协议扩展” weight: 5 keywords: [“协议扩展”, “protocol.Server”, “protocol.StreamServer”, “HTTP”] description: “Hertz 提供的协议扩展。”
得益于 Hertz 的分层设计,除了 Hertz 框架默认自带的 HTTP1/HTTP2/HTTP3 等协议
server,框架的使用者还可以通过 protocol.Server 或 protocol.StreamServer 接口自定义协议 server。
接口定义
protocol.Server
该接口可用于实现基于字节流传输的协议 server,如 HTTP1/HTTP2。
注意:若使用该接口,底层网络库需实现 network.Conn 接口。
type Server interface {
Serve(c context.Context, conn network.Conn) error
}
type ServerFactory interface {
New(core Core) (server protocol.Server, err error)
}
// Core is the core interface that promises to be provided for the protocol layer extensions
type Core interface {
// IsRunning Check whether engine is running or not
IsRunning() bool
// A RequestContext pool ready for protocol server impl
GetCtxPool() *sync.Pool
// Business logic entrance
// After pre-read works, protocol server may call this method
// to introduce the middlewares and handlers
ServeHTTP(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext)
// GetTracer for tracing requirement
GetTracer() tracer.Controller
}
protocol.StreamServer
该接口可用于实现基于流传输的协议 server,如 HTTP3。
注意:若使用该接口,底层网络库需实现 network.streamConn 接口。
type StreamServer interface {
Serve(c context.Context, conn network.StreamConn) error
}
type ServerFactory interface {
New(core Core) (server protocol.Server, err error)
}
// Core is the core interface that promises to be provided for the protocol layer extensions
type Core interface {
// IsRunning Check whether engine is running or not
IsRunning() bool
// A RequestContext pool ready for protocol server impl
GetCtxPool() *sync.Pool
// Business logic entrance
// After pre-read works, protocol server may call this method
// to introduce the middlewares and handlers
ServeHTTP(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext)
// GetTracer for tracing requirement
GetTracer() tracer.Controller
}
协议层扩展三要素
以 protocol.Server 接口为例说明协议层扩展的三要素,protocol.StreamServer 接口的扩展与之类似。
协议层 server 初始化
前面提到的接口其实就是网络层将数据准备好之后的一个标准回调,即当有新的请求建立连接之后,进入到我们的协议层的处理逻辑。 在这个逻辑中我们可以自定义诸如协议解析方式,引入业务 Handler 执行,数据写回等协议层标准行为。这也是我们的自定义 server 的核心逻辑所在。
type myServer struct{
xxx
xxx
}
func (s *myServer)Serve(c context.Context, conn network.Conn) error{
// 解析协议
...
// 转到业务注册的逻辑函数(路由、中间件、Handler)
...
// 将数据写回
...
}
定义一个协议处理逻辑就这么简单,不过解析协议、将数据写回这两个步骤通过入参中提供的 conn 接口能够轻易达成,但转到业务注册的逻辑函数这一步是如何办到的呢?
与上层逻辑交互
一个完整的协议一定少不了引入业务逻辑控制(极少数特殊场景除外),在 Hertz 框架中自定义的协议是如何实现这部分能力的呢?其实,在自定义 server 初始化的过程中,框架已经天然的将这部分能力交给自定义协议 server 了。
type ServerFactory interface {
New(core Core) (server protocol.Server, err error)
}
// Core is the core interface that promises to be provided for the protocol layer extensions
type Core interface {
// IsRunning Check whether engine is running or not
IsRunning() bool
// A RequestContext pool ready for protocol server impl
GetCtxPool() *sync.Pool
// Business logic entrance
// After pre-read works, protocol server may call this method
// to introduce the middlewares and handlers
ServeHTTP(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext)
// GetTracer for tracing requirement
GetTracer() tracer.Controller
}
自定义 server 只需要按照以上接口实现一个协议 server 生成工厂即可,入参里面的 Core,其实就是包含了引入上层逻辑交互以及其他核心应用层接口的具体实现,在初始化自定义 server 的时候, 正常情况只需要将 Core 保存到 server 中,当需要转到业务逻辑时,通过 Core 即可将流程引导到应用层处理逻辑(路由、中间件、逻辑 Handler),当业务逻辑执行完毕返回后,即可根据业务数据进行进一步的数据包写回。
type myServer struct{
suite.Core
xxx
}
func (s *myServer)Serve(c context.Context, conn network.Conn) error{
// 解析协议
...
Core.ServeHTTP(c, ctx)
// 将数据写回
...
}
至此,一个自定义的协议层 server 就开发完毕了。
注册自定义协议 server 到 Hertz 中
按照上述接口完成 server 生成工厂的开发后,将其加载到 Hertz 当中来就非常的容易了,我们在 Hertz 的核心引擎上面天然提供了一个注册自定义协议 server 的接口:
func (engine *Engine) AddProtocol(protocol string, factory suite.ServerFactory) {
engine.protocolSuite.Add(protocol, factory)
}
只需要按照接口指定的参数将我们的自定义 server 生成工厂注册到 engine 上即可。值得注意的一点是,这里注册的
protocol(string)其实和 ALPN 中的协议协商 key 也是一一对应的,
所以,如果是想通过 ALPN 的方式接入自定义的协议 server,直接将 key 指定为对应的 ALPN 协商时的 key 即可。当前 Hertz 默认集成了一个
HTTP1 的协议 server(对应的 key 为"http/1.1"),
如果有自定义 HTTP1 协议处理逻辑的需求,在 AddProtocol 时直接将 key 指定为"http/1.1"即可完成覆盖。
示例代码
以 protocol.Server 接口为例说明,protocol.StreamServer 接口与之类似。
package main
import (
"bytes"
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/errors"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/network"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/suite"
)
type myServer struct {
suite.Core
}
func (m myServer) Serve(c context.Context, conn network.Conn) error {
firstThreeBytes, _ := conn.Peek(3)
if !bytes.Equal(firstThreeBytes, []byte("GET")) {
return errors.NewPublic("not a GET method")
}
ctx := m.GetCtxPool().Get().(*app.RequestContext)
defer func() {
m.GetCtxPool().Put(ctx)
conn.Skip(conn.Len())
conn.Flush()
}()
ctx.Request.SetMethod("GET")
ctx.Request.SetRequestURI("/test")
m.ServeHTTP(c, ctx)
conn.WriteBinary([]byte("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n" +
"Server: hertz\n" +
"Date: Sun, 29 May 2022 10:49:33 GMT\n" +
"Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8\n" +
"Content-Length: 2\n\nok\n"))
return nil
}
type serverFactory struct {
}
func (s *serverFactory) New(core suite.Core) (server protocol.Server, err error) {
return &myServer{
core,
}, nil
}
func main() {
h := server.New()
h.GET("/test", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
hlog.Info("in handler")
})
h.AddProtocol("http/1.1", &serverFactory{})
h.Spin()
}
title: “zerolog” linkTitle: “zerolog” weight: 4 keywords: [“日志扩展”, “zerolog”] description: “Hertz 对接 zerolog 和 lumberjack。”
Logger
var _ hlog.FullLogger = (*Logger)(nil)
type Logger struct {
log zerolog.Logger
out io.Writer
level zerolog.Level
options []Opt
}
New
New 通过 newLogger 函数返回一个新的 Logger 实例
函数签名:
func New(options ...Opt) *Logger
示例代码:
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
)
func main() {
hlog.SetLogger(hertzZerolog.New())
}
From
From 通过 newLogger 用一个已存在的 Logger 返回一个新的 Logger
函数签名:
func From(log zerolog.Logger, options ...Opt) *Logger
示例代码:
package main
import (
"bytes"
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
"github.com/rs/zerolog"
)
func main() {
b := &bytes.Buffer{}
zl := zerolog.New(b).With().Str("key", "test").Logger()
l := hertzZerolog.From(zl)
l.Info("foo")
}
GetLogger
GetLogger 通过 DefaultLogger() 方法返回默认的 Logger 实例和 error
函数签名:
func GetLogger() (Logger, error)
示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
)
func main() {
logger, err := hertzZerolog.GetLogger()
if err != nil {
fmt.printf("get logger failed")
}
}
Option 的相关配置
WithOutput
WithOutput 通过 zerolog 内置的 zerolog.Context.Logger().Output(out).With() 返回一个 Opt 的函数,允许指定 logger
的输出。默认情况下,它设置为 os.Stdout。
函数签名:
func WithOutput(out io.Writer) Opt
示例代码:
package main
import (
"bytes"
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
)
func main() {
b := &bytes.Buffer{}
l := hertzZerolog.New(hertzZerolog.WithOutput(b))
l.Info("foobar")
}
WithLevel
WithLevel 通过 zerolog 内置的 zerolog.Context.Logger().Level(lvl).With() 方法指定 logger
的级别。通过 matchHlogLevel() 将 hlog.Level 转换成 zerolog.level。默认情况下,它设置为 WarnLevel。
函数签名:
func WithLevel(level hlog.Level) Opt
示例代码:
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
)
func main() {
l := hertzZerolog.New(hertzZerolog.WithLevel(hlog.LevelDebug))
l.Debug("foobar")
}
WithField
WithField 通过 zerolog 内置的 zerolog.Context.Interface(name, value) 方法向 logger 的 context 添加一个字段
函数签名:
func WithField(name string, value interface{}) Opt
示例代码:
package main
import (
"bytes"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/json"
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
)
func main() {
b := &bytes.Buffer{}
l := hertzZerolog.New(hertzZerolog.WithField("service", "logging"))
l.SetOutput(b)
l.Info("foobar")
type Log struct {
Level string `json:"level"`
Service string `json:"service"`
Message string `json:"message"`
}
log := &Log{}
err := json.Unmarshal(b.Bytes(), log)//log.service=="logging"
}
WithFields
WithFields 通过 zerolog 内置的 zerolog.Context.Fields(fields) 向 logger 的 context 添加一些字段
函数签名:
func WithFields(fields map[string]interface{}) Opt
示例代码:
package main
import (
"bytes"
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
)
func main() {
b := &bytes.Buffer{}
l := hertzZerolog.New(hertzZerolog.WithFields(map[string]interface{}{
"host": "localhost",
"port": 8080,
})) //...
}
WithTimestamp
WithTimestamp 通过 zerolog 内置的 zerolog.Context.Timestamp() 将时间戳字段添加到 logger 的 context 中
函数签名:
func WithTimestamp() Opt
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
)
func main() {
l := hertzZerolog.New(hertzZerolog.WithTimestamp())
l.Info("foobar")
}
WithFormattedTimestamp
WithFormattedTimestamp 与 WithTimestamp 类似,将格式化的时间戳字段添加到 logger 的 context 中
函数签名:
func WithFormattedTimestamp(format string) Opt
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
"time"
)
func main() {
l := hertzZerolog.New(hertzZerolog.WithFormattedTimestamp(time.RFC3339Nano))
l.Info("foobar")
}
WithCaller
WithCaller 通过 zerolog 内置的 zerolog.Context.Caller() 添加一个 caller 到 logger 的 context 中,caller 会报告调用者的信息
函数签名:
func WithCaller() Opt
示例代码:
//获取路径的最后一个元素
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
"path/filepath"
"strings"
)
func main() {
b := &bytes.Buffer{}
l := zerolog.New(zerolog.WithCaller())//添加了一个调用者
l.SetOutput(b)
l.Info("foobar")
type Log struct {
Level string `json:"level"`
Caller string `json:"caller"`
Message string `json:"message"`
}
log := &Log{}
err := json.Unmarshal(b.Bytes(), log)
if err!=nil {
//...
}
segments := strings.Split(log.Caller, ":")
filePath := filepath.Base(segments[0]) //filepath=="logger.go"
}
WithHook
WithHook 通过 zerolog 内置的 zerolog.Context.Logger().Hook(hook).With() 添加一个 hook 到 logger 的 context 中
函数签名:
func WithHook(hook zerolog.Hook) Opt
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
"github.com/rs/zerolog"
)
type Hook struct {
logs []HookLog
}
type HookLog struct {
level zerolog.Level
message string
}
func main() {
h := Hook{}
l := hertzZerolog.New(hertzZerolog.WithHook(h))
l.Info("Foo")
l.Warn("Bar")
//h.logs[0].level==zerolog.InfoLevel
//h.logs[0].message=="Foo"
//h.logs[1].level==zerolog.WarnLevel
//h.logs[1].message=="Bar"
}
WithHookFunc
WithHookFunc 与 WithHook 类似,添加一个 hook 函数到 logger 的 context 中
函数签名:
func WithHookFunc(hook zerolog.HookFunc) Opt
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
"github.com/rs/zerolog"
)
type HookLog struct {
level zerolog.Level
message string
}
func main() {
logs := make([]HookLog, 0, 2)
l := hertzZerolog.New(hertzZerolog.WithHookFunc(func(e *zerolog.Event, level zerolog.Level, message string) {
logs = append(logs, HookLog{
level: level,
message: message,
})
}))
l.Info("Foo")
l.Warn("Bar")
//h.logs[0].level==zerolog.InfoLevel
//h.logs[0].message=="Foo"
//h.logs[1].level==zerolog.WarnLevel
//h.logs[1].message=="Bar"
}
一个完整的 zerolog 示例
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"os"
"path"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
"gopkg.in/natefinch/lumberjack.v2"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
// 可定制的输出目录。
var logFilePath string
dir := "./hlog"
logFilePath = dir + "/logs/"
if err := os.MkdirAll(logFilePath, 0o777); err != nil {
log.Println(err.Error())
return
}
// 将文件名设置为日期
logFileName := time.Now().Format("2006-01-02") + ".log"
fileName := path.Join(logFilePath, logFileName)
if _, err := os.Stat(fileName); err != nil {
if _, err := os.Create(fileName); err != nil {
log.Println(err.Error())
return
}
}
logger := hertzZerolog.New()
// 提供压缩和删除
lumberjackLogger := &lumberjack.Logger{
Filename: fileName,
MaxSize: 20, // 一个文件最大可达 20M。
MaxBackups: 5, // 最多同时保存 5 个文件。
MaxAge: 10, // 一个文件最多可以保存 10 天。
Compress: true, // 用 gzip 压缩。
}
logger.SetOutput(lumberjackLogger)
logger.SetLevel(hlog.LevelDebug)
hlog.SetLogger(logger)
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
hlog.Info("Hello, hertz")
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "Hello hertz!")
})
h.Spin()
}
适配 hlog 的接口的方法等更多用法详见 hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog。
title: “logrus” linkTitle: “logrus” weight: 2 keywords: [“日志扩展”, “logrus”] description: “Hertz 对接 logrus 和 lumberjack。”
Logger
var _ hlog.FullLogger = (*Logger)(nil)
// Logger logrus impl
type Logger struct {
l *logrus.Logger
}
NewLogger
NewLogger 通过 defaultConfig() 来创建并初始化一个
Logger,便于后续的调用,可将所需配置作为参数传入函数,若不传入参数则安装初始配置创建 Logger
相关配置请参考后面的“option 的配置”。
函数签名:
func NewLogger(opts ...Option) *Logger
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzlogrus "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/logrus"
"github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
)
func main() {
logger := hertzlogrus.NewLogger(hertzlogrus.WithLogger(logrus.New()))
}
option 的相关配置
WithLogger
WithLogger 将 logrus.Logger 传入配置
函数签名:
func WithLogger(logger *logrus.Logger) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzlogrus "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/logrus"
"github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
)
func main() {
stdLogger := logrus.StandardLogger()
l:=hertzlogrus.NewLogger(hertzlogrus.WithLogger(stdLogger))
}
WithHook
WithHook 将传入的 logrus.Hook 添加进配置中的 hook
函数签名:
func WithHook(hook logrus.Hook) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzlogrus "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/logrus"
"github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
)
func main() {
var h logrus.Hook
l := hertzlogrus.NewLogger(hertzlogrus.WithHook(h))
l.Info("Foo")
l.Warn("Bar")
//h.logs[0].level==zerolog.InfoLevel
//h.logs[0].message=="Foo"
//h.logs[1].level==zerolog.WarnLevel
//h.logs[1].message=="Bar"
}
一个完整的 logrus 示例
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"os"
"path"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
hertzlogrus "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/logrus"
"gopkg.in/natefinch/lumberjack.v2"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
// 可定制的输出目录。
var logFilePath string
dir := "./hlog"
logFilePath = dir + "/logs/"
if err := os.MkdirAll(logFilePath, 0o777); err != nil {
log.Println(err.Error())
return
}
// 将文件名设置为日期
logFileName := time.Now().Format("2006-01-02") + ".log"
fileName := path.Join(logFilePath, logFileName)
if _, err := os.Stat(fileName); err != nil {
if _, err := os.Create(fileName); err != nil {
log.Println(err.Error())
return
}
}
logger := hertzlogrus.NewLogger()
// 提供压缩和删除
lumberjackLogger := &lumberjack.Logger{
Filename: fileName,
MaxSize: 20, // 一个文件最大可达 20M。
MaxBackups: 5, // 最多同时保存 5 个文件。
MaxAge: 10, // 一个文件最多可以保存 10 天。
Compress: true, // 用 gzip 压缩。
}
logger.SetOutput(lumberjackLogger)
logger.SetLevel(hlog.LevelDebug)
hlog.SetLogger(logger)
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
hlog.Info("Hello, hertz")
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "Hello hertz!")
})
h.Spin()
}
适配 hlog 的接口的方法等更多用法详见 hertz-contrib/logger/logrus。
title: “zap” linkTitle: “zap” weight: 3 keywords: [“日志扩展”, “zap”] description: “Hertz 对接 zap 和 lumberjack。”
Logger
var _ hlog.FullLogger = (*Logger)(nil)
type Logger struct {
l *zap.SugaredLogger
config *config
}
NewLogger
通过 defaultConfig() 创建并初始化一个 Logger,便于后续的调用,可将所需配置作为参数传入函数,若不传入参数则安装初始配置创建
Logger
相关配置请参考后面的 option 的配置。
函数签名:
func NewLogger(opts ...Option) *Logger
事例代码:
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
hertzzap "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap/zapcore"
)
func main() {
logger := hertzzap.NewLogger(hertzzap.WithZapOptions(zap.WithFatalHook(zapcore.WriteThenPanic)))
hlog.SetLogger(logger)
}
Option 的相关配置
WithCoreEnc
Encoder 是一个提供给日志条目编码器的格式不可知的接口,WithCoreEnc 将 zapcore.Encoder 传入配置
函数签名:
func WithCoreEnc(enc zapcore.Encoder) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzzap "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap/zapcore"
)
func main() {
enc := zapcore.NewJSONEncoder(zap.NewProductionEncoderConfig())
l := hertzzap.NewLogger(hertzzap.WithCoreEnc(enc))
}
WithCoreWs
WithCoreWs 通过内置的 zapcore.AddSync(file) 指定日志写入的位置,将 zapcore.WriteSyncer 传入配置
函数签名:
func WithCoreWs(ws zapcore.WriteSyncer) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzzap "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap/zapcore"
"os"
)
func main() {
ws := zapcore.AddSync(os.Stdout)
l:=hertzzap.NewLogger(hertzzap.WithCoreWs(ws))
}
WithCoreLevel
WithCoreLevel 将 zap.AtomicLevel 传入配置
函数名称:
func WithCoreLevel(lvl zap.AtomicLevel) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzzap "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap"
)
func main() {
lvl := zap.NewAtomicLevelAt(zap.InfoLevel)
l:=hertzzap.NewLogger(hertzzap.WithCoreLevel(lvl))
}
WithCores
WithCores 将 zapcore.Encoder,zapcore.WriteSyncer,zap.AtomicLevel 组合进的 CoreConfig 传入配置
函数签名:
func WithCores(coreConfigs ...CoreConfig) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzzap "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap/zapcore"
"os"
)
func main() {
enc := zapcore.NewJSONEncoder(zap.NewProductionEncoderConfig())
lvl := zap.NewAtomicLevelAt(zap.InfoLevel)
ws := zapcore.AddSync(os.Stdout)
cfg := hertzzap.CoreConfig{
Enc: enc,
Ws: ws,
Lvl: lvl,
}
l := hertzzap.NewLogger(hertzzap.WithCores(cfg))
}
WithZapOptions
WithZapOptions 利用 append() 方法添加原始的 zap 配置
函数签名:
func WithZapOptions(opts ...zap.Option) Option
示例代码:
package main
import (
hertzzap "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap"
)
func main() {
opts := zap.AddCaller()
l := hertzzap.NewLogger(hertzzap.WithZapOptions(opts,zap.Hooks()))
}
}
一个完整的 zap 示例
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"os"
"path"
"time"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
hertzzap "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zap"
"gopkg.in/natefinch/lumberjack.v2"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
// 可定制的输出目录。
var logFilePath string
dir := "./hlog"
logFilePath = dir + "/logs/"
if err := os.MkdirAll(logFilePath, 0o777); err != nil {
log.Println(err.Error())
return
}
// 将文件名设置为日期
logFileName := time.Now().Format("2006-01-02") + ".log"
fileName := path.Join(logFilePath, logFileName)
if _, err := os.Stat(fileName); err != nil {
if _, err := os.Create(fileName); err != nil {
log.Println(err.Error())
return
}
}
logger := hertzzap.NewLogger()
// 提供压缩和删除
lumberjackLogger := &lumberjack.Logger{
Filename: fileName,
MaxSize: 20, // 一个文件最大可达 20M。
MaxBackups: 5, // 最多同时保存 5 个文件。
MaxAge: 10, // 一个文件最多可以保存 10 天。
Compress: true, // 用 gzip 压缩。
}
logger.SetOutput(lumberjackLogger)
logger.SetLevel(hlog.LevelDebug)
hlog.SetLogger(logger)
h.GET("/hello", func(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
hlog.Info("Hello, hertz")
c.String(consts.StatusOK, "Hello hertz!")
})
h.Spin()
}
适配 hlog 的接口的方法等更多用法详见 hertz-contrib/logger/zap。
title: “日志扩展”
linkTitle: “日志扩展”
date: 2023-04-18
weight: 1
keywords: [“日志扩展”]
description: “Hertz 提供对日志的扩展,接口定义在 pkg/common/hlog 中。”
接口定义
Hertz 在 pkg/common/hlog 里定义了 Logger、CtxLogger、FormatLogger
几个接口实现不同的打日志方式,并定义了一个 Control 接口实现 logger 的控制。
用户注入自己的 logger 实现时需要实现上面的所有接口( FullLogger )。Hertz 提供了一个 FullLogger 默认实现。
// FullLogger is the combination of Logger, FormatLogger, CtxLogger and Control.
type FullLogger interface {
Logger
FormatLogger
CtxLogger
Control
}
注意,由于默认 logger 底层使用标准库的
log.Logger实现,其在日志里输出的调用位置依赖于设置的调用深度(call depth),因此封装 hlog 提供的实现可能会导致日志内容里文件名和行数不准确。
注入自己的 logger 实现
Hertz 提供 SetLogger 接口用于注入用户自定义的 logger 实现,也可以使用 SetOutput 接口重定向默认的 logger
输出,随后的中间件以及框架的其他部分可以使用 hlog 中的全局方法来输出日志。
默认使用 hertz 默认实现的 logger。
已支持日志拓展
目前在 Hertz 的开源版本支持的日志扩展都存放在 hertz-logger 中,欢迎大家参与项目贡献与维护。
title: “代码示例” linkTitle: “代码示例” weight: 1 keywords: [“Hertz”, “hertz-examples”, “Bizdemo”, “Server”, “Client”, “Hz”] description: “Hertz 提供了一系列示例代码旨在帮助用户快速上手 Hertz 并了解 Hertz 的特性。”
Hertz 提供了一系列示例代码旨在帮助用户快速上手 Hertz 并了解 Hertz 的特性,参考 hertz-examples 以获取更多信息。
Bizdemo
hertz_gorm
- hertz_gorm :在 hertz server 中使用 gorm 的示例
hertz_gorm_gen
- hertz_gorm_gen :在 hertz server 中使用 gorm/gen & proto IDL 的示例
hertz_jwt
- hertz_jwt :在 hertz server 中使用 jwt 的示例
hertz_session
- hertz_session :在 hertz server 中使用分布式 session 和 csrf 的示例
tiktok_demo
- tiktok_demo :拥有用户、视频、互动、社交功能的仿 tiktok hertz server
hz_kitex_demo
- hz_kitex_demo :hertz 和 kitex 配合使用的示例
Server
启动 Hertz
- hello :启动对于 hertz 来说相当于 “hello world” 的示例
配置
- config :配置 hertz server 的示例
协议
- HTTP1 : hertz 使用 HTTP1 协议的示例
- TLS : hertz 使用 TLS 协议的示例
- HTTP2 : hertz 使用 HTTP2 协议的示例
- HTTP3 : hertz 使用 HTTP3 协议的示例
- Websocket : hertz 使用 Websocket 协议的示例
- SSE : hertz 使用 SSE 协议的示例
路由
- Route :注册路由、使用路由组、参数路由的示例
中间件
- basic_auth :使用 basic auth 中间件的示例
- CORS :使用 CORS 中间件的示例
- custom :自定义中间件的示例
- pprof :使用 pprof 中间件的示例
- requestid :使用 RequestID 中间件的示例
- gzip :在 hertz server 中使用 gzip 中间件的示例
- csrf :在 hertz server 中使用 csrf 中间件的示例
- loadbalance :在 hertz server 中使用 loadbalance 中间件的示例
- Recovery :使用 Recovery 中间件的示例
- jwt :使用 jwt 中间件的示例
- i18n :使用 i18n 中间件的示例
- session :使用 session 中间件的示例
- KeyAuth :使用 KeyAuth 中间件的示例
- Swagger :使用 Swagger 中间件的示例
- access log :使用 access log 中间件的示例
- Secure :使用 Secure 中间件的示例
- Sentry :使用 Sentry 中间件的示例
- Casbin :使用 Casbin 中间件的示例
- ETag :使用 ETag 中间件的示例
- Cache :使用 Cache 中间件的示例
- Paseto :使用 Paseto 中间件的示例
参数绑定及验证
- binding :参数绑定及验证的示例
获取参数
- parameters :获取 query、form、cookie 等参数的示例
文件
- file :关于如何上传,下载文件和搭建静态文件服务的示例
渲染
- render :渲染 json, html, protobuf 的示例
重定向
- redirect :重定向到内部/外部 URI 的示例
流式读/写
- streaming :使用 hertz server 流式读/写的示例
优雅退出
- graceful_shutdown :hertz server 优雅退出的示例
单元测试
- unit_test :使用 hertz 提供的接口不经过网络传输编写单元测试的示例
链路追踪
- tracer :hertz 使用 Jaeger 进行链路追踪的示例
监控
- monitoring :hertz 使用 Prometheus 进行指标监控的示例
多端口服务
- multiple_service :使用 Hertz 启动多端口服务的示例
适配器
Sentinel
- sentinel :sentinel-golang 结合 hertz 使用的示例
反向代理
- reverseproxy :在 hertz server 中使用反向代理的示例
Hlog
- standard :使用 hertz 默认实现的日志的示例
- custom :日志扩展的示例
- zap :在 hertz server 中对接 zap 和 lumberjack 的示例
- logrus :在 hertz server 中对接 logrus 和 lumberjack 的示例
- zerolog :在 hertz server 中对接 zerolog 和 lumberjack 的示例
Opentelemetry
- opentelemetry :使用 obs-opentelemetry 的示例用于对接 opentelemetry
HTTP Trailer
- trailer :使用 HTTP Trailer 的示例
Client
发送请求
- send_request :使用 hertz client 发送 http 请求的示例
配置
- client_config :配置 hertz client 的示例
TLS
- tls :hertz client 发送 tls 请求的示例
添加请求内容
- add_parameters :使用 hertz client 添加请求参数的示例
上传文件
- upload_file :使用 hertz client 上传文件的示例
中间件
- middleware :使用 hertz client middleware 的示例
流式读响应
- streaming_read :使用 hertz client 流式读响应的示例
正向代理
- forward_proxy :使用 hertz client 配置正向代理的示例
HTTP Trailer
- trailer :使用 HTTP Trailer 的示例
Hz
基于 Thrift 生成服务端代码
- thrift :使用 hz 与 thrift 生成服务端代码的示例
基于 Protobuf 生成服务端代码
- protobuf :使用 hz 与 protobuf 生成服务端代码的示例
客户端代码生成
- hz_client :使用 hz 生成客户端代码的示例
自定义模板
- template :使用 hz 自定义模版生成服务端代码的示例
接入第三方插件
- plugin :使用 hz 接入第三方插件的示例
title: “日志” date: 2022-05-23 weight: 1 keywords: [“日志”, “logLevel”] description: “Hertz 提供的日志能力。”
Hertz 提供打印日志的方式,默认打在标准输出。实现在 pkg/common/hlog 中,Hertz
同时也提供了若干全局函数,例如 hlog.Info、hlog.Errorf、hlog.CtxTracef 等,用于调用默认 logger 的相应方法。
如何打印日志
hertz 中可以直接调用 pkg/common/hlog 包下的方法打日志,该方法会调用 defaultLogger 上对应的方法。如实现一个打印
AccessLog 的中间件。
func AccessLog() app.HandlerFunc {
return func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
start := time.Now()
ctx.Next(c)
end := time.Now()
latency := end.Sub(start).Microseconds
hlog.CtxTracef(c, "status=%d cost=%d method=%s full_path=%s client_ip=%s host=%s",
ctx.Response.StatusCode(), latency,
ctx.Request.Header.Method(), ctx.Request.URI().PathOriginal(), ctx.ClientIP(), ctx.Request.Host())
}
}
重定向默认 logger 的输出
可以使用 hlog.SetOutput 来重定向 hlog 提供的默认 logger 的输出。
例如,要把默认 logger 的输出重定向到启动路径下的 ./output.log,可以这样实现:
package main
import (
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
)
func main() {
f, err := os.OpenFile("./output.log", os.O_APPEND|os.O_CREATE|os.O_WRONLY, 0644)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer f.Close()
hlog.SetOutput(f)
... // continue to set up your server
}
logger 的默认输出位置为 os.stdout,在重定向后将不会在终端输出。
如果想同时输出到终端和路径,可参考以下代码:
package main
import (
"io"
"os"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/hlog"
)
func main() {
f, err := os.OpenFile("./output.log", os.O_APPEND|os.O_CREATE|os.O_WRONLY, 0644)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer f.Close()
fileWriter := io.MultiWriter(f,os.Stdout)
hlog.SetOutput(fileWriter)
... // continue to set up your server
}
设置 logLevel
可以使用 hlog.SetLevel 来设置日志等级,高于该日志等级的日志才能够被打印出来。
hlog.SetLevel(hlog.LevelInfo)
目前支持的日志等级有
LevelTrace
LevelDebug
LevelInfo
LevelNotice
LevelWarn
LevelError
LevelFatal
hlog 打印日志并指定日志的 field
以 zerolog 为例,zerolog 中实现了这样的函数:
package main
import (
"bytes"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/json"
hertzZerolog "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zerolog"
)
func main() {
b := &bytes.Buffer{}
l := hertzZerolog.New(hertzZerolog.WithField("service", "logging"))
l.SetOutput(b)
l.Info("foobar")
type Log struct {
Level string `json:"level"`
Service string `json:"service"`
Message string `json:"message"`
}
log := &Log{}
err := json.Unmarshal(b.Bytes(), log)//log.service=="logging"
}
而在 zap 和 logrus 中并未直接实现这样的函数,需要手动添加原始 option
以 zap 为例:
package main
import (
"bytes"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/json"
hertzzap "github.com/hertz-contrib/logger/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap"
)
func main() {
b := &bytes.Buffer{}
l := hertzzap.NewLogger(hertzzap.WithZapOptions(zap.Fields(zap.String("service", "logging"))))
l.SetOutput(b)
l.Info("foobar")
type Log struct {
Level string `json:"level"`
Service string `json:"service"`
Message string `json:"message"`
}
log := &Log{}
err := json.Unmarshal(b.Bytes(), log) //log.service=="logging"
}
关闭 Engine 错误日志
在生产环境中可能会遇到 error when reading request headers 类似的错误,这类错误往往由于 client 侧不规范的行为导致。对于
server 来说除了通过 client IP 定位到具体 client 并告知其整改(如果可以的话)以外,能够做的并不多。
因此 Hertz 提供了一个配置,在初始化时添加如下配置即可关闭这些日志
hlog.SetSilentMode(true)
设置 trace
hertz-contrib/logger 下的 logger 不具备直接的 trace 功能。
可以参照 Trace 文档的日志部分。
日志拓展
目前 hlog 支持 zap , logrus 和 zerolog 的拓展使用,日志拓展 详见。
title: “链路追踪” linkTitle: “链路追踪” weight: 2 keywords: [“链路追踪”] description: “Hertz 提供的链路追踪能力。”
在微服务中,链路追踪是一项很重要的能力,在快速定位问题,分析业务瓶颈,还原一次请求的链路情况等方面发挥重要作用。Hertz 提供了链路追踪的能力,也支持用户自定义链路跟踪。
Hertz 将 trace 抽象为以下接口:
// Tracer is executed at the start and finish of an HTTP.
type Tracer interface {
Start(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) context.Context
Finish(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext)
}
使用 server.WithTracer() 配置添加 tracer,可以添加多个 tracer。
Hertz 会在请求开始之前 (读包之前) 执行所有 tracer 的 Start 方法,在请求结束之后 (写回数据之后) 执行所有 tracer 的 Finish 方法。这种实现时需要注意:
- Start 方法执行时,刚开始接受包,这个时候
requestContext是一个“空”的requestContext,并不能拿到这次请求的相关信息。如果想在解包后中拿到一些信息 (如在 header 中的 traceID 等) 再进行操作时,可以使用中间件能力将 traceID 注入到 span 中。 - 在中间件内对 context 的修改是无效的。
在 requestContext 内存有 traceInfo,其有以下信息
type HTTPStats interface {
Record(event stats.Event, status stats.Status, info string) // 记录事件
GetEvent(event stats.Event) Event // 获取事件
SendSize() int // 获取 SendSize
RecvSize() int // 获取 RecvSize
Error() error // 获取 Error
Panicked() (bool, interface{}) // 获取 Panic
Level() stats.Level // 获取当前 trace 等级
SetLevel(level stats.Level) // 设置 trace 等级,当事件等级高于 trace 等级时不上报
...
}
事件包括:
HTTPStart = newEvent(httpStart, LevelBase) // 请求开始
HTTPFinish = newEvent(httpFinish, LevelBase) // 请求结束
ServerHandleStart = newEvent(serverHandleStart, LevelDetailed) // 业务 handler 开始
ServerHandleFinish = newEvent(serverHandleFinish, LevelDetailed) // 业务 handler 结束
ReadHeaderStart = newEvent(readHeaderStart, LevelDetailed) // 读取 header 开始
ReadHeaderFinish = newEvent(readHeaderFinish, LevelDetailed) // 读取 header 结束
ReadBodyStart = newEvent(readBodyStart, LevelDetailed) // 读取 body 开始
ReadBodyFinish = newEvent(readBodyFinish, LevelDetailed) // 读取 body 结束
WriteStart = newEvent(writeStart, LevelDetailed) // 写 response 开始
WriteFinish = newEvent(writeFinish, LevelDetailed) // 写 response 结束
在 Finish 时可以获取到上述信息。
同时,如果不希望记录这些信息,可以不注册任何 tracer,则框架停止对这些信息的记录。
hertz-contrib 中提供了 opentracing 的扩展方式,也在 hertz-examples 提供了可以从 http 到 rpc 调用的 demo。 仓库:https://github.com/hertz-contrib/tracer
title: “OpenTelemetry” date: 2022-09-01 weight: 4 keywords: [“OpenTelemetry”] description: “Hertz 提供的 OpenTelemetry 能力。”
OpenTelemetry 是 CNCF 的一个开源可观测能力框架,是由一系列工具,API 和 SDK 组成的。可以使 IT 团队能够检测、生成、收集和导出远程监测数据以进行分析和了解软件性能和行为。
hertz-contrib 中提供了 obs-opentelemetry 扩展, 可以使 hertz 通过简易设置就能集成 OpenTelemetry。
特性
Tracing
Tracing 提供了从请求开始接收到处理完毕的整个生命周期的全貌。
obs-opentelemetry 实现了什么:
- 支持在 hertz 服务端和客户端之间启用 http 链路追踪
- 支持通过设置 http header 以启动自动透明地传输对端服务
使用示例
服务端:
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
hertztracing "github.com/hertz-contrib/obs-opentelemetry/tracing"
)
func main() {
tracer, cfg := hertztracing.NewServerTracer()
h := server.Default(tracer)
h.Use(hertztracing.ServerMiddleware(cfg))
// ...
h.Spin()
}
客户端:
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
hertztracing "github.com/hertz-contrib/obs-opentelemetry/tracing"
)
func main() {
c, _ := client.NewClient()
c.Use(hertztracing.ClientMiddleware())
// ...
}
Metric
度量指标(Metric)包含了各种各样的方法和实现。
Metric 包括了追踪样本以及自动将指标与产生它们的追踪样本联系起来。手动将指标和追踪联系起来往往是一项繁琐且容易出错的任务。OpenTelemetry 自动执行这项任务将为运维人员节省大量的时间。
obs-opentelemetry 实现了什么:
- 支持的 hertz http 指标有 [Rate, Errors, Duration]
- 支持服务拓扑图指标 [服务拓扑图]
- 支持 go runtime 指标
Logging
OpenTelemetry 结合了高度结构化的日志 API 以及高速日志处理系统。现有的日志 API 可以通过连接到 OpenTelemetry,以避免对应用程序进行重新测量。
obs-opentelemetry 实现了什么:
- 在 logrus 的基础上适配了 hertz 日志工具
- 实现了链路追踪自动关联日志的功能
import (
hertzlogrus "github.com/hertz-contrib/obs-opentelemetry/logging/logrus"
)
func main() {
hlog.SetLogger(hertzlogrus.NewLogger())
// ...
}
Provider
使用示例
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/obs-opentelemetry/provider"
hertztracing "github.com/hertz-contrib/obs-opentelemetry/tracing"
)
func main() {
serviceName := "echo"
p := provider.NewOpenTelemetryProvider(
provider.WithServiceName(serviceName),
provider.WithExportEndpoint("localhost:4317"),
provider.WithInsecure(),
)
defer p.Shutdown(context.Background())
tracer, cfg := hertztracing.NewServerTracer()
h := server.Default(tracer)
h.Use(hertztracing.ServerMiddleware(cfg))
// ...
h.Spin()
}
Options
| 函数名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| WithServiceName | 配置 service.name 的资源属性 |
| WithDeploymentEnvironment | 配置deployment.environment资源属性 |
| WithServiceNamespace | 配置了service.namespace资源属性 |
| WithResourceAttributes | 配置资源属性 |
| WithResource | 配置资源 (resource.Resource) |
| WithEnableTracing | 是否启用 tracing |
| WithEnableMetrics | 是否启用 metrics |
| WithTextMapPropagator | 设置 propagation.TextMapPropagator |
| WithResourceDetector | 配置 resource.Detector |
| WithHeaders | 配置导出 telemetry 数据的 gRPC 请求头 |
| WithInsecure | 配置是否对导出的 gRPC 客户端使用安全认证 |
完整使用示例
完整的使用示例详见 example
title: “监控” linkTitle: “监控” weight: 3 keywords: [“监控”] description: “Hertz 提供的监控能力。”
框架自身不带任何监控打点,只是提供了 Tracer 接口,用户可以根据需求实现该接口,并通过 WithTracer Option 来注入。
// Tracer is executed at the start and finish of an HTTP.
type Tracer interface {
Start(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) context.Context
Finish(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext)
}
hertz-contrib 中提供了默认的 prometheus 的监控扩展,能够实现:
- 请求量监控
- 时延监控
默认的 tag 有:HTTP Method,statusCode。请求相关的信息存在 RequestContext,在打点上报时可以获取到该变量,用户可以根据自己的需要自行扩展打点功能。使用方式:
Server
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/hertz-contrib/monitor-prometheus"
)
func main() {
···
h := server.Default(server.WithTracer(prometheus.NewServerTracer(":9091", "/hertz")))
h.GET("/ping", func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
ctx.JSON(200, utils.H{"ping": "pong"})
})
h.Spin()
···
}
目前 Client 暂没有暴露 Tracer 接口,但是提供了 中间件 能力,可以通过中间件实现监控能力。
仓库 https://github.com/hertz-contrib/monitor-prometheus
title: “可观测性” linkTitle: “可观测性” weight: 3 keywords: [“可观测性”, “日志”, “链路追踪”, “监控”, “OpenTelemetry”] description: “Hertz 提供的可观测性能力。”
title: “迁移到 Hertz” weight: 7 keywords: [“迁移到 Hertz”] description: “Hertz 提供了其他框架( FastHTTP、Gin ) 迁移至 Hertz 的能力。”
迁移脚本
Hertz-contrib 下提供了其他框架( FastHTTP、Gin ) 迁移至 Hertz 的脚本,具体使用方式如下:
cd your_project_path
sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.github.com/hertz-contrib/migrate/main/migrate.sh)"
脚本处理后,仍有小部分无法自动迁移,需要手动迁移。
迁移小 tip:比如要修改 Header 的 API,那 Header 是在 Request(Response)中,那 Hertz 中的 Api 就是 ctx.Request.Header.XXX()
,其他 API 同理。为了方便用户使用,Hertz 也在 ctx 上添加了高频使用的 API,比如获取 Body 时使用 ctx.Body
就可以,不用使用 ctx.Request.Body() 了。
FastHTTP
处理函数
-
相对于 FastHTTP 的 RequestHandler ,Hertz 的 HandlerFunc 接受两个参数:context.Context 和 RequestContext 。context.Context 用于解决请求上下文无法按需延长的问题,同时请求上下文不再需要实现上下文接口,降低了维护难度。详细可以参考:字节跳动开源 Go HTTP 框架 Hertz 设计实践 。
-
具体例子如下:
// fasthttp request handler
type RequestHandler = func(ctx *fasthttp.RequestCtx)
// the corresponding Hertz request handler
type HandlerFunc = func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext)
UserValue
-
Hertz 提供了两个接口来存储 UserValue,分别是请求上下文 RequestContext.Keys 和标准库的 context.Value。requestContext.Keys 在请求中使用,请求结束就会回收。context.Value 不会在请求结束时就回收,可以用于异步场景(如 log,协程等)。
-
fasthttp 中 Value 和 UserValue 是等价的,但在 Hertz 中 RequestContext.Keys 和 context.Value 分别对应了不同的接口,两者数据不同。
路由
-
Hertz 提供了一套完整高效的路由,且提供了 ctx.Param 方法来获取路由参数。
-
具体例子如下:
// fasthttp + fasthttp router example
func Hello(ctx *fasthttp.RequestCtx) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx, "Hello, %s!\n", ctx.UserValue("name"))
}
func main() {
r := router.New()
r.GET("/hello/{name}", Hello)
...
}
// the corresponding hertz example
func Hello(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
fmt.Fprintf(ctx, "Hello, %s!\n", ctx.Param("name"))
}
func main() {
r := server.Default()
r.GET("/hello/:name", Hello)
...
}
ListenAndServe
- Hertz 不提供 ListenAndServe 等方法,具体监听端口等参数需要在初始化参数中确定,详细参数参考 server package - github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server - Go Packages 。
// fasthttp ListenAndServe
func main() {
...
fasthttp.ListenAndServe(":8080", myHandler)
}
// Hertz example
func main() {
r := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
...
r.Spin()
}
Gin
处理函数
- 相对于 Gin 的 RequestHandler ,Hertz 的 HandlerFunc 接受两个参数:context.Context 和 RequestContext context.Context 即 Gin 中的 ctx.Request.Context() 。详细可以参考:字节跳动开源 Go HTTP 框架 Hertz 设计实践 。
- 具体例子如下:
// Gin request handler
type RequestHandler = func(ctx *gin.Context)
// the corresponding Hertz request handler
type HandlerFunc = func(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext)
参数绑定
- Hertz 目前只支持 Bind 绑定所有的数据,不支持单独绑定 Query 或是 Body 中的数据,详细内容请参考绑定与校验 。
设置 Response 数据
- Hertz 支持乱序设置 Response 的 Header 和 Body,不像 Gin 必须要求先设置 Header,再设置 Body。
- 具体例子如下:
// The example is valid on Hertz
func Hello(c context.Context, ctx *app.RequestContext) {
// First, Set a body
fmt.Fprintf(ctx, "Hello, World\n")
// Then, Set a Header
ctx.Header("Hertz", "test")
}
ListenAndServe
- Hertz 没有实现 http.Handler,不能使用 http.Server 来监听端口。同时,Hertz 具体的监听参数要在初始化参数中确定,详细参数参考 server package - github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server - Go Packages。
// Gin Run or use http.Server
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
...
r.Run(":8080")
// or use http.Server
srv := &http.Server{
Addr: ":8080",
Handler: r,
}
}
// Hertz example
func main() {
r := server.Default(server.WithHostPorts(":8080"))
...
r.Spin()
}
附录
title: “hz 使用 (protobuf)” date: 2023-02-21 weight: 4 description: > keywords: [“hz 使用 (protobuf)”, “protobuf”, “new”, “update”] description: “hz 使用 (protobuf)。”
基于 protobuf IDL 创建项目
new: 创建一个新项目
-
在当前目录下创建 protobuf idl 文件
-
创建 api.proto
api.proto 是 hz 提供的注解文件,内容如下,请在使用了注解的 proto 文件中,import 该文件。
如果想自行拓展注解的使用,请不要以 “5” 作为序号的开头,避免出现冲突。例如 “optional string xxx = 77777;"。
// idl/api.proto; 注解拓展 syntax = "proto2"; package api; import "google/protobuf/descriptor.proto"; option go_package = "/api"; extend google.protobuf.FieldOptions { optional string raw_body = 50101; optional string query = 50102; optional string header = 50103; optional string cookie = 50104; optional string body = 50105; optional string path = 50106; optional string vd = 50107; optional string form = 50108; optional string js_conv = 50109; optional string file_name = 50110; optional string none = 50111; // 50131~50160 used to extend field option by hz optional string form_compatible = 50131; optional string js_conv_compatible = 50132; optional string file_name_compatible = 50133; optional string none_compatible = 50134; // 50135 is reserved to vt_compatible // optional FieldRules vt_compatible = 50135; optional string go_tag = 51001; } extend google.protobuf.MethodOptions { optional string get = 50201; optional string post = 50202; optional string put = 50203; optional string delete = 50204; optional string patch = 50205; optional string options = 50206; optional string head = 50207; optional string any = 50208; optional string gen_path = 50301; // The path specified by the user when the client code is generated, with a higher priority than api_version optional string api_version = 50302; // Specify the value of the :version variable in path when the client code is generated optional string tag = 50303; // rpc tag, can be multiple, separated by commas optional string name = 50304; // Name of rpc optional string api_level = 50305; // Interface Level optional string serializer = 50306; // Serialization method optional string param = 50307; // Whether client requests take public parameters optional string baseurl = 50308; // Baseurl used in ttnet routing optional string handler_path = 50309; // handler_path specifies the path to generate the method // 50331~50360 used to extend method option by hz optional string handler_path_compatible = 50331; // handler_path specifies the path to generate the method } extend google.protobuf.EnumValueOptions { optional int32 http_code = 50401; // 50431~50460 used to extend enum option by hz } extend google.protobuf.ServiceOptions { optional string base_domain = 50402; // 50731~50760 used to extend service option by hz optional string base_domain_compatible = 50731; } extend google.protobuf.MessageOptions { // optional FieldRules msg_vt = 50111; optional string reserve = 50830; // 550831 is reserved to msg_vt_compatible // optional FieldRules msg_vt_compatible = 50831; } -
创建主 IDL
// idl/hello/hello.proto syntax = "proto3"; package hello; option go_package = "hertz/hello"; import "api.proto"; message HelloReq { string Name = 1[(api.query)="name"]; } message HelloResp { string RespBody = 1; } service HelloService { rpc Method1(HelloReq) returns(HelloResp) { option (api.get) = "/hello"; } }
-
-
创建新项目
# 在 GOPATH 外执行,需要指定 go mod 名,如果主 IDL 的依赖和主 IDL 不在同一路径下,需要加入 "-I" 选项,其含义为 IDL 搜索路径,等同于 protoc 的 "-I" 命令 hz new -module example.com/m -I idl -idl idl/hello/hello.proto # 整理 & 拉取依赖 go mod tidy# GOPATH 下执行,如果主 IDL 的依赖和主 IDL 不在同一路径下,需要加入 "-I" 选项,其含义为 IDL 搜索路径,等同于 protoc 的 "-I" 命令 hz new -I idl -idl idl/hello/hello.proto go mod init # 整理 & 拉取依赖 go mod tidy -
修改 handler,添加自己的逻辑
// handler path: biz/handler/hello/hello_service.go // 其中 "/hello" 是 protobuf idl 中 go_package 的最后一级 // "hello_service.go" 是 protobuf idl 中 service 的名字,所有 service 定义的方法都会生成在这个文件中 // Method1 . // @router /hello [GET] func Method1(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) { var err error var req hello.HelloReq err = c.BindAndValidate(&req) if err != nil { c.String(400, err.Error()) return } resp := new(hello.HelloResp) // 你可以修改整个函数的逻辑,而不仅仅局限于当前模板 resp.RespBody = "hello," + req.Name // 添加的逻辑 c.JSON(200, resp) } -
编译项目
go build -
运行项目并测试
运行项目:
./{{your binary}}测试:
curl --location --request GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8888/hello?name=hertz'如果返回
{"RespBody":"hello,hertz"},说明接口调通。
update: 更新一个已有的项目
-
如果你的 protobuf idl 有更新,例如:
// idl/hello/hello.proto syntax = "proto3"; package hello; option go_package = "hertz/hello"; import "api.proto"; message HelloReq { string Name = 1[(api.query)="name"]; } message HelloResp { string RespBody = 1; } message OtherReq { string Other = 1[(api.body)="other"]; } message OtherResp { string Resp = 1; } service HelloService { rpc Method1(HelloReq) returns(HelloResp) { option (api.get) = "/hello"; } rpc Method2(OtherReq) returns(OtherResp) { option (api.post) = "/other"; } } service NewService { rpc Method3(OtherReq) returns(OtherResp) { option (api.get) = "/new"; } } -
切换到执行 new 命令的目录,更新修改后的 protobuf idl
hz update -I idl -idl idl/hello/hello.proto -
可以看到 在 “biz/handler/hello/hello_service.go” 下新增了新的方法; 在 “biz/handler/hello” 下新增了文件 “new_service.go” 以及对应的 “Method3” 方法。
下面我们来开发 “Method2” 接口:
// Method2 . // @router /other [POST] func Method2(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) { var err error var req hello.OtherReq err = c.BindAndValidate(&req) if err != nil { c.String(400, err.Error()) return } resp := new(hello.OtherResp) // 增加的逻辑 resp.Resp = "Other method: " + req.Other c.JSON(200, resp) } -
编译项目
go build -
运行项目并测试
运行项目:
./{{your binary}}测试:
curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8888/other' \ --header 'Content-Type: application/json' \ --data-raw '{ "Other": "other method" }'如果返回
{"Resp":"Other method: other method"},说明接口调通。
更多示例代码请参考 code。
title: “hz 的基本使用” date: 2023-02-21 weight: 2 keywords: [“hz 的基本使用”, “new”] description: “hz 的基本使用。”
基本使用
new: 创建一个 Hertz 新项目
-
创建新项目
# 在 GOPATH 外执行,需要指定 go mod 名 hz new -module hertz/demo # 整理 & 拉取依赖 go mod tidy# GOPATH 下执行,go mod 名字默认为当前路径相对 GOPATH 的路径,也可自己指定 hz new # 整理 & 拉取依赖 go mod init # 上一步在 GOPATH 下执行不会生成 go.mod go mod tidy执行后会在当前目录下生成 Hertz 项目的脚手架。
-
编译项目
go build -
运行项目并测试
运行项目:
./{{your binary}}测试:
curl 127.0.0.1:8888/ping如果返回
{"message":"pong"},说明接口调通。
title: “hz 使用 (thrift)” date: 2023-02-21 weight: 3 keywords: [“hz 使用 (thrift)”, “thrift”, “new”, “update”] description: “hz 使用 (thrift)。”
基于 thrift IDL 创建项目
new: 创建一个新项目
-
在当前目录下创建 thrift idl 文件
// idl/hello.thrift namespace go hello.example struct HelloReq { 1: string Name (api.query="name"); // 添加 api 注解为方便进行参数绑定 } struct HelloResp { 1: string RespBody; } service HelloService { HelloResp HelloMethod(1: HelloReq request) (api.get="/hello"); } -
创建新项目
# 不在`$GOPATH`下的项目通过工具提供的`-module`命令指定一个自定义 module 名称即可: hz new -module example.com/m -idl idl/hello.thrift # 整理 & 拉取依赖 go mod tidy # 查看 go.mod 中 github.com/apache/thrift 版本是否为 v0.13.0,如果不是则继续执行 2.2 小节剩余代码 go mod edit -replace github.com/apache/thrift=github.com/apache/thrift@v0.13.0 # 整理 & 拉取依赖 go mod tidy# 如果当前项目路径处于`$GOPATH`之下则执行以下代码块 hz new -idl idl/hello.thrift go mod init go mod edit -replace github.com/apache/thrift=github.com/apache/thrift@v0.13.0 # 整理 & 拉取依赖 go mod tidy -
修改 handler,添加自己的逻辑
// handler path: biz/handler/hello/example/hello_service.go // 其中 "hello/example" 是 thrift idl 的 namespace // "hello_service.go" 是 thrift idl 中 service 的名字,所有 service 定义的方法都会生成在这个文件中 // HelloMethod . // @router /hello [GET] func HelloMethod(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) { var err error var req example.HelloReq err = c.BindAndValidate(&req) if err != nil { c.String(400, err.Error()) return } resp := new(example.HelloResp) // 你可以修改整个函数的逻辑,而不仅仅局限于当前模板 resp.RespBody = "hello," + req.Name // 添加的逻辑 c.JSON(200, resp) } -
编译项目
go build -
运行项目并测试
运行项目:
./{{your binary}}测试:
curl --location --request GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8888/hello?name=hertz'如果返回
{"RespBody":"hello,hertz"},说明接口调通。
update: 更新一个已有的项目
-
如果你的 thrift idl 有更新,例如:
// idl/hello.thrift namespace go hello.example struct HelloReq { 1: string Name (api.query="name"); } struct HelloResp { 1: string RespBody; } struct OtherReq { 1: string Other (api.body="other"); } struct OtherResp { 1: string Resp; } service HelloService { HelloResp HelloMethod(1: HelloReq request) (api.get="/hello"); OtherResp OtherMethod(1: OtherReq request) (api.post="/other"); } service NewService { HelloResp NewMethod(1: HelloReq request) (api.get="/new"); } -
切换到执行 new 命令的目录,更新修改后的 thrift idl
hz update -idl idl/hello.thrift -
可以看到
在 “biz/handler/hello/example/hello_service.go” 下新增了新的方法
在 “biz/handler/hello/example” 下新增了文件 “new_service.go” 以及对应的 “NewMethod” 方法。下面我们来开发 “OtherMethod” 接口:
// OtherMethod . // @router /other [POST] func OtherMethod(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) { var err error // example.OtherReq 对应的 model 文件也会重新生成 var req example.OtherReq err = c.BindAndValidate(&req) if err != nil { c.String(400, err.Error()) return } resp := new(example.OtherResp) // 增加的逻辑 resp.Resp = "Other method: " + req.Other c.JSON(200, resp) } -
编译项目
go build -
运行项目并测试
运行项目:
./{{your binary}}测试:
curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8888/other' \ --header 'Content-Type: application/json' \ --data-raw '{ "Other": "other method" }'如果返回
{"Resp":"Other method: other method"},说明接口调通。
更多示例代码请参考 code。
title: ‘hz 安装’ date: 2023-02-21 weight: 1 keywords: [“hz 安装”] description: “hz 安装。”
hz 是 Hertz 框架提供的一个用于生成代码的命令行工具。目前,hz 可以基于 thrift 和 protobuf 的 IDL 生成 Hertz 项目的脚手架。
安装
-
确保
GOPATH环境变量已经被正确的定义(例如export GOPATH=~/go)并且将$GOPATH/bin添加到PATH环境变量之中(例如export PATH=$GOPATH/bin:$PATH);请勿将GOPATH设置为当前用户没有读写权限的目录 -
安装 hz:
go install github.com/cloudwego/hertz/cmd/hz@latest -
验证是否安装成功
hz -v, 如果显示如下版本的信息,则说明安装成功hz version v0.x.x
注意,由于 hz 会为自身的二进制文件创建软链接,因此请确保 hz 的安装路径具有可写权限。
运行模式
要使用 thrift 或 protobuf 的 IDL 生成代码,需要安装相应的编译器:thriftgo 或 protoc 。
hz 生成的代码里,一部分是底层的编译器生成的(通常是关于 IDL 里定义的结构体),另一部分是 IDL 中用户定义的路由、method 等信息。用户可直接运行该代码。
从执行流上来说,当 hz 使用 thrift IDL 生成代码时,hz 会调用 thriftgo 来生成 go 结构体代码,并将自身作为 thriftgo 的一个插件(名为 thrift-gen-hertz)来执行并生成其他代码。当用于 protobuf IDL 时亦是如此。
$> hz ... --idl=IDL
|
| thrift-IDL
|---------> thriftgo --gen go:... -plugin=hertz:... IDL
|
| protobuf-IDL
---------> protoc --hertz_out=... --hertz_opt=... IDL
如何安装 thriftgo/protoc:
thriftgo:
GO111MODULE=on go install github.com/cloudwego/thriftgo@latest
protoc:
// brew 安装
$ brew install protobuf
// 官方镜像安装,以 macos 为例
$ wget https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v3.19.4/protoc-3.19.4-osx-x86_64.zip
$ unzip protoc-3.19.4-osx-x86_64.zip
$ cp bin/protoc /usr/local/bin/protoc
// 确保 include/google 放入 /usr/local/include下
$ cp -r include/google /usr/local/include/google
title: ‘hz 命令梳理’ date: 2023-02-21 weight: 7 keywords: [“hz 命令梳理”, “New”, “Update”, “Model”, “Client”] description: “hz 命令梳理。”
命令行参数说明
Global
$ hz --help
NAME:
hz - A idl parser and code generator for Hertz projects
USAGE:
hz [global options] command [command options] [arguments...]
VERSION:
v0.x.x
COMMANDS:
new Generate a new Hertz project
update Update an existing Hertz project
model Generate model code only
client Generate hertz client based on IDL
help, h Shows a list of commands or help for one command
GLOBAL OPTIONS:
--verbose turn on verbose mode (default: false)
--help, -h show help (default: false)
--version, -v print the version (default: false)
- new: 创建一个新的 Hertz 项目
- update: 更新一个已存在的 Hertz 项目
- model: 只生成 model 代码
- client: 基于 IDL 生成 client 侧代码
New
$ hz help new
NAME:
hz new - Generate a new Hertz project
USAGE:
hz new [command options] [arguments...]
OPTIONS:
--idl value [ --idl value ] Specify the IDL file path. (.thrift or .proto)
--service value Specify the service name.
--module value, --mod value Specify the Go module name.
--out_dir value Specify the project path.
--handler_dir value Specify the handler relative path (based on "out_dir").
--model_dir value Specify the model relative path (based on "out_dir").
--router_dir value Specify the router relative path (based on "out_dir").
--client_dir value Specify the client path. If not specified, IDL generated path is used for 'client' command; no client code is generated for 'new' command
--use value Specify the model package to import for handler.
--proto_path value, -I value [ --proto_path value, -I value ] Add an IDL search path for includes. (Valid only if idl is protobuf)
--thriftgo value, -t value [ --thriftgo value, -t value ] Specify arguments for the thriftgo. ({flag}={value})
--protoc value, -p value [ --protoc value, -p value ] Specify arguments for the protoc. ({flag}={value})
--option_package value, -P value [ --option_package value, -P value ] Specify the package path. ({include_path}={import_path})
--no_recurse Generate master model only. (default: false)
--force, -f Force new a project, which will overwrite the generated files (default: false)
--enable_extends Parse 'extends' for thrift IDL (default: false)
--json_enumstr Use string instead of num for json enums when idl is thrift. (default: false)
--unset_omitempty Remove 'omitempty' tag for generated struct. (default: false)
--pb_camel_json_tag Convert Name style for json tag to camel(Only works protobuf). (default: false)
--snake_tag Use snake_case style naming for tags. (Only works for 'form', 'query', 'json') (default: false)
--rm_tag value [ --rm_tag value ] Remove the specified tag
--exclude_file value, -E value [ --exclude_file value, -E value ] Specify the files that do not need to be updated.
--customize_layout value Specify the path for layout template.
--customize_layout_data_path value Specify the path for layout template render data.
--customize_package value Specify the path for package template.
--handler_by_method Generate a separate handler file for each method. (default: false)
--protoc-plugins value [ --protoc-plugins value ] Specify plugins for the protoc. ({plugin_name}:{options}:{out_dir})
--thrift-plugins value [ --thrift-plugins value ] Specify plugins for the thriftgo. ({plugin_name}:{options})
--help, -h show help (default: false)
- idl: 指定 idl 文件路径 (.thrift 或者 .proto)
- service: 指定服务名,为之后做服务发现等功能预留
- module/mod: 指定 go mod 的名字,非 GOPATH 下必须指定,GOPATH 下默认以相对于 GOPATH 的路径作为名字
- out_dir: 指定项目生成路径,默认为当前路径
- handler_dir: 指定 handler 的生成路径,默认为 “biz/handler” (相对路径,基于 out_dir)
- model_dir: 指定 model 的生成路径,默认为 “biz/model” (相对路径,基于 out_dir)
- router_dir: 指定 router 的生成路径,默认为 “biz/router” (相对路径,基于 out_dir)
- client_dir: 指定 client 侧代码的生成路径,如果不指定则不生成;当前为每个 service 生成一个全局的 client,若要生成更完善的 client 侧代码请使用 hz client 命令
- use: 指定 handler 中 import model 包的位置,该参数适用于在生成 handler 代码之前已经生成过 model 代码的场景,使用该命令可直接 import 已有的 model 代码,无需再次生成
- proto_path/I: 当 idl 为 protobuf 时,指定 idl 的搜索路径,同 protoc 的 -I 指令
- thriftgo/t: 透传给 thriftgo 的选项 ({flag}={value})
- protoc/p: 透传给 protoc 的选项 ({flag}={value})
- option_package/P: 指定包的路径 ({include_path}={import_path})
- no_recurse: 只生成主 idl 的 model 代码,默认为 false
- force/f: 强制创建一个新的 hertz 项目,这将会覆盖已生成的文件
- enable_extends: 解析 thrift idl 中的 extends
- json_enumstr: 当 idl 为 thrift 时,json enums 使用 string 代替 num (透传给 thriftgo 的选项)
- unset_omitempty: 当 idl 为 protobuf 时,生成 model field,去掉 omitempty tag;当 idl 为 thrift 时,是否添加 omitempty 根据 field 是 “optional” 还是 “required” 决定
- pb_camel_json_tag: 生成 model field 时将 json tag 的命名风格改为驼峰命名(仅作用于 protobuf)
- snake_tag: tag 使用 snake_case 风格命名 (仅对 form、query、json 生效)
- rm_tag value: 移除指定的 tag
- exclude_file/E: 不需要更新的文件 (相对项目路径,支持多个)
- customize_layout: 自定义项目 layout 模板,具体详见:自定义模板使用
- customize_layout_data_path value: 自定义项目 layout 模板渲染参数,具体详见:自定义模板使用
- customize_package: 自定义项目 package 相关模板,主要可针对 handler 模板进行定制化,具体详见:自定义模板使用
- handler_by_method: 为每一个方法生成一个单独的 handler 文件
- protoc-plugins: 接入 protoc 相关的第三方生成代码插件,具体详见:hz 接入第三方生成代码插件
- thrift-plugins: 接入 thrift 相关的第三方生成代码插件,具体详见:hz 接入第三方生成代码插件
- help/h: 帮助命令
Update
$ hz help update
NAME:
hz update - Update an existing Hertz project
USAGE:
hz update [command options] [arguments...]
OPTIONS:
--idl value [ --idl value ] Specify the IDL file path. (.thrift or .proto)
--module value, --mod value Specify the Go module name.
--out_dir value Specify the project path.
--handler_dir value Specify the handler relative path (based on "out_dir").
--model_dir value Specify the model relative path (based on "out_dir").
--client_dir value Specify the client path. If not specified, IDL generated path is used for 'client' command; no client code is generated for 'new' command
--use value Specify the model package to import for handler.
--proto_path value, -I value [ --proto_path value, -I value ] Add an IDL search path for includes. (Valid only if idl is protobuf)
--thriftgo value, -t value [ --thriftgo value, -t value ] Specify arguments for the thriftgo. ({flag}={value})
--protoc value, -p value [ --protoc value, -p value ] Specify arguments for the protoc. ({flag}={value})
--option_package value, -P value [ --option_package value, -P value ] Specify the package path. ({include_path}={import_path})
--no_recurse Generate master model only. (default: false)
--enable_extends Parse 'extends' for thrift IDL (default: false)
--json_enumstr Use string instead of num for json enums when idl is thrift. (default: false)
--unset_omitempty Remove 'omitempty' tag for generated struct. (default: false)
--pb_camel_json_tag Convert Name style for json tag to camel(Only works protobuf). (default: false)
--snake_tag Use snake_case style naming for tags. (Only works for 'form', 'query', 'json') (default: false)
--rm_tag value [ --rm_tag value ] Remove the specified tag
--exclude_file value, -E value [ --exclude_file value, -E value ] Specify the files that do not need to be updated.
--customize_package value Specify the path for package template.
--handler_by_method Generate a separate handler file for each method. (default: false)
--protoc-plugins value [ --protoc-plugins value ] Specify plugins for the protoc. ({plugin_name}:{options}:{out_dir})
--thrift-plugins value [ --thrift-plugins value ] Specify plugins for the thriftgo. ({plugin_name}:{options})
--help, -h show help (default: false)
- idl: idl 文件路径 (.thrift 或者 .proto)
- module/mod: 指定 go mod 的名字,非 GOPATH 下必须指定,GOPATH 下默认以相对于 GOPATH 的路径作为名字
- out_dir: 指定项目生成路径,默认为当前路径
- handler_dir: 指定 handler 的生成路径,默认为 “biz/handler” (相对路径,基于 out_dir);注意:如果对同一套 idl 进行 update,需要 handler_dir 的值与使用 new 的时候相同,否则会生成冗余的代码,需要用户自行删除。
- model_dir: 指定 model 的生成路径,默认为 “biz/model” (相对路径,基于 out_dir);注意:如果对同一套 idl 进行 update,需要 model_dir 的值与使用 new 的时候相同,否则会生成重复的 model 代码且导致 handler 引用不一致。
- client_dir: 指定 client 侧代码的生成路径,如果不指定则不生成;当前为每个 service 生成一个全局的 client,若要生成更完善的 client 侧代码请使用 hz client 命令。注意:如果对同一套 idl 进行 update,需要 client_dir 的值与使用 new 的时候相同,否则会生成冗余的代码,需要用户自行删除。
- use: 指定 handler 中 import model 包的位置,该参数适用于在生成 handler 代码之前已经生成过 model 代码的场景,使用该命令可直接 import 已有的 model 代码,无需再次生成
- proto_path/I: 当 idl 为 protobuf 时,指定 idl 的搜索路径,同 protoc 的 -I 指令
- thriftgo/t: 透传给 thriftgo 的选项 ({flag}={value})
- protoc/p: 透传给 protoc 的选项 ({flag}={value})
- option_package/P: 指定包的路径,({include_path}={import_path})
- no_recurse: 只生成主 idl 的 model 代码,默认为 false
- enable_extends: 解析 thrift idl 中的 extends
- json_enumstr: 当 idl 为 thrift 时,json enums 使用 string 代替 num (透传给 thriftgo 的选项)
- unset_omitempty: 当 idl 为 protobuf 时,生成 model field,去掉 mitempty tag;当 idl 为 thrift 时,是否添加 omitempty 根据 field 是 “optional” 还是 “required” 决定
- pb_camel_json_tag: 生成 model field 时将 json tag 的命名风格改为驼峰命名(仅作用于 protobuf)
- snake_tag: tag 使用 snake_case 风格命名 (仅对 form、query、json 生效)
- rm_tag value: 移除指定的 tag
- exclude_file/E: 不需要更新的文件 (相对项目路径,支持多个)
- customize_package: 自定义项目 package 相关模板,主要可针对 handler 模板进行定制化,具体详见:自定义模板使用 。注意:对于已经存在的 handler 文件会按照默认模板新增 handler 函数,对于还未存在的 handler 文件,则会按照自定义模板来生成 handler。
- handler_by_method: 为每一个方法生成一个单独的 handler 文件
- protoc-plugins: 接入 protoc 相关的第三方生成代码插件,具体详见:hz 接入第三方生成代码插件
- thrift-plugins: 接入 thrift 相关的第三方生成代码插件,具体详见:hz 接入第三方生成代码插件
- help/h: 帮助命令
Model
$ hz help model
NAME:
hz model - Generate model code only
USAGE:
hz model [command options] [arguments...]
OPTIONS:
--idl value [ --idl value ] Specify the IDL file path. (.thrift or .proto)
--module value, --mod value Specify the Go module name.
--out_dir value Specify the project path.
--model_dir value Specify the model relative path (based on "out_dir").
--proto_path value, -I value [ --proto_path value, -I value ] Add an IDL search path for includes. (Valid only if idl is protobuf)
--thriftgo value, -t value [ --thriftgo value, -t value ] Specify arguments for the thriftgo. ({flag}={value})
--protoc value, -p value [ --protoc value, -p value ] Specify arguments for the protoc. ({flag}={value})
--no_recurse Generate master model only. (default: false)
--json_enumstr Use string instead of num for json enums when idl is thrift. (default: false)
--unset_omitempty Remove 'omitempty' tag for generated struct. (default: false)
--pb_camel_json_tag Convert Name style for json tag to camel(Only works protobuf). (default: false)
--snake_tag Use snake_case style naming for tags. (Only works for 'form', 'query', 'json') (default: false)
--rm_tag value [ --rm_tag value ] Remove the specified tag
--exclude_file value, -E value [ --exclude_file value, -E value ] Specify the files that do not need to be updated.
--help, -h show help (default: false)
- idl: idl 文件路径 (.thrift 或者 .proto)
- module/mod: 指定 go mod 的名字,非 GOPATH 下必须指定,GOPATH 下默认以相对于 GOPATH 的路径作为名字
- out_dir: 指定项目生成路径,默认为当前路径
- model_dir: 指定 model 的生成路径,默认为 “biz/model” (相对路径,基于 out_dir)
- proto_path/I: 当 idl 为 protobuf 时,指定 idl 的搜索路径,同 protoc 的 -I 指令
- thriftgo/t: 透传给 thriftgo 的选项 ({flag}={value})
- protoc/p: 透传给 protoc 的选项 ({flag}={value})
- no_recurse: 只生成主 idl 的 model 代码,默认为 false
- json_enumstr: 当 idl 为 thrift 时,json enums 使用 string 代替 num (透传给 thriftgo 的选项)
- unset_omitempty: 当 idl 为 protobuf 时,生成 model field,去掉 mitempty tag;当 idl 为 thrift 时,是否添加 omitempty 根据 field 是 “optional” 还是 “required” 决定
- pb_camel_json_tag: 生成 model field 时将 json tag 的命名风格改为驼峰命名(仅作用于 protobuf)
- snake_tag: tag 使用 snake_case 风格命名 (仅对 form、query、json 生效)
- rm_tag value: 移除指定的 tag
- exclude_file/E: 不需要更新的文件 (相对项目路径,支持多个)
- help/h: 帮助命令
Client
client 命令的示例及高级设置可参考 hz client 代码生成。
$ hz help client
NAME:
hz client - Generate hertz client based on IDL
USAGE:
hz client [command options] [arguments...]
OPTIONS:
--idl value [ --idl value ] Specify the IDL file path. (.thrift or .proto)
--module value, --mod value Specify the Go module name.
--base_domain value Specify the request domain.
--model_dir value Specify the model relative path (based on "out_dir").
--client_dir value Specify the client path. If not specified, IDL generated path is used for 'client' command; no client code is generated for 'new' command
--use value Specify the model package to import for handler.
--force_client_dir value Specify the client path, and won't use namespaces as subpaths
--proto_path value, -I value [ --proto_path value, -I value ] Add an IDL search path for includes. (Valid only if idl is protobuf)
--thriftgo value, -t value [ --thriftgo value, -t value ] Specify arguments for the thriftgo. ({flag}={value})
--protoc value, -p value [ --protoc value, -p value ] Specify arguments for the protoc. ({flag}={value})
--no_recurse Generate master model only. (default: false)
--enable_extends Parse 'extends' for thrift IDL (default: false)
--json_enumstr Use string instead of num for json enums when idl is thrift. (default: false)
--unset_omitempty Remove 'omitempty' tag for generated struct. (default: false)
--pb_camel_json_tag Convert Name style for json tag to camel(Only works protobuf). (default: false)
--snake_tag Use snake_case style naming for tags. (Only works for 'form', 'query', 'json') (default: false)
--rm_tag value [ --rm_tag value ] Remove the specified tag
--exclude_file value, -E value [ --exclude_file value, -E value ] Specify the files that do not need to be updated.
--customize_layout value Specify the path for layout template.
--customize_layout_data_path value Specify the path for layout template render data.
--customize_package value Specify the path for package template.
--protoc-plugins value [ --protoc-plugins value ] Specify plugins for the protoc. ({plugin_name}:{options}:{out_dir})
--thrift-plugins value [ --thrift-plugins value ] Specify plugins for the thriftgo. ({plugin_name}:{options})
--help, -h show help (default: false)
- idl: idl 文件路径 (.thrift 或者 .proto)
- module/mod: 指定 go mod 的名字,非 GOPATH 下必须指定,GOPATH 下默认以相对于 GOPATH 的路径作为名字
- base_domain: 指定要访问的 domain,可以是域名、IP:PORT、service name(配合服务发现),也可以在 IDL 中通过 注解 声明
- model_dir: 指定 model 的生成路径,默认为 “biz/model” (相对路径,基于 out_dir)
- client_dir: 指定 hertz client 侧代码的生成路径,代码默认生成于 “{$MODULE}/{$MODEL_DIR}/{$namespace}/",可使用该参数修改代码默认生成路径
- use: 指定 hertz client 侧代码中 import model 包的位置,该参数适用于在生成 hertz client 侧代码之前已经生成过 model 代码的场景,使用该命令可直接 import 已有的 model 代码,无需再次生成
- force_client_dir: 指定 client 侧代码的生成路径,且不使用 service_name 作为子路径,如代码默认生成的相对路径为 " hello_service/hello_service.go”、“hello_service/hertz_client.go”,使用该参数后变为 “hello_service.go”、“hertz_client.go”
- proto_path/I: 当 idl 为 protobuf 时,指定 idl 的搜索路径,同 protoc 的 -I 指令
- thriftgo/t: 透传给 thriftgo 的选项 ({flag}={value})
- protoc/p: 透传给 protoc 的选项 ({flag}={value})
- no_recurse: 只生成主 idl 的 model 代码,默认为 false
- enable_extends: 解析 thrift idl 中的 extends
- json_enumstr: 当 idl 为 thrift 时,json enums 使用 string 代替 num (透传给 thriftgo 的选项)
- unset_omitempty: 当 idl 为 protobuf 时,生成 model field,去掉 omitempty tag;当 idl 为 thrift 时,是否添加 omitempty 根据 field 是 “optional” 还是 “required” 决定
- pb_camel_json_tag: 生成 model field 时将 json tag 的命名风格改为驼峰命名(仅作用于 protobuf)
- snake_tag: tag 使用 snake_case 风格命名 (仅对 form、query、json 生效)
- rm_tag value: 移除指定的 tag
- exclude_file/E: 不需要更新的文件 (相对项目路径,支持多个)
- customize_layout: 自定义项目 layout 模板,具体详见:自定义模板使用
- customize_layout_data_path value: 自定义项目 layout 模板渲染参数,具体详见:自定义模板使用
- customize_package: 自定义项目 package 相关模板,主要可针对 handler 模板进行定制化,具体详见:自定义模板使用
- protoc-plugins: 接入 protoc 相关的第三方生成代码插件,具体详见:hz 接入第三方生成代码插件
- thrift-plugins: 接入 thrift 相关的第三方生成代码插件,具体详见:hz 接入第三方生成代码插件
- help/h: 帮助命令
title: ‘IDL 注解说明’ date: 2023-02-21 weight: 6 keywords: [ “IDL 注解说明”, “api 注解”, “Field 注解”, “Method 注解” ] description: “hz 提供的 IDL 注解说明。”
支持的 api 注解
Field 注解可用于 参数绑定及校验
Method 注解可用于生成路由注册相关代码
支持的 api 注解
hz
Field 注解 tag 说明可参考 支持的-tag。
| Field 注解 | |
|---|---|
| 注解 | 说明 |
| api.raw_body | 生成 “raw_body” tag |
| api.query | 生成 “query” tag |
| api.header | 生成 “header” tag |
| api.cookie | 生成 “cookie” tag |
| api.body | 生成 “json” tag |
| api.path | 生成 “path” tag |
| api.form | 生成 “form” tag |
| api.go_tag (protobuf) go.tag (thrift) |
透传 go_tag,会生成 go_tag 里定义的内容 |
| api.vd | 生成 “vd” tag |
| api.none | 生成 “-” tag,详情参考 api.none 注解说明 |
| Method 注解 | |
|---|---|
| 注解 | 说明 |
| api.get | 定义 GET 方法及路由 |
| api.post | 定义 POST 方法及路由 |
| api.put | 定义 PUT 方法及路由 |
| api.delete | 定义 DELETE 方法及路由 |
| api.patch | 定义 PATCH 方法及路由 |
| api.options | 定义 OPTIONS 方法及路由 |
| api.head | 定义 HEAD 方法及路由 |
| api.any | 定义 ANY 方法及路由 |
hz client
除 hz 提供的注解外,为针对 client 的场景,额外增加了两种注解。
| Client 注解 | |
|---|---|
| 注解 | 说明 |
| api.base_domain | 指定默认访问的请求 domain |
使用方法
Field 注解
Thrift:
struct Demo {
1: string Demo (api.query="demo", api.path="demo");
2: string GoTag (go.tag="goTag:\"tag\"");
3: string Vd (api.vd="$!='your string'");
}
Protobuf:
message Demo {
string Demo = 1[(api.query) = "demo", (api.path) = "demo"];
string GoTag = 2[(api.go_tag) = "goTag:"tag""];
string Vd = 3[(api.vd) = "$!='your string'"];
}
Method 注解
Thrift:
service Demo {
Resp Method(1: Req request) (api.get="/route");
}
Protobuf:
service Demo {
rpc Method(Req) returns(Resp) {
option (api.get) = "/route";
}
}
Client 注解
Thrift:
struct Demo {
1: string HeaderValue (api.header="file1");
}
service Demo {
Resp Method(1: Req request) (api.get="/route");
}(
api.base_domain="http://127.0.0.1:8888";
)
Protobuf:
message Demo {
string HeaderValue = 1[(api.header) = "file1"];
}
service Demo {
rpc Method(Req) returns(Resp) {
option (api.get) = "/route";
}
option (api.base_domain) = "http://127.0.0.1:8888";
}
title: “hz 生成代码的结构” date: 2023-02-21 weight: 5 keywords: [“hz 生成代码的结构”] description: “hz 生成代码的结构。”
生成代码的结构
hz 生成的代码结构都类似,下面以 hz 使用 (thrift) 小节中的 thrift 代码为例,说明 hz 和 hz client 生成的代码的含义。
hz
.
├── biz // business 层,存放业务逻辑相关流程
│ ├── handler // 存放 handler 文件
│ │ ├── hello // hello/example 对应 thrift idl 中定义的 namespace;而对于 protobuf idl,则是对应 go_package 的最后一级
│ │ │ └── example
│ │ │ └── hello_service.go // handler 文件,用户在该文件里实现 IDL service 定义的方法,update 时会查找当前文件已有的 handler 并在尾部追加新的 handler
│ │ └── ping.go // 默认携带的 ping handler,用于生成代码快速调试,无其他特殊含义
│ ├── model // idl 内容相关的生成代码
│ │ └── hello // hello/example 对应 thrift idl 中定义的 namespace;而对于 protobuf idl,则是对应 go_package
│ │ └── example
│ │ └── hello.go // thriftgo 的产物,包含 hello.thrift 定义的内容的 go 代码,update 时会重新生成
│ └── router // idl 中定义的路由相关生成代码
│ ├── hello // hello/example 对应 thrift idl 中定义的 namespace;而对于 protobuf idl,则是对应 go_package 的最后一级
│ │ └── example
│ │ ├── hello.go // hz 为 hello.thrift 中定义的路由生成的路由注册代码;每次 update 相关 idl 会重新生成该文件
│ │ └── middleware.go // 默认中间件函数,hz 为每一个生成的路由组都默认加了一个中间件;update 时会查找当前文件已有的 middleware 在尾部追加新的 middleware
│ └── register.go // 调用注册每一个 idl 文件中的路由定义;当有新的 idl 加入,在更新的时候会自动插入其路由注册的调用;勿动
├── go.mod // go.mod 文件,如不在命令行指定,则默认使用相对于 GOPATH 的相对路径作为 module 名
├── idl // 用户定义的 idl,位置可任意
│ └── hello.thrift
├── main.go // 程序入口
├── router.go // 用户自定义除 idl 外的路由方法
├── router_gen.go // hz 生成的路由注册代码,用于调用用户自定义的路由以及 hz 生成的路由
├── .hz // hz 创建代码标志,无需改动
├── build.sh // 程序编译脚本,Windows 下不能运行,可直接使用 go build 命令编译程序
├── script
│ └── bootstrap.sh // 程序运行脚本,Windows 下不能运行,可直接运行 main.go
└── .gitignore
hz client
.
├── biz // business 层,存放业务逻辑相关流程
│ └── model // idl 内容相关的生成代码
│ └── hello // hello/example 对应 thrift idl 中定义的 namespace;而对于 protobuf idl,则是对应 go_package
│ └── example
│ ├── hello.go // thriftgo 的产物,包含 hello.thrift 定义的内容的 go 代码,update 时会重新生成
│ └── hello_service // 基于 idl 生成的类似 RPC 形式的 http 请求一键调用代码,可与 hz 生成的 server 代码直接互通
│ ├── hello_service.go
│ └── hertz_client.go
│
├── go.mod // go.mod 文件,如不在命令行指定,则默认使用相对于 GOPATH 的相对路径作为 module 名
└── idl // 用户定义的 idl,位置可任意
└── hello.thrift
title: ‘注意事项’ date: 2023-02-21 weight: 8 keywords: [“注意事项”, “protobuf”, “thrift”] description: “使用 hz 时的注意事项。”
使用 protobuf IDL 时的 biz 层代码生成位置
model 文件的位置
我们希望用户在定义 protobuf idl 的时候指定 go_package,这样一来符合 protobuf 的语义,二来生成的 model 位置可以通过 go_package 来决定。如果用户不指定 go_package,hz 会默认将 proto 文件的 package 作为 go_package,可能会有一些预期外的命名冲突。
目前 hz 为统一管理生成的 model,对 “go_package” 进行了一些处理,其规则如下:
假设当前项目是 github.com/a/b (module=github.com/a/b):
- go_package=“github.com/a/b/c/d”: 会在 “/biz/model/c/d” 下生成代码;
- go_package=“github.com/a/b/biz/model/c/d”: 会在 “/biz/model/c/d” 下生成 model,其中 “biz/model” 是默认的 model 生成路径,可使用 “–model_dir” 选项修改;
- go_package=“x/y/z”: 会在 “biz/model/x/y/z” 下生成代码(相对路径补全);
- go_package=“biz/model/c/d”: 会在"biz/model/biz/model/c/d” 下生成代码。
推荐用户定义如 “{$MODULE}/{$MODEL_DIR}/x/y/z” (其中 {$MODEL_DIR} 默认为"biz/model", 用户也可使用 “model_dir” 选项来定义) 这样的 “go_package”。
handler 文件的位置
handler 文件会取 go_package 最后一级作为生成路径。
例如,若 go_package = “hello.world”,其生成路径会是:
${项目路径}/${handler_dir}/world
router 文件的位置
router 注册文件同样会取 go_package 最后一级作为生成路径。
例如,若 go_package = “hello.world”,其生成路径会是:
${项目路径}/${router_dir}/world
使用 thrift IDL 时的 biz 层代码生成位置
hz 对于 thrift idl 的定义无特殊要求,符合语法规范即可。代码的生成路径会和 thrift 的 namespace 相关。
例如,可以这样定义 namespace:
namespace go hello.world
model 生成的路径会是:
${项目路径}/${model_dir}/hello/world
handler 文件会取 namespace 作为生成路径,其生成路径会是:
${项目路径}/${handler_dir}/hello/world
router 注册文件同样会取 namespace 作为生成路径,其生成路径会是:
${项目路径}/${router_dir}/hello/world
使用 update 命令时的行为说明
-
使用自定义路径的注意事项
hz 为了用户使用方便,提供了自定义 handler 路径、model 路径、模板等功能。但是 hz 在创建一个新项目的时候并没有保存当前项目的信息,所以在使用 update 命令时可以认为是一种无状态的更新。因此对于同一套 idl 在 new 和 update 的时候,使用了不同的自定义信息,可能会产生重复的代码,举个例子,如下:
创建新项目:
hz new -idl demo.thrift // 此时,hz 会把 model 生成在 "biz/model"下更新项目:
hz update -idl demo.thrift --model_dir=my_model // 此时,hz 不会更新"biz/model"下的 model 代码,而是会在"my_model"下;这时"biz/model"和"my_model"下的代码就会重复,且新生成的 handler 会依赖"my_model",之前的 handler 会依赖"biz/model",这时就需要用户手动删除&改动一些代码了。因此,我们希望用户使用 update 命令的时候,自定义的路径 “client_dir”、“model_dir”、“handler_dir”,最好和 new 相同。
-
update handler 的行为
hz 在 new 项目的时候会根据默认模板/自定义模板来生成 handler,其中每个 service 生成一个文件,该文件包含了该 service 定义的所有 handler 代码;如果 idl 定义了多个 service,则每个 service 都会生成一个文件,这些文件都在同一路径下;举个例子:
// demo.thrift namespace go hello.example service Service1 { HelloResp Method1(1: HelloReq request) (api.get="/hello"); } service Service2 { HelloResp Method2(1: HelloReq request) (api.get="/new"); } // 那么该 idl 生成的 handler 文件如下: ${handler_dir}/${namespace}/service1.go -> method1 ${handler_dir}/${namespace}/service2.go -> method2当该 idl 增加了新的 method 后,就会在对应 service 的文件的末尾追加 handler 模板;注意这里追加的 handler 会使用默认的模板,新生成 service 文件会根据情况使用自定义模板。
-
update router 的行为
hz 在 new 的时候生成的 router 代码主要有如下三个:
- biz/router/${namespace}/${idlName}.go: 每个主 idl 都会生成对应的路由注册代码文件,该文件以路由组的方式注册 idl 中定义的所有路由,并设置默认的中间件。
- biz/router/${namespace}/middleware.go: 每个主 idl 对应的默认中间件函数,用户可修改中间件函数,以此为特定的路由增加特定的中间件逻辑。
-
biz/router/register.go:该文件负责调用不同 idl 生成的路由注册;比如我在两个 idl “demo1.thrift”、“demo2.thrift” 中都定义了 service,那么这两个文件都会生成对应的路由注册代码。register.go 负责调用这两部分的路由注册函数。
基于上述描述,给出 router 在 update 时的行为描述:
-
biz/${namespace}/${idlName}.go: 每次都基于 idl 重新生成,用户不要改该文件代码,否则会丢失代码。
- biz/${namespace}/middleware.go: 每次都会在尾部追加目前没有的 middleware。
- biz/router/register.go: 如果有新增的 idl 会插入新的 idl 的路由注册方式。
使用 Windows 操作系统时的注意事项
使用 hz 命令创建项目时将用到 symlink,在 Windows
操作系统下你可能需要 开启开发者模式
来启用用户权限的 symlink。
在基于 protobuf IDL 创建项目时,你需要手动安装 protoc 命令行工具
至 PATH 环境变量,另外如果你使用 google/protobuf 包下的文件,你需要将 protoc-win64.zip 中 include 目录下的所有文件放在
protoc 同一目录。
title: “hz 代码生成” weight: 6 keywords: [“hz 代码生成”] description: “Hertz 提供的代码生成工具 hz。”
title: ‘hz 接入第三方生成代码插件’ date: 2023-01-21 weight: 3 keywords: [“插件”, “ThriftGo”, “Protoc”, “go_package”] description: “hz 接入第三方生成代码插件。”
目前,hz 的代码生成是基于 “thriftgo” 和 “protoc” 的插件模式生成的,这对于接入一些第三方的插件提供了很大的帮助,尤其是对于 " protoc" 来说,目前其支持的插件生态相当丰富。
因此,hz 提供了拓展第三方插件的方法。
ThriftGo 插件扩展
使用方法
hz new --idl={YOUR-IDL.thrift} --thrift-plugins={PLUGIN-NAME}
如果插件需要传一些选项的话,如下:
hz new --idl={YOUR-IDL.thrift} --thrift-plugins={PLUGIN-NAME}:{YOUR-OPTION1,YOUR-OPTION2} --mod={YOUR_MODULE}
示例
目前,thriftgo 提供一个生成结构体参数验证函数的插件 “thrift-gen-validator”,可在生成 model 的时候一并生成结构体参数验证函数。
-
安装:
go install github.com/cloudwego/thrift-gen-validator@latest -
使用:
hz new --idl=idl/hello.thrift --thrift-plugins=validator -
代码:code
Protoc 插件拓展
Protoc 插件相关的代码生成位置与 proto 文件的 go_package 有关,详情可 参考。
使用方法
hz new --idl={YOUR-IDL.proto} --protoc-plugins={PLUGIN-NAME}
如果插件需要传一些选项的话,如下:
hz new --idl={YOUR-IDL.proto} --protoc-plugins={PLUGIN_NAME}:{OPTION1,OPTION2}:{OUT_DIR} --mod={YOUR_MODULE}
示例
这里以使用 hz 时集成 protoc-gen-openapi 插件用来生成 openapi 3.0 文档为例。
-
安装:
go install github.com/google/gnostic/cmd/protoc-gen-openapi@latest -
定义 idl 的 go_package:“middleware/hertz/biz/model/psm”
-
使用:
hz new -I=idl --idl=idl/hello/hello.proto --protoc-plugins=openapi::./docs --mod=middleware/hertz -
代码:code
title: “hz 自定义模板使用” date: 2023-02-20 weight: 2 keywords: [“hz client”, “layout”, “package”] description: “hz 自定义模板使用。”
Hertz 提供的命令行工具 (以下称为"hz") 支持自定义模板功能,包括:
- 自定义 layout 模板 (即生成代码的目录结构,这些结构与具体的 idl 定义无关,不需要 idl 也可以直接生成)
- 自定义 package 模板 (即与 idl 定义相关的代码结构,包括 handler、model、router 等)
以 hz 生成代码的结构 中的代码结构为例(集成 hz 和 hz client 生成的代码),介绍 hz 提供的默认模板:
.
├── biz
│ ├── handler // biz/handler 为默认 handler_dir,可通过 --handler_dir 修改
│ │ ├── hello // handler 相关代码,与 idl 有关,package 模板生成
│ │ │ └── example
│ │ │ └── hello_service.go
│ │ └── ping.go // layout 模板生成
│ ├── model // biz/model 为默认 model_dir,可通过 --model_dir 修改
│ │ └── hello
│ │ └── example
│ │ └── hello.go // 由 hz 调用 thriftgo 生成,不涉及 layout 模板和 package 模板
│ │ └── hello_service // 调用 hz client 命令得到,与 idl 有关,package 模板生成
│ │ └── hello_service.go
│ │ └── hertz_client.go
│ └── router // biz/router 为默认 router_dir,可通过 --router_dir 修改
│ ├── hello // router 相关代码,与 idl 有关,package 模板生成
│ │ └── example
│ │ ├── hello.go
│ │ └── middleware.go
│ └── register.go // 未指定 idl 时,由 layout 模板生成;指定 idl 时,由 package 模板生成
├── go.mod // go.mod 文件,layout 模板生成
├── main.go // 程序入口,layout 模板生成
├── router.go // 用户自定义除 idl 外的路由方法,layout 模板生成
└── router_gen.go // hz 生成的路由注册代码,用于调用用户自定义的路由以及 hz 生成的路由,layout 模板生成
├── .hz
├── build.sh // 程序编译脚本,layout 模板生成
├── script
│ └── bootstrap.sh // 程序运行脚本,layout 模板生成
└── .gitignore // layout 模板生成
用户可自己提供模板以及渲染参数,并结合 hz 的能力,来完成自定义的代码生成结构。
layout 模板
hz 利用了 go template 支持以 “yaml” 的格式定义 layout 模板,并使用 “json” 定义模板渲染数据。
用户可根据默认模板来修改或重写,从而满足自身需求。
注意:当在命令行中未指定自定义模板渲染文件时,hz 会使用 默认渲染参数 渲染自定义 layout 模板,此时应保证自定义 layout 模板的渲染参数在 默认渲染参数 的范围内。
默认 layout 模板
注:以下的 body 均为 go template
layouts:
# 生成的 dal 的目录,只有目录下有文件才会生成
- path: biz/dal/
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: ""
# 生成的 handler 的目录,只有目录下有文件才会生成
- path: biz/handler/
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: ""
# 生成的 model 的目录,只有目录下有文件才会生成
- path: biz/model/
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: ""
# 生成的 service 的目录,只有目录下有文件才会生成
- path: biz/service/
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: ""
# 项目 main.go 文件
- path: main.go
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator.
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
register(h)
h.Spin()
}
# go.mod 文件,需要模板渲染数据 {{.GoModule}} {{.UseApacheThrift}} 才能生成
- path: go.mod
delims:
- '{{'
- '}}'
body: |-
module {{.GoModule}}
{{- if .UseApacheThrift}}
replace github.com/apache/thrift => github.com/apache/thrift v0.13.0
{{- end}}
# .gitignore 文件
- path: .gitignore
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: "*.o\n*.a\n*.so\n_obj\n_test\n*.[568vq]\n[568vq].out\n*.cgo1.go\n*.cgo2.c\n_cgo_defun.c\n_cgo_gotypes.go\n_cgo_export.*\n_testmain.go\n*.exe\n*.exe~\n*.test\n*.prof\n*.rar\n*.zip\n*.gz\n*.psd\n*.bmd\n*.cfg\n*.pptx\n*.log\n*nohup.out\n*settings.pyc\n*.sublime-project\n*.sublime-workspace\n!.gitkeep\n.DS_Store\n/.idea\n/.vscode\n/output\n*.local.yml\ndumped_hertz_remote_config.json\n\t\t
\ "
# handler 中的 ping.go 文件,需要模板渲染数据 {{.HandlerPkg}} 才能生成
- path: biz/handler/ping.go
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator.
package {{.HandlerPkg}}
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/utils"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
)
// Ping .
func Ping(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
c.JSON(consts.StatusOK, utils.H{
"message": "pong",
})
}
# 定义路由注册的文件,需要模板渲染数据 {{.RouterPkgPath}} 才能生成
- path: router_gen.go
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator. DO NOT EDIT.
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
router "{{.RouterPkgPath}}"
)
// register registers all routers.
func register(r *server.Hertz) {
router.GeneratedRegister(r)
customizedRegister(r)
}
# 自定义路由注册的文件,需要模板渲染数据 {{.HandlerPkgPath}} 才能生成
- path: router.go
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator.
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
handler "{{.HandlerPkgPath}}"
)
// customizeRegister registers customize routers.
func customizedRegister(r *server.Hertz){
r.GET("/ping", handler.Ping)
// your code ...
}
# 默认路由注册文件,不要修改,需要模板渲染数据 {{.RouterPkg}} 才能生成
- path: biz/router/register.go
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator. DO NOT EDIT.
package {{.RouterPkg}}
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
// GeneratedRegister registers routers generated by IDL.
func GeneratedRegister(r *server.Hertz){
//INSERT_POINT: DO NOT DELETE THIS LINE!
}
# 编译脚本,需要模板渲染数据 {{.ServiceName}} 才能生成
- path: build.sh
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: |-
#!/bin/bash
RUN_NAME={{.ServiceName}}
mkdir -p output/bin
cp script/* output 2>/dev/null
chmod +x output/bootstrap.sh
go build -o output/bin/${RUN_NAME}
# 运行脚本,需要模板渲染数据 {{.ServiceName}} 才能生成
- path: script/bootstrap.sh
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: |-
#!/bin/bash
CURDIR=$(cd $(dirname $0); pwd)
BinaryName={{.ServiceName}}
echo "$CURDIR/bin/${BinaryName}"
exec $CURDIR/bin/${BinaryName}
模板渲染参数文件
hz 使用了 “json” 来指定渲染数据,包括全局的渲染参数和各个文件的渲染参数。
全局渲染参数在各个文件中都能使用,文件渲染参数只能用于所属文件。
全局渲染参数
全局渲染参数的 key 为 “*",hz 默认提供了如下五个全局渲染参数:
| 渲染参数名 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| GoModule | - | go module,可通过 –module 指定 |
| ServiceName | hertz_service | 服务名,可通过 –service 指定 |
| UseApacheThrift | - | idl 为 thrift 时为 true,否则为 false |
| HandlerPkg | handler | handler_dir 的最后一级路径,可通过 –handler_dir 修改 |
| RouterPkg | router | router_dir 的最后一级路径,可通过 –router_dir 修改 |
注意:除 UseApacheThrift 外,其它参数都可以通过命令行指定,此时若在自定义渲染参数文件中也指定了该参数,应保证两处参数的值一致,否则可能会出现问题。因此我们建议,在使用自定义模板时 ServiceName, HandlerPkg, RouterPkg 不需要在命令行中指定,在渲染参数文件中指出即可,GOPATH 外指定 go mod 时应保证两处的一致性。
用户可以根据需求自定义全局渲染参数名和值,但需保证 key 为 “*"。
文件渲染参数
hz 默认提供了如下文件渲染参数:
{
"router_gen.go": {
"RouterPkgPath": "{GoModule}/biz/router",
"HandlerPkgPath": "{GoModule}/biz/handler"
},
"router.go": {
"RouterPkgPath": "{GoModule}/biz/router",
"HandlerPkgPath": "{GoModule}/biz/handler"
}
}
文件渲染参数仅作用于所属文件,key 为文件名(基于 out_dir 的相对路径),值可任意定义。
自定义一个 layout 模板
目前,hz 生成的项目 layout 已经是一个 hertz 项目最最最基础的骨架了,所以不建议删除现有的模板里的文件。
不过如果用户想要一个别的 layout,当然也可以根据自身需求来删除相应的文件 (除"biz/register.go"外,其余都可以动)
我们十分欢迎用户来贡献自己的模板。
下面假设用户只想要 “main.go” 以及 “go.mod” 文件,那么我们对默认模板进行修改,如下:
template
// layout.yaml
layouts:
# 项目 main.go 文件
- path: main.go
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator.
package main
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"{{.GoModule}}/biz/router"
)
func main() {
h := server.Default()
router.GeneratedRegister(h)
// do what you wanted
// add some render data: {{.MainData}}
h.Spin()
}
# go.mod 文件,需要模板渲染数据{{.GoModule}}才能生成
- path: go.mod
delims:
- '{{'
- '}}'
body: |-
module {{.GoModule}}
{{- if .UseApacheThrift}}
replace github.com/apache/thrift => github.com/apache/thrift v0.13.0
{{- end}}
# 默认路由注册文件,没必要修改
- path: biz/router/register.go
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator. DO NOT EDIT.
package router
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
)
// GeneratedRegister registers routers generated by IDL.
func GeneratedRegister(r *server.Hertz){
//INSERT_POINT: DO NOT DELETE THIS LINE!
}
render data
{
"*": {
"GoModule": "github.com/hertz/hello",
"ServiceName": "hello",
"UseApacheThrift": true
},
"main.go": {
"MainData": "this is customized render data"
}
}
命令:
hz new --mod=github.com/hertz/hello --idl=./hertzDemo/hello.thrift --customize_layout=template/layout.yaml --customize_layout_data_path=template/data.json
package 模板
package 模板与 idl 定义相关,包括 handler、model、router 等。
用户可根据默认模板来修改或重写,从而满足自身需求。
默认 package 模板
layouts:
# path 只表示 handler.go 的模板,具体的 handler 路径由默认路径和 handler_dir 决定
- path: handler.go
delims:
- '{{'
- '}}'
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator.
package {{.PackageName}}
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
{{- range $k, $v := .Imports}}
{{$k}} "{{$v.Package}}"
{{- end}}
)
{{range $_, $MethodInfo := .Methods}}
{{$MethodInfo.Comment}}
func {{$MethodInfo.Name}}(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
var err error
{{if ne $MethodInfo.RequestTypeName "" -}}
var req {{$MethodInfo.RequestTypeName}}
err = c.BindAndValidate(&req)
if err != nil {
c.String(consts.StatusBadRequest, err.Error())
return
}
{{end}}
resp := new({{$MethodInfo.ReturnTypeName}})
c.{{.Serializer}}(consts.StatusOK, resp)
}
{{end}}
# path 只表示 router.go 的模板,具体的路径由默认路径和 router_dir 决定
- path: router.go
delims:
- '{{'
- '}}'
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator. DO NOT EDIT.
package {{$.PackageName}}
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
{{range $k, $v := .HandlerPackages}}{{$k}} "{{$v}}"{{end}}
)
/*
This file will register all the routes of the services in the master idl.
And it will update automatically when you use the "update" command for the idl.
So don't modify the contents of the file, or your code will be deleted when it is updated.
*/
{{define "g"}}
{{- if eq .Path "/"}}r
{{- else}}{{.GroupName}}{{end}}
{{- end}}
{{define "G"}}
{{- if ne .Handler ""}}
{{- .GroupName}}.{{.HttpMethod}}("{{.Path}}", append({{.MiddleWare}}Mw(), {{.Handler}})...)
{{- end}}
{{- if ne (len .Children) 0}}
{{.MiddleWare}} := {{template "g" .}}.Group("{{.Path}}", {{.MiddleWare}}Mw()...)
{{- end}}
{{- range $_, $router := .Children}}
{{- if ne .Handler ""}}
{{template "G" $router}}
{{- else}}
{ {{template "G" $router}}
}
{{- end}}
{{- end}}
{{- end}}
// Register register routes based on the IDL 'api.${HTTP Method}' annotation.
func Register(r *server.Hertz) {
{{template "G" .Router}}
}
# path 只表示 register.go 的模板,具体的路径由默认路径和 router_dir 决定
- path: register.go
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator. DO NOT EDIT.
package {{.PackageName}}
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
{{$.DepPkgAlias}} "{{$.DepPkg}}"
)
// GeneratedRegister registers routers generated by IDL.
func GeneratedRegister(r *server.Hertz){
//INSERT_POINT: DO NOT DELETE THIS LINE!
{{$.DepPkgAlias}}.Register(r)
}
- path: model.go
delims:
- ""
- ""
body: ""
# path 只表示 middleware.go 的模板,middleware 的路径和 router.go 相同
- path: middleware.go
delims:
- '{{'
- '}}'
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator.
package {{$.PackageName}}
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
)
{{define "M"}}
func {{.MiddleWare}}Mw() []app.HandlerFunc {
// your code...
return nil
}
{{range $_, $router := $.Children}}{{template "M" $router}}{{end}}
{{- end}}
{{template "M" .Router}}
# path 只表示 client.go 的模板,仅当使用 hz new --client_dir 或 hz update --client_dir 时生成,路径由 out_dir 和 client_dir 决定
- path: client.go
delims:
- '{{'
- '}}'
body: |-
// Code generated by hertz generator.
package {{$.PackageName}}
import (
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/config"
)
type {{.ServiceName}}Client struct {
client * client.Client
}
func New{{.ServiceName}}Client(opt ...config.ClientOption) (*{{.ServiceName}}Client, error) {
c, err := client.NewClient(opt...)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &{{.ServiceName}}Client{
client: c,
}, nil
}
# handler_single 表示单独的 handler 模板,用于 update 的时候更新每一个新增的 handler
- path: handler_single.go
delims:
- '{{'
- '}}'
body: |+
{{.Comment}}
func {{.Name}}(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
// this my demo
var err error
{{if ne .RequestTypeName "" -}}
var req {{.RequestTypeName}}
err = c.BindAndValidate(&req)
if err != nil {
c.String(consts.StatusBadRequest, err.Error())
return
}
{{end}}
resp := new({{.ReturnTypeName}})
c.{{.Serializer}}(consts.StatusOK, resp)
}
# middleware_single 表示单独的 middleware 模板,用于 update 的时候更新每一个新增的 middleware_single
- path: middleware_single.go
delims:
- '{{'
- '}}'
body: |+
func {{.MiddleWare}}Mw() []app.HandlerFunc {
// your code...
return nil
}
# hertz_client 由 hz client 命令生成,详细代码请参考 https://github.com/cloudwego/hertz/blob/develop/cmd/hz/generator/package_tpl.go#L271
- path: hertz_client.go
delims:
- '{{'
- '}}'
# idl_client 由 hz client 命令生成,详细代码请参考 https://github.com/cloudwego/hertz/blob/develop/cmd/hz/generator/package_tpl.go#L862
- path: idl_client.go
delims:
- '{{'
- '}}'
模板渲染参数
注意:与 layout 模板不同,自定义 package 模板没有提供渲染数据的功能,这里主要是因为这些渲染数据是 hz 工具解析生成的,所以暂时不提供自己写渲染数据的功能。可以修改下模板里面与渲染数据无关的部分,以满足自身需求。
下面介绍 hz 默认提供的模板渲染参数。
-
文件路径渲染:在指定文件路径的时候使用如下渲染数据
type FilePathRenderInfo struct { MasterIDLName string // master IDL name GenPackage string // master IDL generate code package HandlerDir string // handler generate dir ModelDir string // model generate dir RouterDir string // router generate dir ProjectDir string // projectDir GoModule string // go module ServiceName string // service name, changed as services are traversed MethodName string // method name, changed as methods are traversed HandlerGenPath string // "api.gen_path" value } -
单个文件的渲染数据:在单独定义一个文件时使用的渲染数据,可根据 “IDLPackageRenderInfo” 的定义解出所有 IDL 的信息
type CustomizedFileForIDL struct { *IDLPackageRenderInfo FilePath string FilePackage string } -
Method 级别的渲染数据:当指定 “loop_method” 时,会使用到的渲染数据,会以每个 method 为单位生成一个文件
type CustomizedFileForMethod struct { *HttpMethod // 每个 method 定义的解析出来的具体信息 FilePath string // 当循环生成 method 文件时,该文件路径 FilePackage string // 当循环生成 method 文件时,该文件的 go package 名 ServiceInfo *Service // 该 method 所属的 service 定义的信息 } type HttpMethod struct { Name string HTTPMethod string Comment string RequestTypeName string ReturnTypeName string Path string // 请求路由 Serializer string OutputDir string Models map[string]*model.Model } -
Service 级别的渲染数据:当指定 “loop_service” 时,会使用到的渲染数据,会以每个 service 为单位生成一个文件
type CustomizedFileForService struct { *Service // 该 service 的具体信息,包括 service 名字,servide 内定义的 method 的信息等 FilePath string // 当循环生成 service 文件时,该文件路径 FilePackage string // 当循环生成 service 文件时,该文件的 go package 名 IDLPackageInfo *IDLPackageRenderInfo // 该 service 所属的 IDL 定义的信息 } type Service struct { Name string Methods []*HttpMethod ClientMethods []*ClientMethod Models []*model.Model // all dependency models BaseDomain string // base domain for client code }
自定义一个 package 模板
与 layout 模板一样,用户同样可以自定义 package 模板。
就 package 提供的模板来说,一般用户可能只有自定义 handler.go 模板的需求,因为 router.go/middleware.go/register.go 一般与 idl 定义相关而用户无需关心,一般也无需修改。
因此,用户可根据自身的需求来自定义生成的 handler 模板,加速开发速度;但是由于默认的 handler 模板集成了一些 model 的信息以及 package 信息,所以需要 hz 工具来提供渲染数据。这部分用户可根据自身情况酌情来修改,一般建议留下 model 信息。
覆盖默认模板
目前,hz 本身自带了如下的模板:
- handler.go
- router.go
- register.go
- middleware.go
- client.go
- handler_single.go
- middleware_single.go
- idl_client.go
- hertz_client.go
以上这些模板是工具运行最基础的模板,在自定义模板的时候:
- 如果指定了同名模板会覆盖掉默认的内容
- 如果没指定同名模板会使用默认的模板
因此,大家在自定义模板的时候需要根据自己的实际情况来考虑是否需要覆盖掉这些模板。
注意:用户在自定义模板时若要覆盖上述模板只需指出文件名,无需给出相对路径(如 handler.go),但新增自己的实现时需要给出基于 out_dir 的相对路径。
添加一个新的模板
考虑到大家有时可能需要针对 IDL 的某些信息新增自己的一些实现,例如为每个生成的 handler 加一下单测等需求。因此,hz 的模板里允许用户自定义新的模板,渲染参数可参考 模板渲染参数。
模板形式:
- path: biz/Fgy/{{$HandlerName}}.go // 路径 + 文件名,支持渲染数据
loop_method: bool // 是否按照 idl 中定义的 method 生成多个文件,配合 path 渲染使用
loop_service: bool // 是否按照 idl 中定义的 service 生成多个文件,配合 path 渲染使用
update_behavior: // 在使用 hz update 的时候对于该文件的更新行为
type: string // 更新行为:skip/cover/append
append_key: string // 在 append 行为的时候,指定追加的渲染数据源,method/service
insert_key: string // 在 append 行为的时候追加逻辑的 “key”,根据这个 key 判断是否需要进行追加
append_content_tpl: string // 在 append 行为的时候,指定追加内容的模板
import_tpl: []string // 要新增的 import 的模板
body: string // 生成文件的模板内容
下面给出一个简单的自定义 handler 模板的示例:
example
example:https://github.com/cloudwego/hertz-examples/tree/main/hz/template
-
修改默认 handler 的内容
-
为 handler 新增一个单测文件
layouts:
- path: handler.go
body: |-
{{$OutDirs := GetUniqueHandlerOutDir .Methods}}
package {{.PackageName}}
import (
"context"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/protocol/consts"
{{- range $k, $v := .Imports}}
{{$k}} "{{$v.Package}}"
{{- end}}
{{- range $_, $OutDir := $OutDirs}}
{{if eq $OutDir "" -}}
"{{$.ProjPackage}}/biz/service"
{{- else -}}
"{{$.ProjPackage}}/biz/service/{{$OutDir}}"
{{- end -}}
{{- end}}
"{{$.ProjPackage}}/biz/utils"
)
{{range $_, $MethodInfo := .Methods}}
{{$MethodInfo.Comment}}
func {{$MethodInfo.Name}}(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
var err error
{{if ne $MethodInfo.RequestTypeName "" -}}
var req {{$MethodInfo.RequestTypeName}}
err = c.BindAndValidate(&req)
if err != nil {
utils.SendErrResponse(ctx, c, consts.StatusOK, err)
return
}
{{end}}
{{if eq $MethodInfo.OutputDir "" -}}
resp,err := service.New{{$MethodInfo.Name}}Service(ctx, c).Run(&req)
if err != nil {
utils.SendErrResponse(ctx, c, consts.StatusOK, err)
return
}
{{else}}
resp,err := {{$MethodInfo.OutputDir}}.New{{$MethodInfo.Name}}Service(ctx, c).Run(&req)
if err != nil {
utils.SendErrResponse(ctx, c, consts.StatusOK, err)
return
}
{{end}}
utils.SendSuccessResponse(ctx, c, consts.StatusOK, resp)
}
{{end}}
update_behavior:
import_tpl:
- |-
{{$OutDirs := GetUniqueHandlerOutDir .Methods}}
{{- range $_, $OutDir := $OutDirs}}
{{if eq $OutDir "" -}}
"{{$.ProjPackage}}/biz/service"
{{- else -}}
"{{$.ProjPackage}}/biz/service/{{$OutDir}}"
{{end}}
{{- end}}
- path: handler_single.go
body: |+
{{.Comment}}
func {{.Name}}(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {
var err error
{{if ne .RequestTypeName "" -}}
var req {{.RequestTypeName}}
err = c.BindAndValidate(&req)
if err != nil {
utils.SendErrResponse(ctx, c, consts.StatusOK, err)
return
}
{{end}}
{{if eq .OutputDir "" -}}
resp,err := service.New{{.Name}}Service(ctx, c).Run(&req)
{{else}}
resp,err := {{.OutputDir}}.New{{.Name}}Service(ctx, c).Run(&req)
{{end}}
if err != nil {
utils.SendErrResponse(ctx, c, consts.StatusOK, err)
return
}
utils.SendSuccessResponse(ctx, c, consts.StatusOK, resp)
}=
- path: "{{.HandlerDir}}/{{.GenPackage}}/{{ToSnakeCase .ServiceName}}_test.go"
loop_service: true
update_behavior:
type: "append"
append_key: "method"
insert_key: "Test{{$.Name}}"
append_tpl: |-
func Test{{.Name}}(t *testing.T) {
h := server.Default()
h.{{.HTTPMethod}}("{{.Path}}", {{.Name}})
w := ut.PerformRequest(h.Engine, "{{.HTTPMethod}}", "{{.Path}}", &ut.Body{Body: bytes.NewBufferString(""), Len: 1},
ut.Header{})
resp := w.Result()
assert.DeepEqual(t, 201, resp.StatusCode())
assert.DeepEqual(t, "", string(resp.Body()))
// todo edit your unit test.
}
body: |-
package {{.FilePackage}}
import (
"bytes"
"testing"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/test/assert"
"github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/common/ut"
)
{{range $_, $MethodInfo := $.Methods}}
func Test{{$MethodInfo.Name}}(t *testing.T) {
h := server.Default()
h.{{$MethodInfo.HTTPMethod}}("{{$MethodInfo.Path}}", {{$MethodInfo.Name}})
w := ut.PerformRequest(h.Engine, "{{$MethodInfo.HTTPMethod}}", "{{$MethodInfo.Path}}", &ut.Body{Body: bytes.NewBufferString(""), Len: 1},
ut.Header{})
resp := w.Result()
assert.DeepEqual(t, 201, resp.StatusCode())
assert.DeepEqual(t, "", string(resp.Body()))
// todo edit your unit test.
}
{{end}}
MVC 模板实践
Hertz 提供了 一个 MVC 自定义模版的最佳实践,代码详见 code 。
注意事项
使用 package 模板的注意事项
一般来说,用户使用 package 模板的时候大多数是为了修改默认的 handler 模板;不过,目前 hz 没有提供单个 handler 的模板,所以当 update 已经存在的 handler 文件时,会使用默认 handler_single 模板在 handler 文件尾追加新的 handler function。当对应的 handler 文件不存在的时候,才会使用自定义模板来生成 handler 文件。
title: ‘api.none 注解说明’ date: 2023-04-23 weight: 5 keywords: [“api.none”, “thrift”, “protobuf”] description: “hz 提供的 api.none 注解说明。”
介绍
hz 生成的代码会自动为结构体添加 go tag,从而方便进行参数绑定。 而用户结构体的中某些"域"可能不想参与参数绑定或者序列化过程,因此我们提供了 “api.none” 注解, 使得生成的结构体的"域"的 go tag 为 “-",从而避免参与参数绑定。
thrift
定义:
struct HelloReq{
1: string Hertz (api.none="true");
}
生成内容:
type HelloReq struct {
Hertz string `thrift:"Hertz,1" form:"-" json:"-" query:"-"`
}
protobuf
定义:
message HelloReq {
optional string Hertz = 1 [(api.none) = "true"];
}
生成内容:
type HelloReq struct {
state protoimpl.MessageState
sizeCache protoimpl.SizeCache
unknownFields protoimpl.UnknownFields
Hertz *string `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=Hertz" json:"-" form:"-" query:"-"`
}
title: “更多特性” weight: 9 keywords: [“更多特性”, “自定义模板”, “第三方插件”, “hz client”, “api.none”] description: “hz 提供的更多特性。”
title: ‘hz client 代码生成’ date: 2023-02-20 weight: 4 keywords: [“hz client”, “高级设置”] description: “hz client 代码生成。”
介绍
基于 IDL 生成类似 RPC 形式的 http 请求一键调用,屏蔽掉创建和初始化 hertz client 的繁琐操作,并且实现和 hz 生成的 server 代码直接互通。
该命令需指定 idl,否则不会生成任何内容。
hz client 命令梳理可以参考 hz client。
hz client 生成的代码结构可以参考 hz client。
生成代码示例可以参考 code 。
示例
本示例基于 thrift 给出,protoc 与之类似。
定义 IDL
IDL 的定义和语义与目前的定义完全相同,所以基本不用修改原先的 IDL 即可生成 client 代码。
但是为针对 client 的场景,增加了两种注解, api.base_domain:指定默认访问的请求 domain。
namespace go toutiao.middleware.hertz_client
struct FormReq {
1: string FormValue (api.form="form1"); // form 注解用来声明 form 参数 ("multipart/form-data")
}
struct QueryReq {
1: string QueryValue (api.query="query1"); // query 注解用来声明请求的 query 参数
}
struct PathReq {
1: string PathValue (api.path="path1"); // path 注解用来声明 url 中的路由参数
}
struct BodyReq {
1: string BodyValue (api.body="body"); // body 注解不管是否声明都将整个结构体以 json 的形式设置到 body
2: string QueryValue (api.query="query2");
}
struct Resp {
1: string Resp;
}
service HelloService {
// api.post 用来声明请求的路由
Resp FormMethod(1: FormReq request) (api.post="/form", api.handler_path="post");
Resp QueryMethod(1: QueryReq request) (api.get="/query", api.handler_path="get");
Resp PathMethod(1: PathReq request) (api.post="/path:path1", api.handler_path="post");
Resp BodyMethod(1: BodyReq request) (api.post="/body", api.handler_path="post");
}(
// api.base_domain 用来指定默认的 client 请求的 domain
api.base_domain="http://127.0.0.1:8888";
)
生成 client 代码
hz client --mod=a/b/c --idl=../idl/psm.thrift --model_dir=model --client_dir=hertz_client -t=template=slim
高级设置
client 配置
以 thrift IDL 生成的代码为例
func main() {
generatedClient, err := hello_service.NewHelloServiceClient("https://www.example.com"),
hello_service.WithHertzClientOption() // 指定 client 配置
}
请求级别的配置
以 thrift IDL 生成的代码为例
func main() {
generatedClient, err := hello_service.NewHelloServiceClient(
"http://toutiao.hertz.testa", // 指定 psm 作为域名
)
// 在发起调用的时候可指定请求级别的配置
resp, rawResp, err := generatedClient.QueryMethod(
context.Background(),
QueryReq,
config.WithSD(true), // 指定请求级别的设置,用来开启服务发现
config.WithReadTimeout(), // 指定请求读超时
)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
}
设置 client 中间件
以 thrift IDL 生成的代码为例
func main() {
generatedClient, err := hello_service.NewHelloServiceClient(
"http://toutiao.hertz.testa", // 指定 psm 作为域名
hello_service.WithHertzClientMiddleware(), // 指定 client 的中间件
)
}
设置全局 header
以 thrift IDL 生成的代码为例
有一些通用的 header 可能每次请求都需要携带,或者是一些不能定义到 IDL 中的 header,这时我们就可以通过 “WithHeader” 注入这些 header,使得每次发送请求都会携带这些 header。
func main() {
generatedClient, err := hello_service.NewHelloServiceClient(
"http://toutiao.hertz.testa", // 指定 psm 作为域名
hello_service.WithHeader(), // 指定每次发送请求都需要携带的 header
)
}
配置 TLS
以 thrift IDL 生成的代码为例
Hertz client 的 TLS 走的是标准网络库,因此在使用生成的一键调用时需要配置为标准网络库。
func main() {
generatedClient, err := hello_service.NewHelloServiceClient("https://www.example.com"),
hello_service.WithHertzClientOption(
client.WithDialer(standard.NewDialer()), // 使用标准库
client.WithTLSConfig(clientCfg), // TLS 配置
)
}
自定义 hertz client
以 thrift IDL 生成的代码为例
func main() {
generatedClient, err := hello_service.NewHelloServiceClient("https://www.example.com"),
hello_service.WithHertzClient() // 指定自定义 hertz client
}
title: “概览” linkTitle: “概览” weight: 1 keywords: [“HTTP”, “Hertz”, “架构设计”, “框架特点”, “框架性能”] description: “Hertz 架构设计、框架特点、框架性能。”
CloudWeGo-Hertz
Hertz[həːts] 是一个 Golang 微服务 HTTP 框架,在设计之初参考了其他开源框架 fasthttp、gin、echo 的优势, 并结合字节跳动内部的需求,使其具有高易用性、高性能、高扩展性等特点,目前在字节跳动内部已广泛使用。 如今越来越多的微服务选择使用 Golang,如果对微服务性能有要求,又希望框架能够充分满足内部的可定制化需求,Hertz 会是一个不错的选择。
架构设计
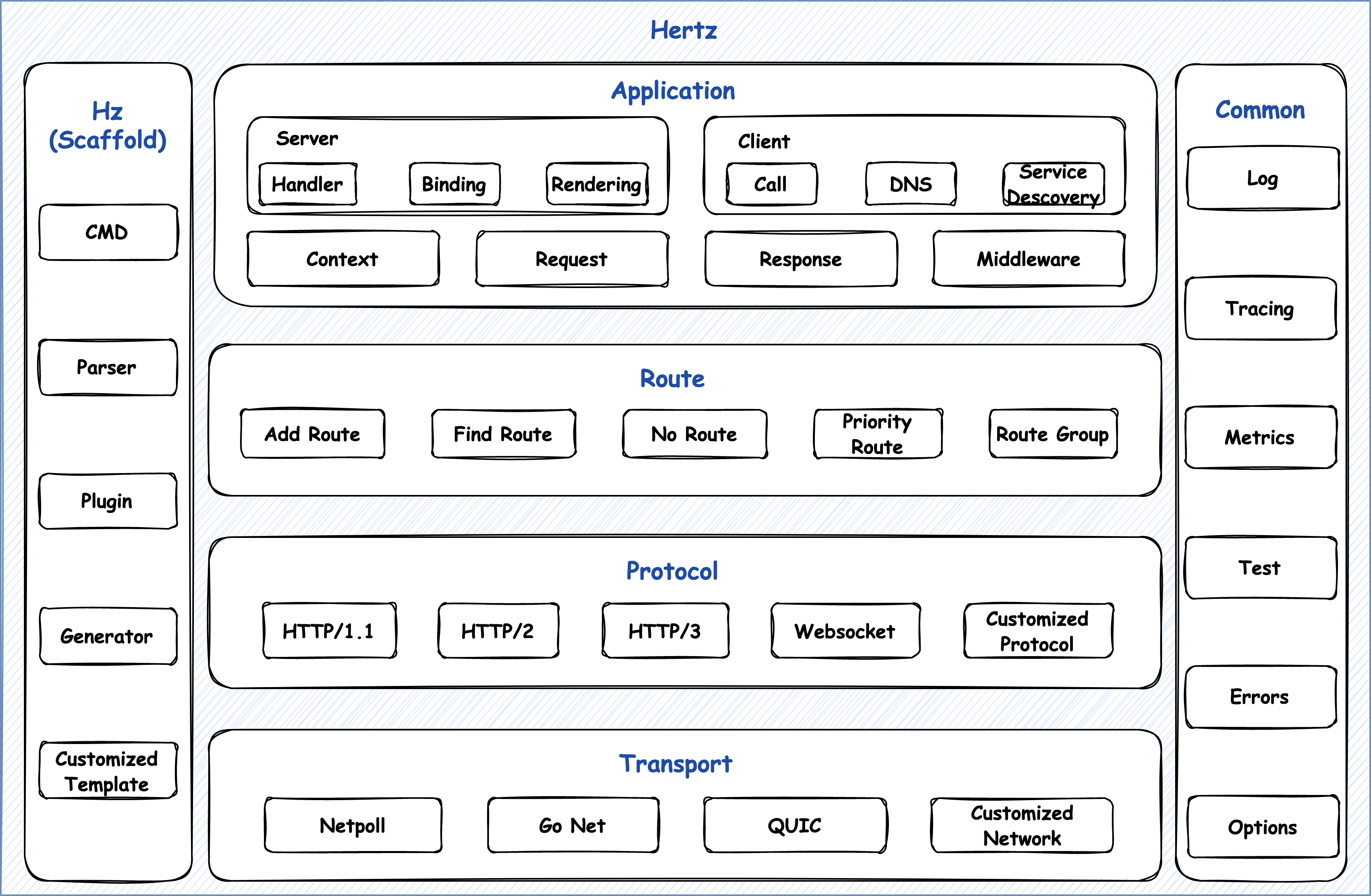
框架特点
-
高易用性
在开发过程中,快速写出来正确的代码往往是更重要的。因此,在 Hertz 在迭代过程中,积极听取用户意见,持续打磨框架,希望为用户提供一个更好的使用体验,帮助用户更快的写出正确的代码。
-
高性能
Hertz 默认使用自研的高性能网络库 Netpoll,在一些特殊场景相较于 go net,Hertz 在 QPS、时延上均具有一定优势。关于性能数据,可参考下图 Echo 数据。
四个框架的对比:
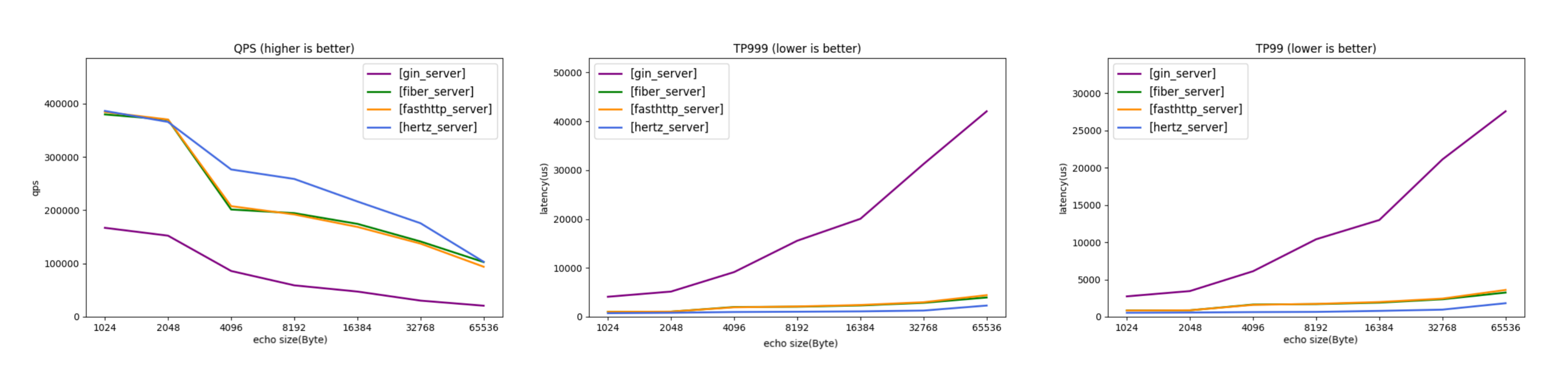
三个框架的对比:
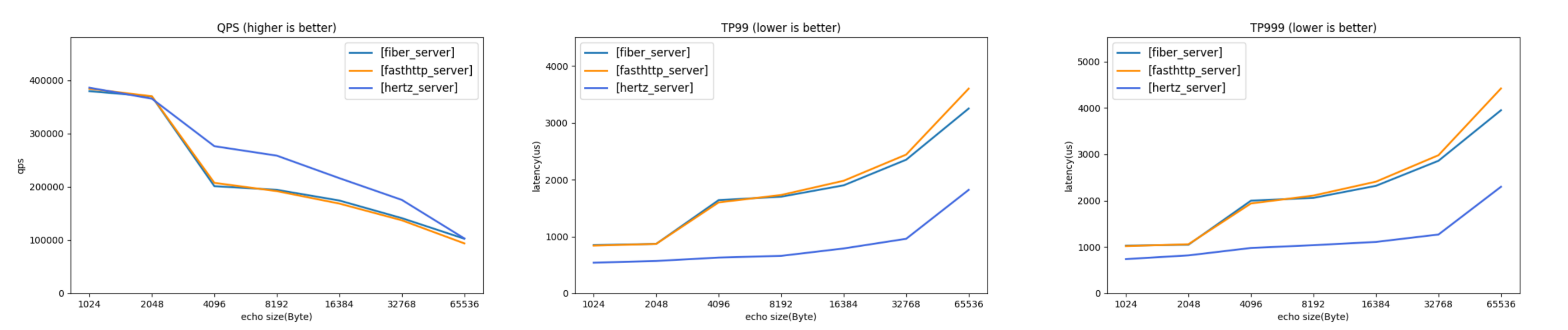
关于详细的性能数据,可参考 https://github.com/cloudwego/hertz-benchmark。
-
高扩展性
Hertz 采用了分层设计,提供了较多的接口以及默认的扩展实现,用户也可以自行扩展。同时得益于框架的分层设计,框架的扩展性也会大很多。目前仅将稳定的能力开源给社区,更多的规划参考 RoadMap。
-
多协议支持
Hertz 框架原生提供 HTTP1.1、ALPN 协议支持。除此之外,由于分层设计,Hertz 甚至支持自定义构建协议解析逻辑,以满足协议层扩展的任意需求。
-
网络层切换能力
Hertz 实现了 Netpoll 和 Golang 原生网络库 间按需切换能力,用户可以针对不同的场景选择合适的网络库,同时也支持以插件的方式为 Hertz 扩展网络库实现。
框架性能
性能测试只能提供相对参考,工业场景下,有诸多因素可以影响实际的性能表现。
我们提供了 hertz-benchmark 项目用来长期追踪和比较 Hertz 与其他框架在不同情况下的性能数据以供参考。
相关项目
- Netpoll: 自研高性能网络库,Hertz 默认集成
- Hertz-Contrib: Hertz 扩展仓库,提供中间件、tracer 等能力
- Example: Hertz 使用例子
相关文章
title: “配置说明” linkTitle: “配置说明” weight: 1 keywords: [“配置说明”] description: “Hertz 配置说明。”
Server
Server 侧的配置项均在初始化 Server 时采用 server.xxx 的方式,如
package main
import "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server"
func main() {
h := server.New(server.WithXXXX())
...
}
| 配置名称 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| WithTransport | network.NewTransporter | 更换底层 transport,默认值:netpoll.NewTransporter |
| WithHostPorts | string | 指定监听的地址和端口 |
| WithKeepAliveTimeout | time.Duration | tcp 长连接保活时间,一般情况下不用修改,更应该关注 idleTimeout。默认值:1min |
| WithReadTimeout | time.Duration | 底层读取数据超时时间。默认值:3min |
| WithIdleTimeout | time.Duration | 长连接请求链接空闲超时时间。默认值:3min |
| WithMaxRequestBodySize | int | 配置最大的请求体大小,默认 4M(4M 对应的填的值是 4*1024*1024) |
| WithRedirectTrailingSlash | bool | 自动根据末尾的 / 转发,例如:如果 router 只有 /foo/,那么 /foo 会重定向到 /foo/ ;如果只有 /foo,那么 /foo/ 会重定向到 /foo。默认开启 |
| WithRemoveExtraSlash | bool | RemoveExtraSlash 当有额外的 / 时也可以当作参数。如:user/:name,如果开启该选项 user//xiaoming 也可匹配上参数。默认关闭 |
| WithUnescapePathValues | bool | 如果开启,请求路径会被自动转义(eg. ‘%2F’ -> ‘/')。如果 UseRawPath 为 false(默认情况),则 UnescapePathValues 实际上为 true,因为 .URI().Path() 将被使用,它已经是转义后的。设置该参数为 false,需要配合 WithUseRawPath(true)。默认开启 (true) |
| WithUseRawPath | bool | 如果开启,会使用原始 path 进行路由匹配。默认关闭 |
| WithHandleMethodNotAllowed | bool | 如果开启,当当前路径不能被匹配上时,server 会去检查其他方法是否注册了当前路径的路由,如果存在则会响应"Method Not Allowed”,并返回状态码 405; 如果没有,则会用 NotFound 的 handler 进行处理。默认关闭 |
| WithDisablePreParseMultipartForm | bool | 如果开启,则不会预处理 multipart form。可以通过 ctx.Request.Body() 获取到 body 后由用户处理。默认关闭 |
| WithStreamBody | bool | 如果开启,则会使用流式处理 body。默认关闭 |
| WithNetwork | string | 设置网络协议,可选:tcp,udp,unix(unix domain socket),默认为 tcp |
| ContinueHandler | func(header *RequestHeader) bool | 在接收到 Expect 100 Continue 头之后调用 ContinueHandler。使用 ContinueHandler,服务器可以决定是否根据标头读取可能很大的请求正文 |
| PanicHandler | HandlerFunc | 处理 panic,用来生成错误页面并返回 500 |
| NotFound | HandlerFunc | 当路由匹配不上时被调用的 handler |
| WithExitWaitTime | time.Duration | 设置优雅退出时间。Server 会停止建立新的连接,并对关闭后的每一个请求设置 Connection: Close 的 header,当到达设定的时间关闭 Server。当所有连接已经关闭时,Server 可以提前关闭。默认 5s |
| WithTLS | tls.Config | 配置 server tls 能力 |
| WithListenConfig | net.ListenConfig | 设置监听器配置,可用于设置是否允许 reuse port 等 |
| WithALPN | bool | 是否开启 ALPN。默认关闭 |
| WithTracer | tracer.Tracer | 注入 tracer 实现,如不注入 Tracer 实现,默认关闭 |
| WithTraceLevel | stats.Level | 设置 trace level,默认 LevelDetailed |
| WithWriteTimeout | time.Duration | 写入数据超时时间,默认值:无限长 |
| WithRedirectFixedPath | bool | 如果开启,当当前请求路径不能匹配上时,server 会尝试修复请求路径并重新进行匹配,如果成功匹配并且为 GET 请求则会返回状态码 301 进行重定向,其他请求方式返回 308 进行重定向。默认关闭 |
| WithBasePath | string | 设置基本路径,前缀和后缀必须为 /。默认为 / |
| WithMaxKeepBodySize | int | 设置回收时保留的请求体和响应体的最大大小。单位:字节。默认值:4 * 1024 * 1024 |
| WithGetOnly | bool | 如果开启则只接受 GET 请求。默认关闭 |
| WithKeepAlive | bool | 如果开启则使用 HTTP 长连接。默认开启 |
| WithAltTransport | network.NewTransporter | 设置备用 transport。默认值:netpoll.NewTransporter |
| WithH2C | bool | 设置是否开启 H2C。默认关闭 |
| WithReadBufferSize | int | 设置读缓冲区大小,同时限制 HTTP header 大小。默认值:4 * 1024 |
| WithRegistry | registry.Registry, *registry.Info | 设置注册中心配置,服务注册信息。默认值:registry.NoopRegistry, nil |
| WithAutoReloadRender | bool, time.Duration | 设置自动重载渲染配置。默认值:false, 0 |
| WithDisablePrintRoute | bool | 设置是否禁用 debugPrintRoute。默认不禁用 |
| WithOnAccept | func(conn net.Conn) context.Context | 设置在 netpoll 中当一个连接被接受但不能接收数据时的回调函数,在 go net 中在转换 TLS 连接之前被调用。默认值:nil |
| WithOnConnect | func(ctx context.Context, conn network.Conn) context.Context | 设置 onConnect 函数。它可以接收来自 netpoll 连接的数据。在 go net 中,它将在转换 TLS 连接后被调用。默认值:nil |
Server Connection 数量限制:
- 如果是使用标准网络库,无此限制
- 如果是使用 netpoll,最大连接数为 10000
(这个是 netpoll
底层使用的 gopool
)控制的,修改方式也很简单,调用 gopool 提供的函数即可:
gopool.SetCap(xxx)(main.go 中调用一次即可)。
Client
Client 侧的配置项均在初始化 Client 时采用 client.xxx 的方式
package main
import "github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/client"
func main() {
c, err := client.NewClient(client.WithXxx())
...
}
| 配置名称 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| WithDialTimeout | time.Duration | 连接建立超时时间,默认 1s |
| WithMaxConnsPerHost | int | 设置为每个 host 建立的最大连接数,默认 512 |
| WithMaxIdleConnDuration | time.Duration | 设置空闲连接超时时间,当超时后会关闭该连接,默认 10s |
| WithMaxConnDuration | time.Duration | 设置连接存活的最大时长,超过这个时间的连接在完成当前请求后会被关闭,默认无限长 |
| WithMaxConnWaitTimeout | time.Duration | 设置等待空闲连接的最大时间,默认不等待 |
| WithKeepAlive | bool | 是否使用长连接,默认开启 |
| WithRetryConfig | …retry.Option | 设置 client 的 retry config。Hertz 版本需 >= v0.4.0 |
| int | 设置最大调用次数,调用失败则会重试。默认 1 次即不重试。v0.4.0 版本废止,该版本之前可用,建议升级 Hertz 版本 >= v0.4.0 并使用 WithRetryConfig 替代 | |
| WithClientReadTimeout | time.Duration | 设置读取 response 的最长时间,默认无限长 |
| WithTLSConfig | *tls.Config | 双向 TLS 认证时,设置 client 的 TLS config |
| WithDialer | network.Dialer | 设置 client 使用的网络库,默认 netpoll |
| WithResponseBodyStream | bool | 设置是否使用流式处理,默认关闭 |
| WithDialFunc | client.DialFunc | 设置 Dial Function |
| WithWriteTimeout | time.Duration | 写入数据超时时间,默认值:无限长 |
title: “版本说明” linkTitle: “版本说明” weight: 2 keywords: [“版本说明”] description: “Hertz 版本说明。”
Hertz 遵从 语义化版本 2.0.0 发布版本。
- 主版本号:Hertz 提供的 API 出现不兼容的情况时,升级该版本号
- 次版本号:Hertz 提供新的功能特性同时保持向下兼容时,升级该版本号
- 修订号:Hertz 的代码提供小的特性或向下兼容的优化和问题修复时,升级该版本号
title: “参考” linkTitle: “参考” weight: 5 keywords: [“配置说明”, “版本说明”] description: “Hertz 相关参考。”